An empty space with no gas particles or pressure is called a ____________.
Vacuum
What is the SI unit for pressure?
Pascals (Pa)
What does dalton's law state?
The sum of partial pressures of a mixture is equal to the total pressure in the container.
If the volume of a container of gas is reduced, what will happen to the pressure inside the container?
A __________ is the substance being dissolved and the __________ is doing the dissolving.
Describe a saturated solution.
A solution that cannot dissolve any more solute at a given temperature
Formula for molarity?
M = mol/L
What is the name of the device used to measure atmospheric pressure
A barometer
What are the conditions of STP and what does STP stand for?
****Must get both parts for points
0°C and 1 atm
Standard temperature and pressure
Describe the relationship between the average kinetic energy of a gas particle and the temperature of its container.
When the temperature increases, the AKE of the gas particle increases and vice versa. They are directly proportional.
What happens to the temperature of a gas when it is compressed?
The temperature increases
Miscible liquids
What happens to the solubility of a gas at high temperatures?
What about solids? +100
Decreases the solubility of the gas
Increases the solubility of the solid
Formula for molality?
m = mol/ kg
Describe a gas in terms of volume, shape, and how its particles take up space.
Gases do not have a definite volume or definite shape. They take the shape and volume of their container and are easily compressible substances. The particles of a gas are spread far apart and free floating.
What is the conversion factor comparing atms, mm Hg, and kPa?
1 atm = 760 mm Hg = 101.3 kPa
List the characteristics of a gas that affects partial pressure.
*****Must get all of them for points
Number of moles
Temperature
Size of the container
Write all 5 gas law formulas and label which formula belongs to which law.
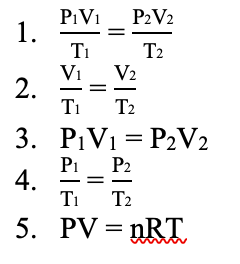 Labeled on the board.
Labeled on the board.
What is the term for the process in which solvent particles surround solute particles to form a solution?
Solvation
What does Henry's law state?
States that at a given temperature, the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas above the liquid.
What is the volume of an 5.0M solution containing 11.2 moles of KCl dissolved in a solution?
2.2 L
Describe how pressure is built up in a container in terms of gas particles.
Pressure is caused by the number of collisions gas particles have with the walls of the container.
Convert 1.5 atmospheres to kPa.
150 kPa.
A mixture of gases contain oxygen, nitrogen, and argon. The partial pressures of oxygen (O₂) and nitrogen (N₂) are 200.0 kPa, and 150 kPa, respectivel. What is the partial pressure of argon (Ar), in atm, if the total pressure of the gas mixture is 500.0 kPa?
1.5 atm
A sealed steel gas tank contains nitrogen gas at a pressure of 2.00 atm and a temperature of 300 K. If the tank is heated to a temperature of 450 K, what will be the new pressure of the gas (assuming the volume remains constant)?
3.0 atm
Name 3 characteristics that can increase the rate in which a solute dissolves in a solvent.
What is a seed crystal?
A particle of solute added to a supersaturated solution to help begin or speed up crystallization.
How many grams of NaOH must be dissolved into 0.9 kg of water to create a solution with a molality of 4.63 mol/ kg?
167 or 200 g of NaOH
State the main points of the kinetic molecular theory.
Gases are made up of small, hard spherical particles that travel at a rapid and constant speed in linear paths. They take up a very small amount of space and do not have any intermolecular forces affecting them. Collisions between gas particles are perfectly elastic.
How many mm Hg are in 400 kPa?
3000 mm Hg
A mixture of 10.5% H₂, 51.7% O₂, and 37.8% CO₂ has a total pressure of 5.2 atm. What is the partial pressure of each of the gases?
0.55 atm H2
2.7 atm O2
2.0 atm CO2
A sample of carbon dioxide gas (CO₂) occupies 3.50 L at a pressure of 416 kPa and a temperature of 25ºC. How many moles of CO₂ are present in the container?
0.59 moles
Determine if CH3OH is soluble in water. Explain how you determined that.
******Must answer both parts for points
Yes, it is soluble. This can be determined by determining the polarity of the compound. Since it is polar and like dissolves like, water can dissolve this compound.
If a large amount of solute is added to a solution, how can we describe that solution?
Concentrated
A solution is made by dissolving 350.0 g of Mg3(PO4)2 in 4500 g of water. What is the molality of the solution?
0.30 m