Molecules that consist of a single piece of DNA- human cell has 46 of them.
What are chromosomes?
This enzyme unzips the double helix.
What is DNA helicase?
Name for 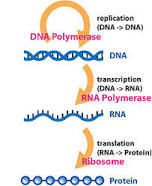
What is the central dogma (of molecular biology)?
Or What is gene expression? (technically that does not include replication though)
The product of translation
What is a protein? (or an amino acid chain)
Various forms of a gene that are the result of mutation.
What are alleles?
The 2 components of the backbone of a DNA strand.
What are phosphates and deoxyribose?
They showed genes are made of DNA in bacteria.
Who are Avery McLeod and McCarty?
This enzyme joins the Okazaki fragments.
What is DNA ligase?
The sequence needed for RNa Polymerase to bind to a gene and begin transcription.
What is a promoter (or TATA box specifically for a eukaryotic gene)?
This is enzyme that carries out translation.
What is a ribosome?
A base substitution that changes one amino acid in the encoded polypeptide.
What is a missense mutation?
The type of bonds between a base pair
What are Hydrogen bonds?
These people are credited with discovering the shape of DNA
Who are Watson and Crick?
This enzyme joins nucleotides and follows base pairing rules to make the complementary DNA strand.
What is DNA polymerase?
The molecule produced during transcription.
What is RNA?
This RNA type carries the correct amino acids to the ribosome.
What is tRNA (transfer RNA)?
A mutation that changes many amino acids.
What is a frameshift mutation (deletion, insertion)?
The name for the rules: A pairs with T or U, G pairs with C
What are complementarity or base-pairing rules?
They used density gradient centrifugation and a heavy nitrogen isotope to show DNA rrplication is semiconservative.
Who are Meselson and Stahl?
The property of replication (proposed by Watson and Crick, then demonstrated by Meselson and Stahl) where each new DNA has one original strand paired to a newly-made strand.
What is semiconservative?
This enzyme joins RNA bases to make an RNA complementary to the DNA template.
What is RNA polymerase?
The name for the 3 base sequence that specifies the first amino acid in a protein - most always AUG.
What is 'a start codon'?
The term for conditions or chemicals that increase the frequency of mutations.
What are mutagens?
The term for the fact that the backbones of the DNA strands in a double helix run in opposite 5'-> 3' directions.
What is antiparallel?
Reported that for any DNA, %G+C= % A+T, %G=%C and %A=%T
Who is Chargaff?
Where DNA replication is occurring, the term for the strand that replicates in one continuous strand, and the term for the strand that is replicated discontinuously in a series of short fragments.
What are the leading (continous) and lagging (discontinuous) strands?
The strand of the gene that is used as the pattern for transcription.
What is the coding strand?
UAA, UAG, or UGA, any sequence that causes translation to end.
What are stop codons?
The type of mutation that converts a codon that stood for an amino acid into a stop codon.
What is a nonsense mutation?
The name for the covalent bonds that join nucleotides into a polynucleotide strand (found in the backbone of the strand).
What are phosphodiester bonds?
They performed the "blender experiment" showing DNA (genes) not protein, enters bacteria when a virus infects the cell.
Who are Hershey and Chase?
There is one of these Y shaped structures at each end of the replication bubble.
What is a replication fork?
The sequence that signals the enzyme to stop transcription.
What is a terminator?
The number of codons in the genetic code
What is 64?
In addition to errors during replication, another type of event that can lead to mutations
What is damage to DNA?
The general terms for the larger nucleic acid bases (A and G), and the term for the smaller bases (C, T, U).
What are purines (larger, As and Gs) and pyrimidines (smaller, C, T and U)?
Franklin and Wilkins used X-ray diffraction results to discover DNA has this basic shape (expanded on by Watson and Crick).
What is a helix?
The sequence needed for replication of a molecule of DNA to start
What is an origin of replication (Origin, or Ori for short)?
Post transcriptional modifications: Terms for the long string of bases added to the 3' end of a eukaryotic RNA, and the modified G added to the 5' end of a eukaryotic pre mRNA.
What are the poly A tail and the 5' "cap"?
The genetic code is considered degenerate or redundant because multiple __________ can be associated with the same ____________________
What is multiple codons and the same amino acid?
The repetive sequences at the end of eukaryotic chromosomes- they get shorter with each cell division.
What are telomeres?
The name for the enzyme that adds protective structures to the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes. It is inappropriately activated in many cancer cells.
What is telomerase?
The term for noncoding sequences removed from a eukaryotic pre-mRNA by the ribozymes in "sNRNP"s.
What are introns?
In order, the 3 sites on the ribosome all the tRNAs after the first one move through
What are the A, then P, then E sites?
The enzyme that builds short RNA fragments for DNA Polymerase to add deoxyribonucleotides to during replication.
What is primase?
The location where transcription occurs in a eukaryotic cell.
What is the nucleus?
The name for the 3 bases on a tRNA that base pair with part of an mRNA
What is the anti-codon?