_____ reactions ultimately reach equilibrium.
reversible
16.03
Answer the question based on the decomposition reaction of carbon dioxide:
3H2(g)+N2(g) ->^2 2NH3(g)
triangleH=-92.0kJ
a. Add N2 and the amount of NH3 will...
increase
review sheet
Ammonia decomposes and forms an equilibrium mixture with hydrogen and nitrogen according to the given reaction.
When pure ammonia was placed in a vessel and allowed to reach equilibrium at a given temperature, the mixture was found to contain 0.22 M N2. Calculate the equilibrium concentration of NH3.
The equilibrium constant at that temperature is 250.
2NH3(g) ->^2 N2(g)+3H2(g)
[NH3]=0.016 M
16.35
Kp=__(RT) trianglen
Kc
16.14
a. when Qc ? Kc, the reaction proceeds to the right.
b. Qc ? Kc, the reaction proceeds to the left.
c. Qc ? Kc, the reaction is at equilibrium.
a. <
b. >
c. =
16.29
What is a helpful tool to use when navigating a partial pressure problem?
an ice table
16.63
triangleG^o: _____ free energy
triangleG: free energy at _____ point
standard
any
16.69
When a _____ is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system, will respond by shifting in the direction that _____ the effect of the _____.
stress
minimizes
stress
16.83
For heterogenous reversible reactions, what species are not shown in Kc and why?
solids and pure liquids are constants and do not appear in the Kc expression.
16.11
Answer the question based on the decomposition reaction of carbon dioxide:
3H2(g)+N2(g) ->^2 2NH3(g)
triangleH=-92.0kJ
a. remove N2 and the amount of H2 will...
increase
review sheet, question 10
For the following reaction, Kc at 400 K is 7.0. If 0.50 mol of Br2 and 0.50 mol Cl2 are introduced into a 1.0 L container at 400 K, what will be the equilibrium concentration of BrCl?
Br2(g)+Cl2(g) ->^2 2BrCl(g)
0.285
review sheet, question 7
Write the equilibrium expression for each:
a. O2(g)+2H2(g) ->^2 2H2O(l)
b. H2O(g)+C(s) ->^2 CO(g)+H2(g)
a. Kc=[1]/[O2][H2]2
b. Kc=[CO][H2]/[H2O]
16.13
true or false: Qc= [products]/[reactants]
true
16.28
At 850^oC , the equilibrium constant, Kp, for the reaction C(s)+CO2(g) ->^2 2CO(g) has a value of 10.7. If the total pressure in the system at equilibrium is 1.000 atm, what is the partial pressure of carbon monoxide at equilibrium?
0.921 atm
16.65
Consider: 2A(g)+B(g) -> 2C(g)
If triangleG^o =50.0 kJ/mol at T= 25^oC and Pa=Pb=1 atm and Pc=2 atm, what is the value of triangleG ? (R=8.314 J/Kmol)
53.4 kJ/mol
16.72
Which of the following are considered forms of stress on a system?
a. the addition of a reactant or product
b. the removal of a reactant or product
c. a change in volume of the system, resulting in a change in concentration or partial pressure of the reactants and products
d. a temperature change
e. all of the above
f. a, c, d only
letter e
16.83
a. At equilibrium, Qc ? Kc
b. At non-equilibrium, Qc ? Kc
a. =
b. does not =
16.05
Answer the question based on the decomposition reaction of carbon dioxide:
3H2(g)+N2(g) ->^2 2NH3(g)
triangleH=-92.0kJ
a. increase pressure and the equilibrium shifts...
right
review sheet, question 10
Consider the reaction below. A reaction mixture initially contains 2.0 M SO2 and some solid Cu. Determine the equilibrium concentration of SO2 if Kc for the reaction is 4.0.
Cu(s)+SO2(g) ->^2 CuS(s)+O2(g)
0.4 M
review sheet, question 9
Write the equilibrium expression for each:
a. CaCO3(s) ->^2 CaO(s)+CO2(g)
b. Hg(l)+Hg2+(aq) ->^2 Hg22+(aq)
c. 2Fe(s)+3H2O(l) ->^2 Fe2O3(s)+2H2(g)
a. Kc=[CO2]
b. Kc=[Hg22+]/[Hg2+]
c. Kc=[H2]2
16.13
How would you write this in Qc form:
N2(g)+3H2(g) ->^2 2NH3(g)
([NH_3 ]^2)/([N_2][H_2]^3)
16.30
The equilibrium constant Kp for the following reaction is 0.0025 at 2127^oC . If a container is charged with 8.00 atm of nitrogen and 5.00 atm of oxygen and the mixture is allowed to reach equilibrium, what will be the equilibrium partial pressure of nitrogen?
N2(g)+O2(g) ->^2 2NO(g)
7.85 atm
16.63
H2(g)+I2(g) ->^2 2HI(g)
triangleG^o at 25^oC=2.60(kJ)/(mol)
If PH2=2.0 atm; PI2=2.0 atm; and PHI=3.0 atm
What is triangleG ? Is it spontaneous or non spontaneous?
4.60 kJ/mol
nonspontaneous
16.73
a. When a substance is added, the equilibrium shifts to decrease it by using it.
The reaction will shift ____ (from) the side you are adding to.
b. When a substance is removed, the equilibrium shifts to increase it by using it.
The reaction will shift ____ (from) the side you are removing from.
a. away
b. towards
16.84
Kc is known as the...
Qc is known as the...
equilibrium constant
reaction quotient
16.04-05
Answer the question based on the decomposition reaction of carbon dioxide:
3H2(g)+N2(g) ->^2 2NH3(g)
triangleH=-92.0kJ
a. increase temperature and the amount of H2 will...
increase
review sheet, question 10
N2O4 decomposes to NO2. The equilibrium constant in the gas phase is 0.36 at 100^oC .
If a 1.00 L flask initially contains 0.100 M N2O4, what will be the equilibrium concentration of NO2?
0.12 M
16.55-57
Consider the equilibrium N2(g)+3H2(g) ->^2 2NH3(g) at a certain temperature. An equilibrium mixture in an 8.00 L vessel contains 1.60 mol NH3, 0.800 mol N2, and 1.20 mol H2. What is the value of Kc?
119
16.10
Calculate the Reaction Quotient, Q, when 1.00 mol of HF(g), 0.371 mol of H2(g), and 0.750 mol of F2(g) are mixed in a 5.00 L flask.
2HF(g) ->^2 H2(g)+F2(g)
Kc= 1.00*10^-2
Q=0.278
review sheet, question 4.a
Suppose 15.00 g of solid ammonium hydrogen sulfide is introduced into a 500. mL flask at 25^oC , the flask is sealed, and the system is allowed to reach equilibrium. What is the partial pressure of ammonia in this flask if Kp=0.108 at 25^oC for the following reaction?
NH4HS(g) ->^2 NH3(g)+H2S(g)
0.329 atm
16.66
H2(g)+I2(g) ->^2 2HI(g)
triangleG^o at 25^oC=2.60(kJ)/(mol)
If PH2=2.0 atm; PI2=2.0 atm; and PHI=1.0 atm
What is triangleG ? Is it spontaneous or non spontaneous?
-0.8 kJ/mol
spontaneous
16.74
H2S is a contaminant commonly found in natural gas. It is removed by reaction with oxygen to produce elemental sulfur.
2H2S(g)+O2(g) ->^2 2S(s)+2H2O(g)
For each scenario, determine whether the equilibrium will shift right, left, or neither:
1. addition of O2(g)
2. removal of H2S(g)
3. removal of H2O(g)
4. addition of S(s)
1. right
2. left
3. right
4. neither
16.85
large Kc=______ favored. Reaction is _____
small Kc=______ favored. Reaction is _____
products, spontaneous
reactants, non-spontaneous
16.27
Answer the question based on the decomposition reaction of carbon dioxide:
3H2(g)+N2(g) ->^2 2NH3(g)
triangleH=-92.0kJ
a. add NH3 and the temperature of the system will...
decrease
review sheet, question 10
For the following reaction, 3.000 mol of each species is put in a 1.500 L vessel. Calculate the equilibrium concentration of each species.
H2(g)+F2(g) ->^2 2HF(g)
Kc= 1.15*10^2
[H2]=[F2] 0.47 M
[HF]= 5.06 M
16.58-60
What is Kc and Kp for the following expression:
N2O4(g) ->^2 2NO2(g)
Kc= [NO2]2/[N2O4]
Kp= (P^2NO_2)/(PN_2O_4)
16.14
A container is filled with 0.83 M ammonia, 0.35 M oxygen, 0.65 M nitrogen, and 1.34 M water vapor at a temperature of 300^oC . Calculate the reaction quotient and state whether the reaction will proceed in the forward or reverse direction.
4NH3(g)+3O2(g) ->^2 2N2(g)+6H2O(g)
Kc=12.11
Qc=120
120>12.11
Qc>Kc
the reaction will proceed in the reverse direction
review sheet, question 5
Consider the following reaction. A reaction mixture initially contains 0.56 atm CO2 and 0.32 atm CO. Determine the total pressure in the container once equilibrium is reached. Kp for the reaction at this temperature is 2.25.
CO2(g)+C(graphite) ->^2 2CO(g)
1.14 atm
review sheet, question 8
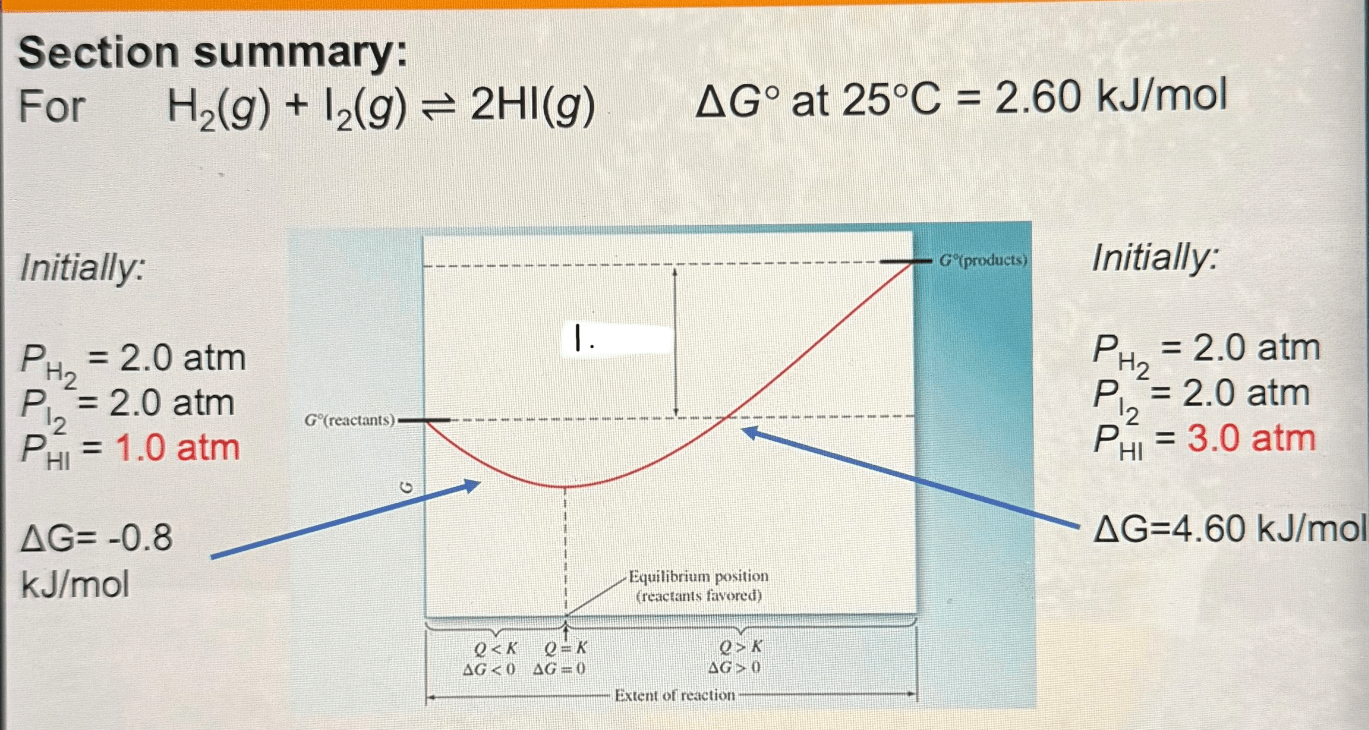
What belongs in the white box labeled "1."
triangleG^o is positive
16.76
8CO(g)+17H2(g) ->^2 C8H18(g)+8H2O(g)
Suppose the reaction is at equilibrium at 200oC, then is suddenly cooled to condense the octane (C8H18), and then the remaining gases are reheated to 200oC. In which direction will the equilibrium shift?
right
15.86
true or false: When both sides of the equilibrium reaction have the same number of moles of gas, pressure has an increasing effect on equilibrium, according to Le Châtelier's Principle.
false, pressure has no effect on the equilibrium
16.88
Answer the question based on the decomposition reaction of carbon dioxide:
3H2(g)+N2(g) ->^2 2NH3(g)
triangleH=-92.0kJ
a. remove NH3 and the system will shift...
right
Pure NO2 is placed in a vessel and the temperature is brought to 200 K, where the equilibrium constant, Kc, is 0.0015. At equilibrium, the concentration of NO was measured to 0.0800 M. Determine the equilibrium concentration of NO2.
2NO2(g) ->^2 2NO(g)
+O2(g)
0.413 M NO2
review sheet, question 6
The value of Kc at 227^oC is 0.0952 for the following reaction:
CH3OH(g) ->^2 CO(g)+2H2(g)
What is Kp at the temperature?
Kp=160.
16.16
2NH3(g) ->^2 N2(g)+3H2(g)
A 50.0 L vessel contains 1.00 mol N2, 3.00 mol H2, and 0.500 mol NH3. In which direction (toward reactants or toward products) will the system shift to reestablish equilibrium at 400oC?
Kc for the reaction at 400oC is 2.00
0.043
Qc<Kc so it proceeds towards products
16.31
A mixture of 5.75 atm of H2 and 5.75 atm of I2 is contained in a 1.0 L vessel at 430^oC . The equilibrium constant (Kp) for the reaction at this temperature is 54.3. Determine the equilibrium partial pressures of H2,I2, and HI.
PH2=P12=1.23 atm, PHI=9.04 atm
16.61

-3.1 kJ/mol
spontaneous
16.77
In which direction will the equilibrium shift when the pressure is increased?
8CO(g)+17H2(g) ->^2 C8H18(g)+8H2O(g)
right
16.91