Research
Variables
Measurements
Statistics
Potpourri
100
Kerlinger described this as: "an interrogative sentence that asks: 'What relationship exists between two or more variables?'"
What is a research problem
100
Defined as having the ability to vary or have different values.
What is a variable.
100
Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio.
What are scales or levels of measurement
100
Descriptive statistic which utilizes mean, median and mode for normal distributions
What is central tendency
100
The three main measures of central tendency
What is the mean, median and mode
200
Variable that cannot be manipulated because it is a characteristic of the participant.
What is an attribute independent variable.
200
Defined as remaining the same without change.
What is a constant.
200
Three or more ordered levels, but the the frequency of the scales is not normally distributed.
What are ordinal variables
200
Indicates the percentage of participants in each category, whether those be ordered or unordered categories.
What is a frequency distribution
200
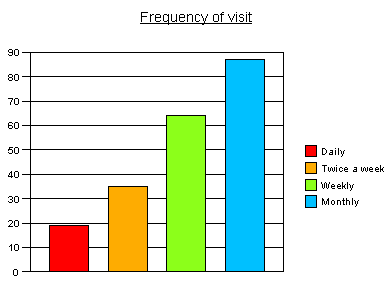
What is a bar chart
300
Commonly used to describe the values of an independent variable.
What are levels of a variable.
300
The outcome or criterion of a study.
What is the dependent variable.
300
Two categories either ordered or unordered.
What are dichotomous variables
300

What is a box-and-whisker plot
300
Standard deviation is the most common measure of ________.
What is variability
400
Used for complex research that has multiple variables.
What are Groups or Sets of Variables
400
Descriptions of a variable in terms of the operations used to produce it or techniques used to measure it.
What is an operational definition.
400
Three or more unordered categories
What are nominal variables
400
Frequency distributions, central tendency and variability.
What are descriptive statistics
400
The best measure of variability, for ordinal data, depicted by box and whisker plot
What is the interquartile range
500
The treatment an experimental group receives during a study is an example of an ________.
What is an active independent variable
500
Not of interest in a particular study but could influence the dependent variable.
What are extraneous variables.
500
Interval scale, continuous, dimensional and quantitative are terms associated with these variables.
What are normally distributed variables
500

What is a normal distribution or bell curve?
500
Three percentages under the area of the normal curve from 1 - 3 standard deviations
What are 68%, 95% and 99%