vibrations in the ground that result from movement along breaks in Earth’s lithosphere
earthquake
a weak spot in the crust where molten material, or magma, comes to the surface
a volcano
Ring of Fire: major volcanic belt of volcanoes that rim the ________
pacific ocean
Which volcanoes form when cinders from a vent, pile up around the vent, forming a steep- cone-shaped mountain
cinder cone volcano
Magma high in Silica content causes what kind of eruption
explosive eruption
DJ***Earthquakes result from the build up and release of _______along active plate boundaries
stress
lava vs magma
Magma: molten mixture of rock, gases, and water vapor from the mantle.
Lava: molten material that has reached the surface.
what are things scientists (such as the USGS) look at to monitor volcanos?
earthquake activity
changes in the shape of the volcano
Gas emissions
Past eruptions to evaluate possible future eruptions
which type of eruption:
Magma is thick and sticky
Dissolved gases cannot escape
Trapped gasses build up pressure until they explode
explosive eruption
What are the three stages of a volcano? explain them
Active: is erupting, or has shown signs that it may erupt in the near future
Dormant: does not show signs of erupting in the near future
Extinct: unlikely to erupt
a force that acts on rock to change its shape or volume.
stress
Most volcanoes occur along _______ plate boundaries
divergent
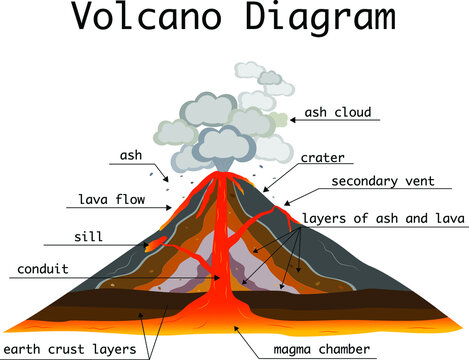
Where is the magma chamber?
4.
What type of eruption:
Magma flows easily; the gas dissolved in the magma bubbles out gently
quiet eruption
What is one example of a different type of volcanic activity?
Hot Spring: groundwater heated by a nearby body of magma rises to the surface and collects in a natural pool
Geyser: forms when rising hot water and steam become trapped underground in a narrow crack
Geothermal energy: a clean, reliable energy source provided by water heated by magma.
Lava Plateau: high, level area formed by lava flows hardening on top of each other over time.
Caldera:A large hole at the top of a volcano formed when the roof of a volcano’s magma chamber collapses
a break in the crust (lithosphere) where one block of rock moves toward, away from, or past one another
fault
string of volcanic islands is called what
island arc
What is the volcano pipe?
long tube that connects the magma chamber to Earth’s surface
Thin layers of lava pour out of a vent and harden on top of previous layers forming a wide gently sloping mountain.--which type of volcano
shield volcano
volcano benefits vs hazards
Volcanic ash is high in phosphorus and potassium, which make very fertile soil for growing fruits and vegetables.
Lava burns everything in its path and set fires.
Volcanic ash can bury towns, damage crops, and clog car engines
Can cause landslides
focus vs epicenter
focus: the actual place underground where the rocks break producing vibrations (seismic waves).
Epicenter: the place on Earth’s surface directly above the focus.
an area where magma from deep within the mantle melts through the crust is called what? also give an examples
hot spot volcanoes; Hawaiian Islands, Yellowstone National Park
Where is the vent?

5
Layers of lava alternate with layers of ash, cinders, and bombs--which type of volcano
composite volcano
Explain what geothermal energy is
Geothermal energy: a clean, reliable energy source provided by water heated by magma.
A source of electricity
Piped in to produce steam, which turns the turbine, which then turns the generator.