What are the 4 components vital to the mechanical function of the heart?
Heart muscle
Heart Valves
Blood supply
Blood vessels
the pathway of electrical impulses that controls the heart's pumping action
cardiac conduction system
What is the isoelectric line?
straight line between upward and downward movements or baseline
What wave directly corresponds to the contraction (depolarization) of the atria?
P Wave
How many seconds is 1 large square?
.20 seconds
What is the six-second method?
Counting the QRS waves in a six second strip and multiplying by 10
What generates or creates electrical impulses that spread throughout the heart?
Specialized tissue
What is the intrinsic rate?
the normal firing rate (expressed in beats per minute) associated with a part of the heart's electrical conduction system
a wave and a segment taken together is called what?
interval
This wave corresponds to the contraction (depolarization) of the ventricles
QRS wave
How many seconds is 1 small square?
.04 seconds
method of calculating rate by counting the large blocks between two R waves and then divide that number into 300.
Large block method
What triggers the mechanical contraction of the heart muscle?
Electrical impulses
What is the primary pacemaker of the heart?
Sinoatrial node (SA node)
what is several ekg waves considered together?
complex
What wave follows the QRS wave and corresponds to the relaxation (repolarization) of the ventricles?
T Wave
what is the overall pattern of the heartbeat called?
Heart rhythm
method of determining the heart rate by counting the small blocks between two consecutive R waves and dividing that number into 1500
Small block method
What is cardiac output?
amount of blood, measured in liters that the heart pumps each minute
What is the intrinsic rate of the AV node?
40-50 bpm or-60
What is the shape and direction of waves, complexes, and segments on an ekg tracing referred to?
Morphology
What is the segment between the QRS wave and the T wave called?
ST segment
Speed at which the heart is beating is called what?
Heart rate
What is this rhythm
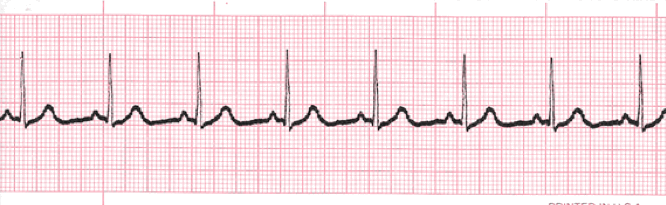
Normal Sinus Rhythm
what is cardiac output per minute?
amount of blood pumped with each heartbeat (stroke volume) multiplied by the number of heartbeats per minute
What is the intrinsic rate of the purkinje fibers?
20-40 bpm
When the electrical system of the heart is functioning normally what is the rhythm produced?
Normal Sinus Rhythm
If the ST segment is elevated, what is it called?
Myocardial Infarction or heart attack
What are the 6 steps used to analyze an ekg tracing? You must name all 6 correctly
1. determine heart rate
2. examine rhythm for regularity
3. presence or absence of P waves and is it uniform and the same across rhythm
4. Measure length of PR interval (<.20)
5. Measure length of QRS interval(<.12)
6. Identify the rhythm
What is a rhythm in which QRS complexes may look alike or different from each other, and do not repeat with consistent timing?
Irregular rhythm