True or False: Diabetes does not affect glucose usage or storage.
False. Diabetes DOES affect glucose usage and storage.
True/False: Lipids are generally soluble in water.
False. They are not soluble in water.
True/False: The primary structure of a protein is just the sequence of amino acids, it is always read from N-terminal to C-terminal.
True.
True/False: DNA is synthesized from 3' to 5'.
False.
What are the metabolic reaction pathways that breakdown of food molecules called?
Catabolism
What type of carbohydrate is the below structure?
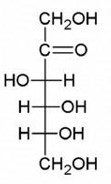
Fructose
What is the correct way to number the following fatty acid?
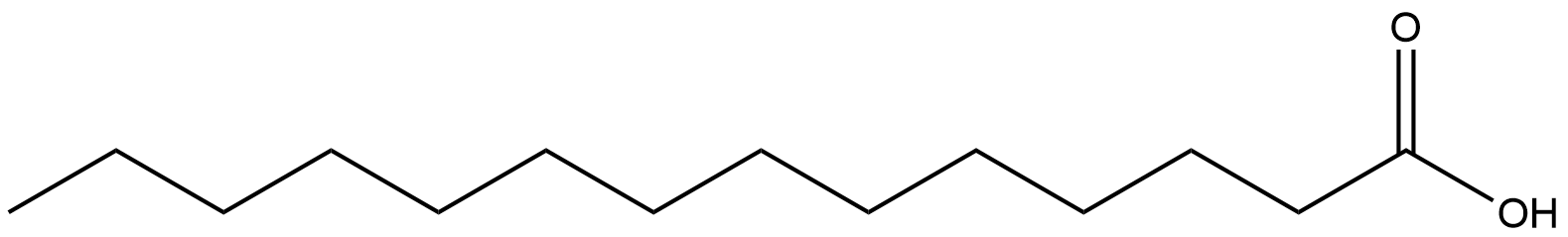
14:0
True/False: An amino acid is considered essential because cells lack the ability to synthesize them.
True. These amino acids are: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine .
Which blood type is the universal donor? Universal reciever?
O, AB
The FDA considers foods that contain less than _____ grams of trans fats to have no trans fats.
0.5 grams
What is a non-protein portion of an enzyme called that is essential for enzymatic activity?
Cofactor
Which nucleotide is found only in RNA? Which type of sugar?
Uracil, Ribose
What is the primary energy storage molecule of a cell?
ATP
How many chiral carbons does the following carbohydrate have?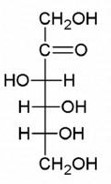
3
What is the correct way to number the following fatty acid?
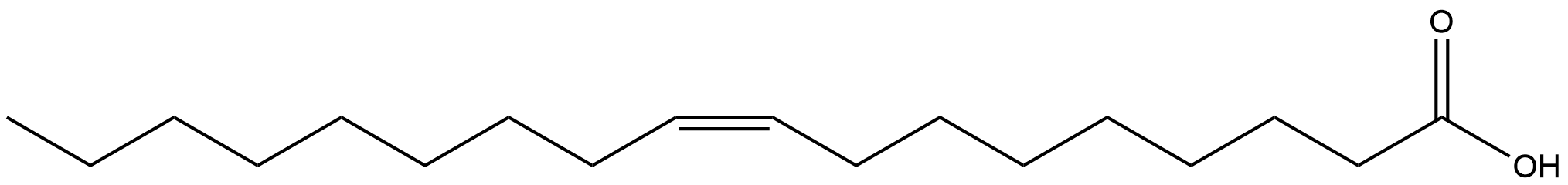
18:1
Which amino acid can form disulfide bonds?
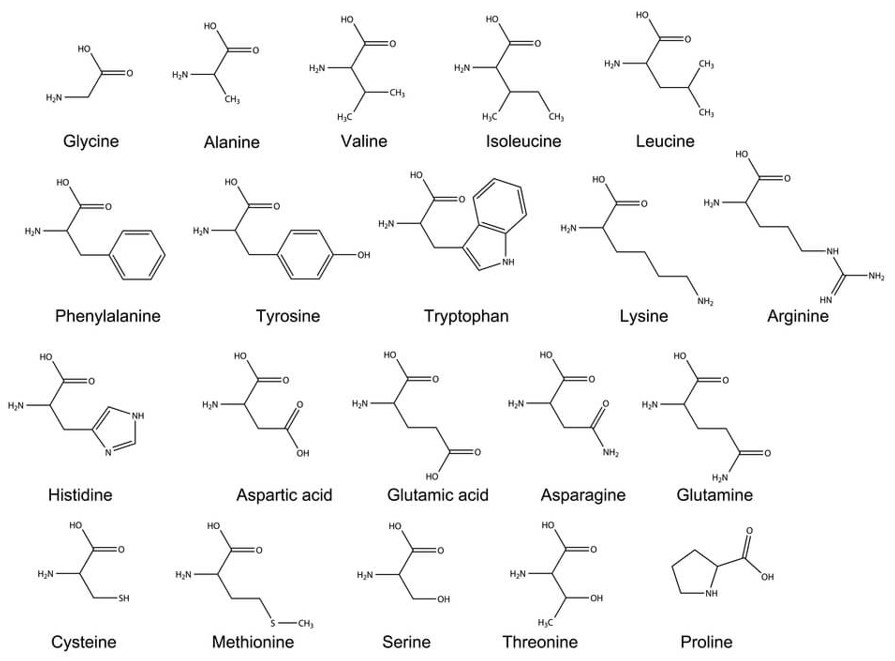
Cysteine
Which saccharide do the brain and red blood cells use for energy?
Glucose
Adrenal gland.
True/False: Enzymes have no effect on the activation energy of a reaction.
False.
Which amino acid is always the first amino acid of a protein?
Methionine
Pyruvate is converted to what molecule under aerobic conditions after glycolysis?
Acetyl-CoA
From the carbohydrate structure below; which numbered carbon is the anomeric carbon?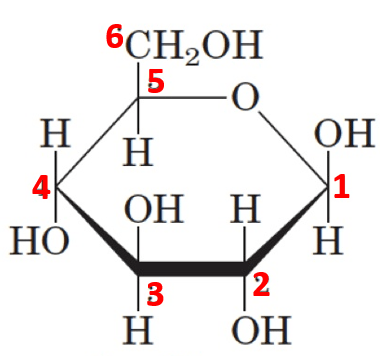
1
What is the correct way to number the following fatty acid?
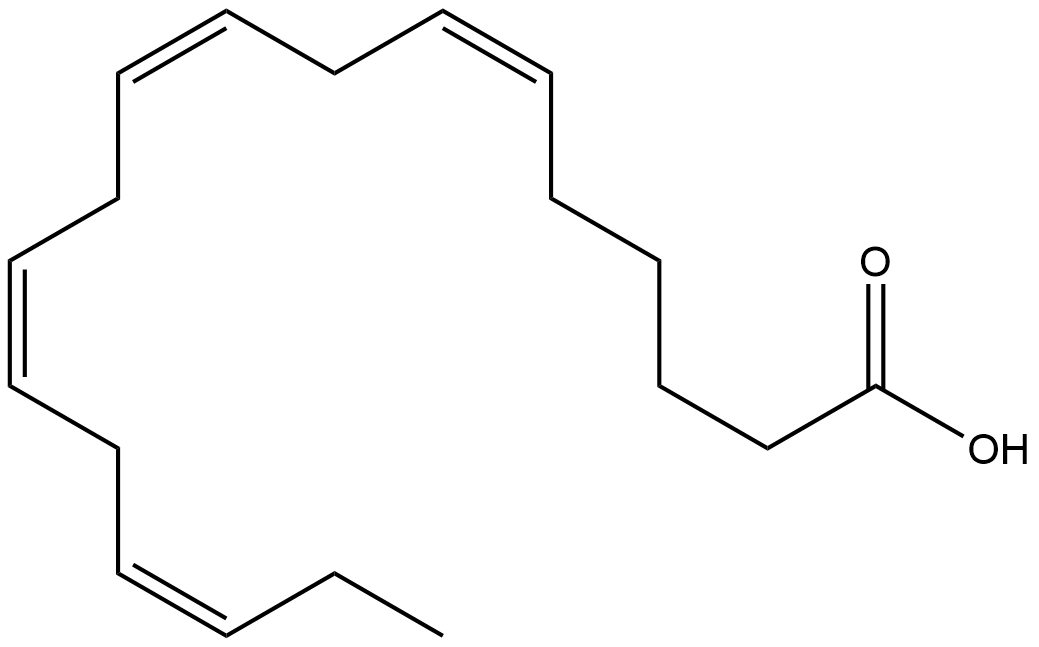
18:4
What is the first amino acid in all protein synthesis?
Methionine
True/False: Galactose is a common disaccharide.
False. Galactose is a monosaccharide.
Fatty Acids are composed of long, unbranched carbon chains with which functional group at one end?
Carboxylic acid?
Globular, Membrane, and _______ are examples of tertiary protein structures.
Fibrous
What is the copying of genetic information into mRNA version called?
Transcription
The oxidation of a 22-carbon fatty acid results in the production of _______ acetyl-CoA molecules after a total of _______ rounds of β-oxidation:
11 acetyl-CoA; 10 rounds
The closest IUPAC name for the below carbohydrate? 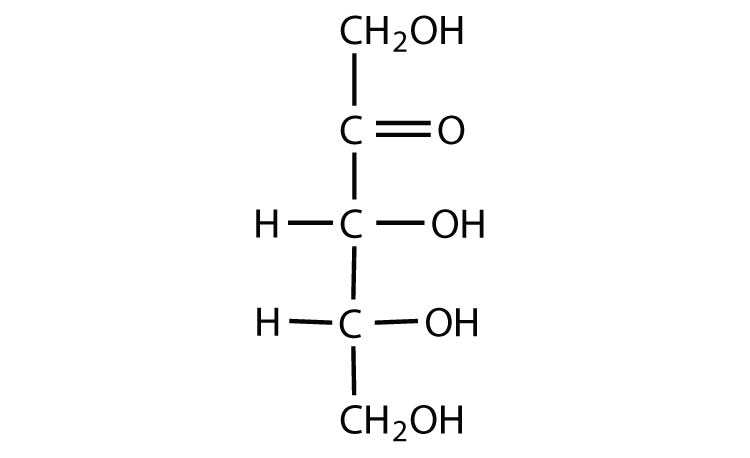
1,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxy-2-pentanone
The following structure is best described by which of class of lipids?
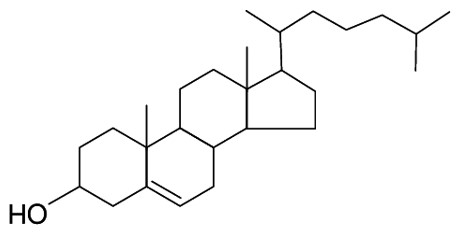
Steroid
An amino acid is made up of a carboxylic acid, an _______, and a side chain.
amine
Maltose is enzymatically cleaved into which two saccharides?
Glucose and Glucose
The passage of Na+ ions across a cell membrane that requires energy is termed?
Active transport.
A peptide bond between two amino acids is what type of functional group?
Amide
DNA wraps around proteins called _______ to form structures termed chromatin.
Histones
What is the breakdown of fatty acids for energy called?
beta-oxidation
The carbohydrate below is D or L? Which numbered carbon determines this?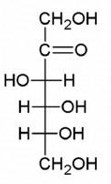
D-fructose; #5 carbon
The following structure is best described by which class of lipids?
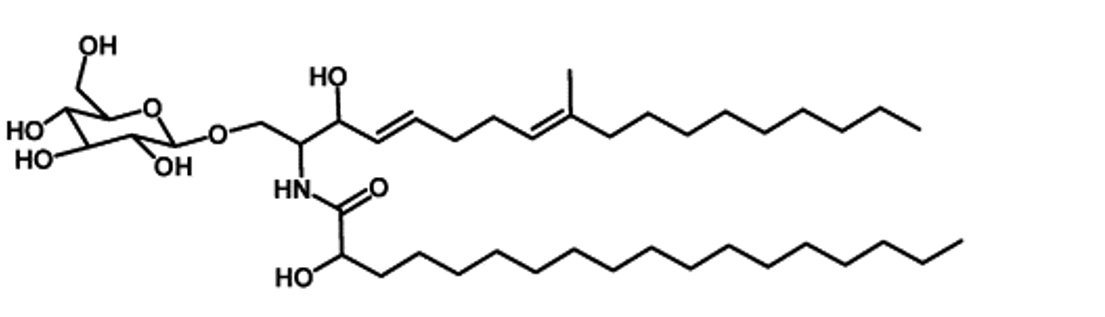
What amino acid sequence does the following DNA sequence encode for? (Use single, capitalized letters)
5’-GGGCTAGTACCCCACTTGTCA-3’
3’-CCCGATCATGGGGTGAACAGT-5’
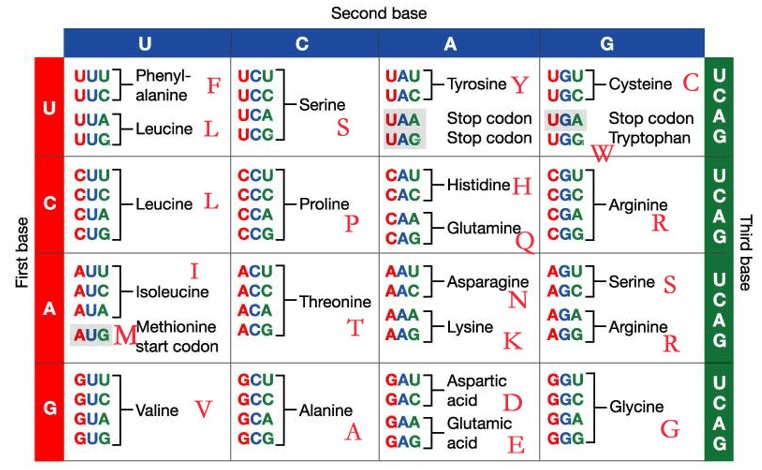
G-L-V-P-H-L-S
Name a saccharide humans are unable to digest because we lack the enzyme to do so.
Cellulose
Bile salts are synthesized from what lipid?
Cholesterol
What is the name of the reactant in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
Substrate
What is the term for DNA base pair binding?
Complementarity
Ketone bodies can occur due to the breakdown of fats in the body which lowers the blood pH to 7.4, or "acidic" levels. Which of the following is ARE ketone bodies?
Acetate, Acetone, Acetoacetate, beta-Hydroxybutyrate
Acetone, Acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate
What is the name of the bond that holds this disaccharide together?
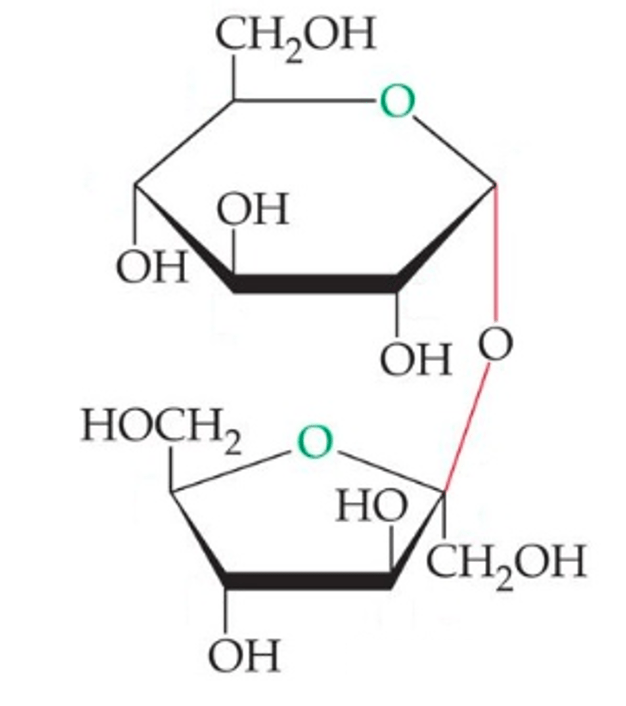
alpha(1-2)beta glycosidic bond
The following structure is best described by which class of lipids?
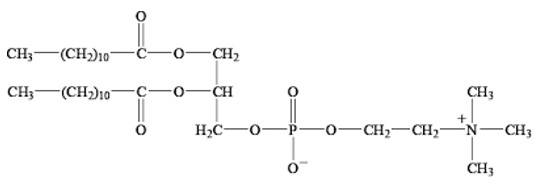
Glycerophospholipid
What amino acid sequence does the following DNA sequence encode for? (Use single, capitalized letters)
5’-ATGCCAGTAGGCCACTTGTCA-3’
3’-TACGGTCATCCGGTGAACAGT-5’
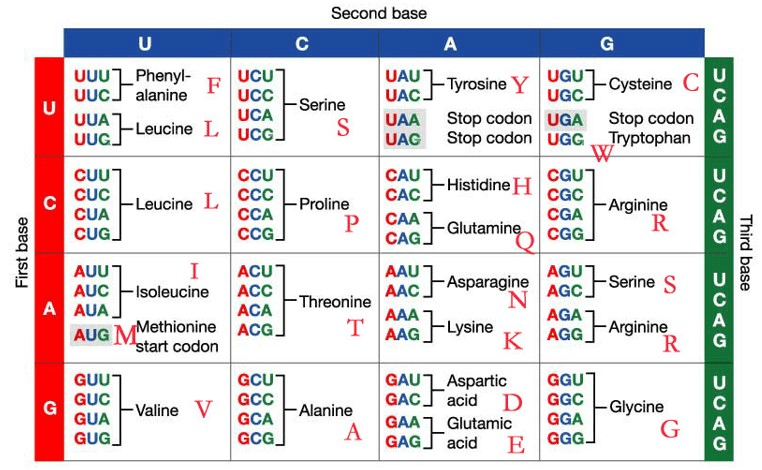
M-P-V-G-H-L-S