What is an ion? Give an example.
An atom that has gained or lost electrons, giving it a charge. Ex: Na⁺,Cl⁻, etc.
What causes water molecules to stick together?
The property of cohesion (due to hydrogen bonding)
What are the building blocks (monomers) of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides (simple sugars like glucose).
What are the building blocks (monomers) of proteins?
Amino acids
What does it mean for something to be alive?
It must show all six characteristics of life.
What’s the difference between a chemical bond and an intermolecular force?
Chemical bonds (like covalent or ionic) hold atoms together within a molecule; intermolecular forces (like hydrogen bonds or Van der Waals) attract separate molecules to one another.
What property allows small insects to walk on water?
Surface tension, caused by cohesive hydrogen bonds.
What 3 elements are found in carbohydrates?
Carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O).
What are the four levels of protein structure?
Primary (chain of amino acids), secondary (folding like helices/sheets), tertiary (3D shape), quaternary (multiple chains)
Name two of the six characteristics of life.
Must list 2 of the following: Growth, reproduction, metabolism, response to stimuli, organization, homeostasis, adaptation.
What type of bond forms when atoms share electrons equally?
Nonpolar covalent bond.
What pH value is considered neutral and is also the pH of pure water?
pH 7
Compare and contrast carbohydrates and lipids.
Carbs: quick energy, polar, hydrophilic. Lipids: long-term energy, nonpolar, hydrophobic.
What are the two types of nucleic acids, and what do they do?
DNA (stores genetic info) and RNA (carries out instructions to make proteins)
What does “metabolism” mean?
All chemical reactions that occur within an organism to maintain life.
What type of bond forms between water molecules and why?
Hydrogen bonds, formed due to the attraction between the partial positive hydrogen of one molecule and the partial negative oxygen of another.
What is a buffer, and why is it important for living organisms?
A buffer is a weak acid or base that helps maintain a stable pH in organisms, aiding homeostasis.
What is the function of glycogen in animals?
It stores energy in muscles and the liver for later use.
Describe the structure of DNA
Double helix made of two strands held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases (A–T, C–G)
What does homeostasis mean, and give one example.
Maintaining internal stability; example could be body temperature regulation, blood pH balance, etc.
How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in this element (assume this is the neutral Carbon-12 isotope)?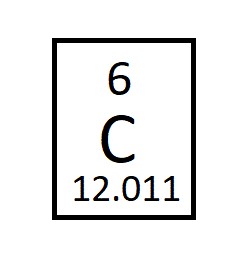
A standard, neutral carbon atom has 6 protons, 6 electrons, and 6 neutrons in the common Carbon-12 isotope.
To find the protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom from the periodic table, first locate the element to find its atomic number (6), which equals the number of protons and, for a neutral atom, the number of electrons. Then, use the element's approximate atomic mass (e.g., 12 for carbon-12) and subtract the atomic number from it to find the number of neutrons (12 - 6 = 6 neutrons).
Why does ice float on water, and why is this important for life?
Ice is less dense due to hydrogen bonds forming a crystalline structure with more open space; this insulates aquatic life in winter.
What are two of the three types of lipids, and what are their functions?
List 2 of these:
triglycerides (energy storage)
phospholipids (cell membranes)
steroids (hormones and signaling)
How do proteins and nucleic acids work together to support life?
DNA provides instructions for building proteins, which perform nearly all cell functions.
How do living things adapt over time?
Through changes in genetic traits passed across generations that help survival in changing environments.