the dissipation of energy through the production of heat and occurs in specialised tissues including brown adipose tissue and skeletal muscle
thermogenesis
This is the hierarchical organization in bodies from smallest to largest.
Cells, tissues, organs, organ systems
These are three examples of osmoregulatory organs.
Flatworms ->Protonephridea
Annelids and molluscs -> Nephridia
Crustaceans -> Antennal glands
Insects & spiders -> Malpighian tubules
Vertebrates -> Kidneys
This is the term for the exchange of heat between two fluids flowing in opposite directions
Countercurrent heat exchange:
A secreted chemical formed in specialized cells that travels in body fluids in small amounts, and acts on a specific type of target cell, changing the target cell’s functioning in some way
Hormone
What kind of nitrogenous waste do I produce?
Urea
Rule stating that enzyme reactions double with 10 degree temp change.

Q10
In contrast to ____ symmetry, which is best suited for stationary or limited-motion lifestyles, ____ symmetry allows for streamlined and directional motion and specialization of different sections of the body.
radial symmetry, bilateral
These are the three types of epithelial tissue.
1.Squamous cells
2.Cuboidal cells
3.Columnar cells
These are the three types of mechanisms for regulation of homeostatic regulation, what they mean, and an example of each (ex. morphological, etc.)
Morphological – physical characteristics that aid in homeostasis; ex. Fur
Physiological – physical mechanisms that are used to maintain homeostasis; ex. Sweating, “antifreeze” chemical production
Behavioral – behavioral mechanism used to regulate homeostasis; ex. Sunbathing; beetle that holds abdomen up at an angle to gather moisture
This is the mechanisms by which adrenaline works and its function.
Raises blood glucose, blood flow, blood pressure, heart rate, increases metabolism, constricts certain blood vessels as an alarm or stress response to fight-or-flight efforts
Endotherm or Ectotherm?
Endotherm
Core body temperature (CBT) has a 24-h rhythm that increases in the daytime and decreases at night, with minimum temperature occurring in the early morning. This rhythmic variation usually has an amplitude greater than 1.0°C
Circadian Rhythm
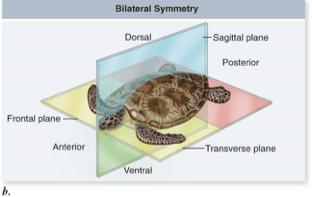
Label anterior end, posterior, dorsal, and ventral

Tendons, ligaments, cartilage are a part of this system
Skeleton system
This is the difference between endotherms and ectotherms and an example of organisms of each.
Endotherms generate metabolic heat (mostly homeothermic, maintaining stable temperature, but some heterothermic, temp varies based on metabolism), birds and mammals
Ectotherms do not generate heat and therefore conform to ambient temperature, fish, reptiles, and insects
This is the organ that releases insulin, which lowers blood glucose level and glucagon, which raises blood glucose level
Pancreas

I am an osmoregulator, do I have to deal with a hypotonic or a hypertonic environment?
Whats an example of an osmoconformer?

Saltwater-hypertonic
Fresh-hypotonic
Osmoconformers include marine inverts

__A__ happens during the winter season. Here animals stay in dormant condition during low temperature. On the other hand, __B__ occurs during the summer season. During high temperature, animals stay inactive to save energy.
An example of A
An example of B
Hibernation
Aestivation
Adaptive advantage of body cavities.
Organs that lie in solid tissue are squeezed or compressed every time the animal moves, a body cavity permits them freedom of movement, for example providing for more efficient transport of gut contents
Name two types of involuntary muscle types, what they do, and where they are found.
Smooth:Walls of blood vessels, stomach, and intestines-> Powers rhythmic contractions to move substances through vessels
Cardiac: Walls of heart-> Interconnected cells promote rapid spread of signal initiating contraction of heart
This is a list of the three forms of nitrogenous waste in order of their toxicity from most to least with examples of the sorts of organisms that produce each type
Ammonia – bony fish and aquatic inverts, least energetically expensive but most toxic – requires lots of water to flush away toxicity, which makes sense in an aquatic environment
Urea – mammals, amphibians, and cartilaginous fish, less toxic and water soluable
Uric acid – reptiles, birds and insects, most energetically expensive but also saves the most water, least toxic
______ Pituitary releases hormones made in the hypothalamus including oxytocin, which is involved in human bonding and ADH (Antidiuretic hormone) which promotes retention of water by kidneys
While the ______ Pituitary releases growth hormones, prolactin, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and the melanocyte stimulating hormone.
Posterior Pituitary
Anterior Pituitary
What hormones might a dairy farmer give cows to help produce milk?

Prolactin and oxytocin
______biologist, author, and conservationist whose influential book Silent Spring and other writings are credited with advancing the global environmental movement and stopping the use of ______.

Rachel Carson, DDT