We always try to satisfy this rule when drawing Lewis dot structures.
What is the octet rule?
This determines the function of all molecules in a biological system.
What is molecular shape?
This type of covalent bond, formed by overlap of atomic orbitals head-to-head, is found once in single bonds, once in double bonds, and once in triple bonds.
What is a sigma bond?
This is what occurs between structures with the same arrangement of atoms, but different connections.
What is resonance?
This is the theory that molecules have orbitals in the same way that atoms have orbitals.
What is molecular orbital theory?
This is what determines the best Lewis structures when deciding between multiple.
What are formal charges?
{# valence electrons in free atom} - {# unshared electrons} - 1/2{# shared electrons}
{# valence electrons} - {# of balls + # of sticks}
In the following diagram, this is the point on the graph that represents the distance between the atom ideal to form a bond.
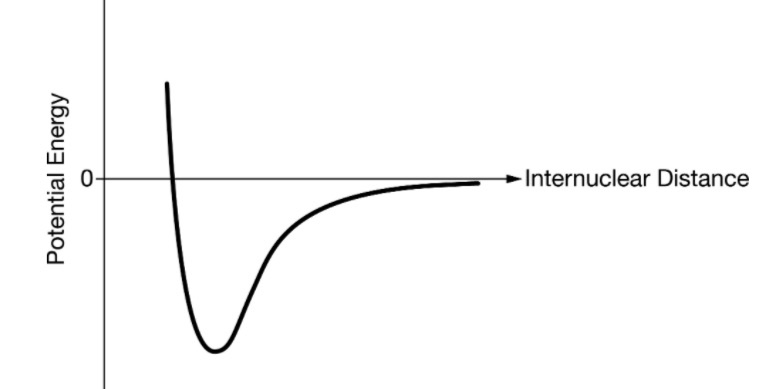
What is the very bottom?
Pi bonds, formed by side-to-side overlap of this type of orbital, occur once in double bonds and twice in triple bonds.
What are p-orbitals?
This type of orbital draws the two nuclei of an atom closer together and tends to be lower in energy.
What are bonding orbitals?
This is the equation that can be used to find out the MO bond order.
What is 1/2[bonding electrons - antibonding electrons]
Draw the Lewis dot structure for XeF4. The molecule is this level of polar.
What is non-polar due to symmetry?
What is symmetry?
This type of orbital is a combination of atomic orbitals of the same atom.
What are hybrid orbitals?
This type of reaction absorbs heat from its surroundings and will therefore consider heat to be a reactant in the chemical reaction.
What are endothermic reactions?
This is the bonding/antibonding electron configuration for B2.
Note: there should be a 2 next to the parentheses for the antibonding 2s orbital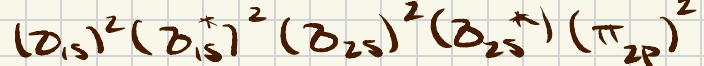
This is the molecular geometry for CH2O.
What is trigonal planar?
An orbital in which electron charge is concentrated towards the outer edges (far side of the nuclei), therefore drawing the nuclei apart.
What is an anti-bonding orbital?
For a bond to form between two atomic orbitals, there must be an overlap and each atomic orbital must contain this.
What is an unpaired electron?
This is what we call a species with one or more unpaired electron(s) that is highly reactive.
What is a free radical?
These have the same atom connectivity but differ in spatial arrangement. These also include geomtric and spatial.
What are stereoisomers?
Draw the Lewis dot structure for NO2-. What is the molecular geometry?

What is bent?
This is the VSEPR shape that corresponds to an atomic arrangement of AX4E2.
What is square planar?
This type of bonding orbital will contain no nodes (zero probability of electrons being found there).
What are bonding orbitals?
This is a compound that has an even number of electrons but does not have enough electrons to form an octet around each atom.
What is an electron-deficient compound?
If there is only one chiral carbon in a molecule, its mirror image will be a different compound. This is known as a type of isomer your nose can detect.
What is an enantiomer?