What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
DNA --> RNA --> Protein
The process in which the instructions on how to build a protein is read from the DNA and made into mRNA.
transcription
a change in the sequence of bases in DNA or RNA
mutation
controlling gene expression to make sure the correct proteins are made when and where they are needed
gene regulation
What is the monomer of DNA show below?

nucleotide
Scientists credited with figuring out the structure of the DNA molecule.
James Watson & Francis Crick
The parts of the mRNA that code for a protein and are not edited during the mRNA processing by the ribozymes.
exons
The type of mutation that happens in body cells and cannot be passed on to offspring.
somatic mutation
A region of DNA in prokaryotes that consists of one or more genes that encode the proteins for a specific function and the proteins that control its expression.
operon
What process is happening in the figure below?

translation
What is Erwin Chargaff's base pairing rules?
A=T & G=C
There is approximately the same amount of adenine and thymine in an organism as well as guanine and cytosine.
What amino acids are coded for in the following strand of DNA:
TAC - AGG - CAG - GGT - ACT
met - ser - val - pro - stop
Beneficial mutations are the "raw" material for what biological process/theory?
evolution
Disease caused from mutations that allow the cells to divide rapidly and without limits
cancer
Name the molecules (A, B, & C) below.

A = mRNA
B = rRNA
C = tRNA
Scientist who used x-ray diffraction of DNA to get the following picture:
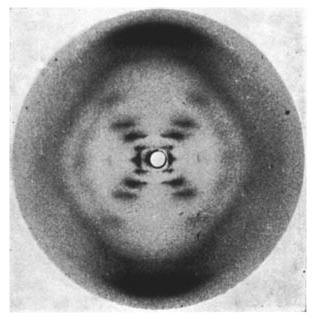
Rosalind Franklin
Type of mRNA processing that adds a "tail" consisting of a string of A's
polyadenylation
Type of point mutation in which the mutated codon codes for the same amino acid
silent
Genes that control development in eukaryotic organisms.
homeobox (hox) genes
What enzyme below is unzipping the DNA molecule (#9)?

helicase
Scientist who repeated Griffith's transformation experiment and treated the heat-killed S strain extract with various enzymes to see what was causing the transformation.
Oswald Avery
What are the three characteristics of the genetic code?
1) Universal 2) Unambiguous 3) Redundant
________________ mutations occur when a deletion or insertion of a nucleotide changes the reading frame of the triplet code.
Frameshift
What are the two types of genes in which mutations can cause cancer?
tumor suppressor & proto-oncogenes
What is the enzyme (#8) that adds nucleotides to the new DNA strand?

DNA polymerase