What is the equation for photosynthesis?
6H2O + 6CO2 +Sunlight --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is the equation for Cellular Respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
What are the stages of the CELL CYCLE (not mitosis)?
Interphase (G1, S, and G2), Mitosis, and Cytokinesis.
How many daughter cells does Meiosis produce? What are they called?
4. Gametes.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Genotype is the genetic information (what alleles are present). Phenotype is the EXPRESSION of those alleles.
Where does photosynthesis take place in plant cells?
Chloroplast (thylakoids within the Chloroplasts).
What is the first step of cellular respiration and what happens?
Glycolysis. Glucose is taken and broken down into two pyruvate molecules.
What stage of Mitosis is this?
 `
`
Telophase
What stage of Meiosis is this?

Anaphase 1
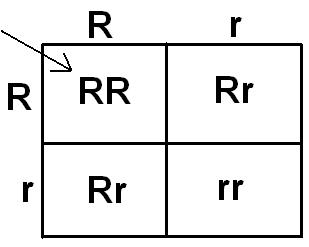
Which of the following are homozygous recessive, heterozygous, and homozygous dominant?
RR, rr, Rr
Homozygous Recessive = rr
Heterozygous = Rr
Homozygous dominant = RR
Explain what happens during the "light-dependent reaction" of Photosynthesis.
Light excites electrons and helps split H2O into O2 and Hydrogen ions. These hydrogen ions get transported across a gradient via the Electron Transport Chain (ETC). ATP is formed.
Light and H20 --> O2 and ATP
What is the second step of cellular respiration and what happens?
Krebs Cycle. Pyruvate is taken and broken down to form some ATP and some NADH and FADH2. Releases CO2.
What stage of mitosis is this?

Prophase
What stage of Meiosis is this?
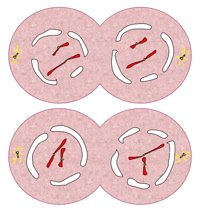
Telophase II
If R is the allele for red hair, and r is the allele for pink hair, what will be the phenotypic ratio of the offspring below?
75% Red Hair
25% Pink Hair
Explain what happens during the Calvin Cycle?
ATP from the light dependent reaction takes CO2 molecules and creates glucose (using RUBISCO).
What is the third step of cellular respiration and explain what happens?
Electron Transport Chain. Massive amounts of NADH and FADH2 transport electrons down the chain, creating gradients and creating massive amounts of ATP (32-34 to be exact). Oxygen is needed as a final receptor for electron, otherwise it will be aerobic respiration.
What stage of mitosis is this?

Metaphase
What do haploid and diploid mean?
Diploid is 2n, meaning there are 2 complete sets of Chromosomes (one from mom, one from dad). In humans this number is 46.
Haploid is n, meaning there is only one set of chromosomes (with mixed genes). In humans this is 23 (gametes are haploid cells).
What will be the genotypic ratio of the offspring in the following Punnet Square?

TT - 0%
Tt - 50%
tt - 50%
Do plants undergo cellular respiration?
YES! Plants also do cellular respiration (they also need ATP in their cells), and so they also emit CO2, however they absorb much more.
How is active vs. passive transport necessary for Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration?
Proton gradients are created with active transport in Electron Transport Chain (energy taken from SUN in photosynthesis, and NADH/FADH2 in respiration). Then facilitated diffusion using ATP synthase creates ATP as the gradients reach equilibrium.
What is the role of cyclins in a cell? What can happen if cyclins aren't functioning.
To signal the cell to divide. Helps regulate the cell cycle. Disruptions can cause CANCER!!
What are TWO main differences between Meiosis and Mitosis?
In metaphase I, pairs of homologous chromosomes line up at the equator and cross over, while in Mitosis it is only sister chromatids that line up.
Define Mendel's law of segregation?
Law of segregation. During gamete formation, the alleles for each gene segregate from each other so that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene.