what are atoms?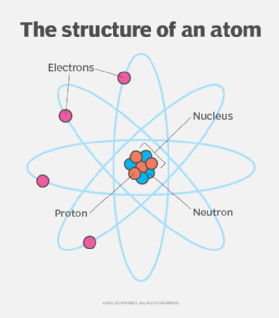
The attraction between a hydrogen atom on one water molecule and an oxygen atom on a different water molecule is known as hydrogen bonding.
What is a hydrogen bond?
Giant-molecules, made of thousands of smaller molecules. Formed by a process called polymerization, which is when monomers merge to form polymers.
There are 4 types of these.
What are macromolecules?
A process when reactants change into a product
What is a chemical reaction?
List the 4 types of macromolecules.
Carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and protein.
The combination of positively charged atoms, and no charge atoms.Otherwise known as the center of an atom
What is the nucleus?
A substance that is dissolved, and a substance that dissolves the other substance. Often compared to salt and water.
What is a solute and solvent?
A macromolecule that serves as energy for the body. Can be simple or complex. Contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO)
ex. bread, pasta, vegetables
What is a carbohydrate?
The result of a chemical reaction. Starts with the letter p
What is a product?
A substance created by chemically combining two or more elements in a very specific way
What is a compound?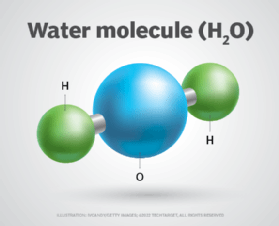
Version of element with the same amount of protons, but a different amount of neutrons
What is an isotope?
Attraction between molecules of the same substance.
What is cohesion?
A type of macromolecule that is made up of fatty acids and glycerol combined. They contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO). Usually used as a insulator
ex. fats, oils, waxes
What is a lipid?
Substance that is used in a chemical reaction to make new substances. Starts with the letter r.
What is a reactant?
The attraction of molecules of DIFFERENT substances
what is adhesion
The bond in which one or more electrons move from one atom to another
What is an ionic bond??
A scale which represents/measures how acidic (the number of H+ ions), or basic (the number of OH- ions) a solution is.
What is pH scale?
A type of macromolecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen (CHON). They are made of amino acids.
ex. meat, eggs, dairy
What is a protein?
Cells produce this. A substance that quickens the pace of a chemical reaction by lowering reaction activation energy
What is a catalyst?
building blocks of protein
What are amino acids?
The subtle attraction of molecules close together; an intermolecular force of attraction. Can allow animals to stick on surface, defying gravity. Often seen at work on a geckos feet.
What is the Van der Waals Forces?
Fragile acids that keep pH level steady. They can interact with sharp acids/bases and prevent changes in pH.
What is a buffer?
A type of macromolecule that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus (CHONP). Made of nucleotides, and transfers genetic information in cells.
ex. DNA, RNA
What is a nucleic acid?:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/RNA_vs_DNA-5b633a1fc9e77c002ca252a1.jpg)
A protein that speeds up chemical reactions. Acts as biological catalyst. Is often compared to a puzzle piece, as it connects to a substrate
What is an enzyme?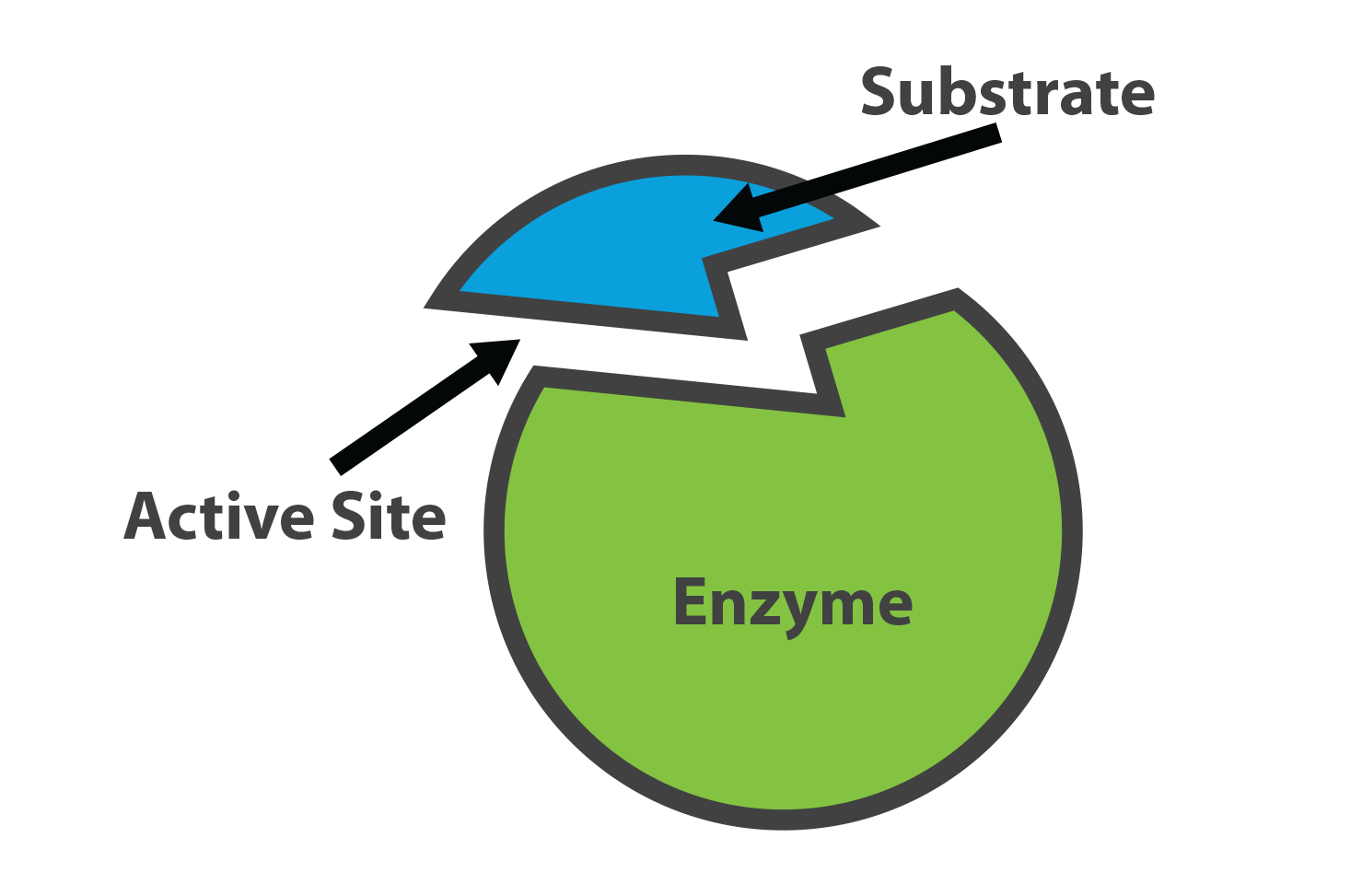
Composed of 2 or more elements, or compounds mixed together physically. Like salt and pepper, or sugar and sand
starts with the letter m
What is a mixture?