This is the mass of a single molecule of dihydrogen sulfide.
What is 5.66 x 10-23 g/atom?
This experiment proved that light is capable of acting as a particle.
What is the photoelectric effect?
This type of orbital draws the two nuclei of an atom closer together and tends to be lower in energy.
What are bonding orbitals?
Consider the following molecule: XeOF4. Determine the hybridization of the central xenon atom and describe the molecular geometry.
What is sp3d2 and square pyramidal?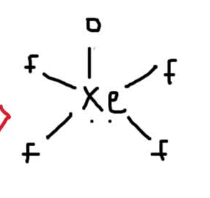
A sample of mercury (Hg) has a mass of 0.0852 kilograms. This is the volume of the mercury sample in μm3 (micrometers), given that the density of mercury is 13.6 g/cm3.
What is 6.27 x 1012 μm3?
This is the balanced reaction for the combustion of ethane (C2H6) in oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide and water vapor.
What is 2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) --> 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)?
This is the ground state electron configuration of Rhenium (Re).
What is [Xe]4f145d56s2?
This is the VSEPR shape and electron geometry that corresponds to an atomic arrangement of AX4E2.
What is square planar and octahedral?
Count up all of the sigma and pi bonds.
σ - 62
π - 12
This is the percent by weight of sulfur in C2H6S.
What is 51.60%?
These are the balanced, ionic, and net ionic reactions for the reaction of aqueous sodium sulfate with aqueous barium chloride.
What is:
1. Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) --> 2NaCl(aq) + BaSO4(s)
2. 2Na+ + SO42- + Ba2+ + 2Cl- --> 2Na+ + 2Cl- + BaSO4(s)
3. SO42- + Ba2+ --> BaSO4(s)
This is the wavelength of a light wave with a frequency of 2.07 x 1014 /s, in nm.
What is 1450 nm?
Draw the Lewis dot structure for NO2-. This is the molecular geometry.

What is bent?
An unknown compound has the formula CxHyOz. You burn 0.1523g of the compound and isolate 0.3718g of CO2 and 0.1522g H2O. What is the empirical formula of the compound?
C4H8O
This is the hybridization of the central atom of SF6.
What is sp3d2?
Consider the reaction of solid aluminum with chlorine gas to produce aluminum chloride. If you only have 1 mol of Al and 1 mol of chlorine gas, which is the limiting reactant, how many moles of product are formed, how many moles of excess reactant are left over?
2Al+3Cl2→2AlCl3
Chlorine is limiting, 0.67 moles of aluminum chloride formed, 0.33 moles of aluminum are excess.
Consider the following elements: Na, Mg, and Al. Out of these three, this atom will have the highest second ionization energy. Explain.
What is Na?
The removal of a second electron from Na would be removing an electron from a stable noble gas configuration, whereas for Mg and Al the second electron will be removed from the outer 3s shell.
Draw the MO diagram for O2. What is the bond order in order of most to least stable for O2-, O2, O2+.
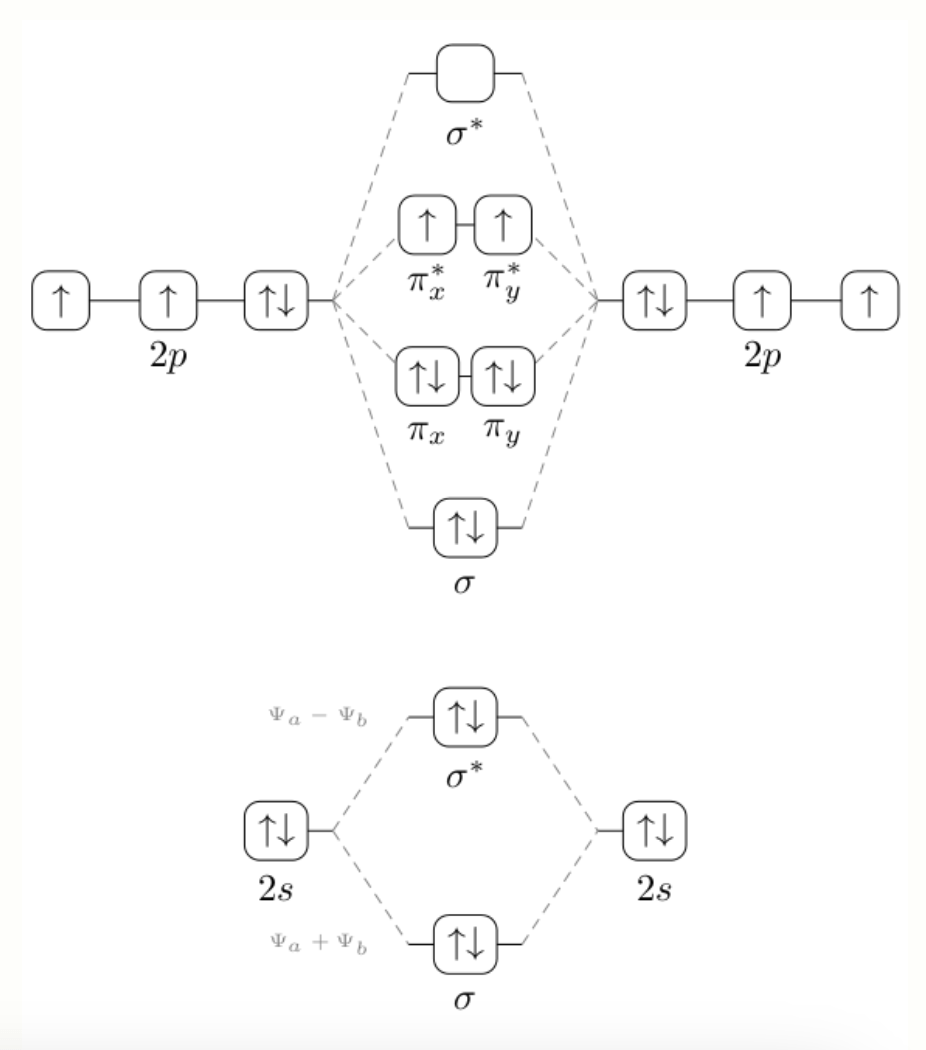
Bond order: O2+ > O2 > O2-
What is the molecular orbital diagram for IBr-? Is the bond in IBr+, IBr, or IBr- longer?
IBr- > IBr > IBr+
This is the change in enthalpy for the combustion of ethane 2C2H6 + 7O2 --> 4CO2 + 6H2O. (Use the reference sheet on Canvas for bond enthalpy information). Is this an endothermic or exothermic reaction?
What is -2784 kJ/mol and is exothermic?
You have a molecule that is 40% Carbon, 6.7% Hydrogen, and 53.3% O. What is the empirical formula of this compound? If the molecule has a molar mass of ~90 g/mol, what is the molecular formula?
CH2O - empirical formula
C3H6O3 - molecular formula
Use effective nuclear charge to explain atomic radius, ionization energy, and electron affinity trends. If there are exceptions to this trend, please explain.
Effective nuclear charge increases from left to right across a period, which will cause atomic radius to shrink, increase ionization energy, increase electron affinity.
Example of exception for ionization energy: Nitrogen has singly paired orbitals in the 2p energy shell, while oxygen has one full orbital and 2 singly paired orbitals. Electrons have negative charge and therefore repel each other, meaning energy needs to be inputted to force two electrons into one orbital. In oxygen, one of the orbitals already has two electrons, so removing one electron will be decently simple as the orbital would prefer to have only a singly paired electron. Nitrogen though has a very stable subshell due to the single pairing, meaning removing an electron from neutral oxygen will be easier than removing an electron from neutral nitrogen.
Example of exception in electron affinity: Phosphorus has three orbitals with singly paired electrons, which is a very stable configuration so it is difficult to add more electrons and force them to begin pairing up. Silicon has an empty orbital though, so adding another electron into the p subshell will not be very difficult, making it so that it has a higher electron affinity than phosphorus does.
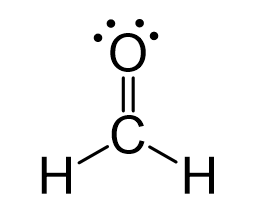
For CH2O:
1. Draw lewis dot structure
2. Determine the electron geometry and molecular shape
3. Count sigma/pi bonds
4. Determine hybridization of the central atom
1. 
2. trigonal planar, trigonal planar
3. 3 σ bonds, 1 π bond
4. sp2
Compare the MO diagram for O2 and F2. Which of the two diagrams would have orbitals that are higher in energy?
(Hint: there is a helpful diagram in Tuesday's lecture notes)
O2 orbitals will be higher in energy. 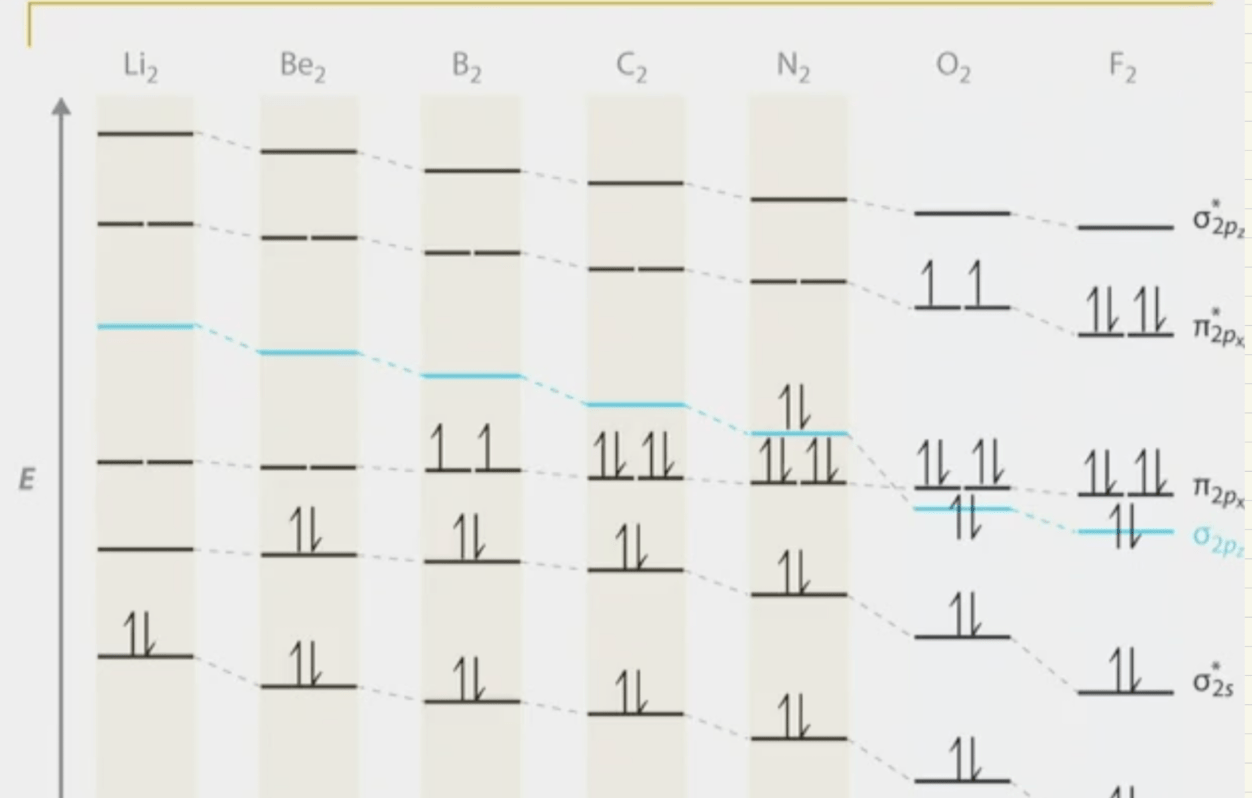
greater nuclear charge of fluorine pulls its atomic and molecular orbitals to lower energy levels, while oxygen's lower nuclear charge results in higher-energy orbitals
Rank these from highest to lowest melting point:
CCl4, C3H6O, H2O, C6H14, NaCl
NaCl > H2O > C3H6O > C6H14 > CCl4