What types of elements form ionic bonds? Covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds are formed between metals and nonmetals, covalent bonds are formed between nonmetals.
lithium bromide
LiBr
Formula mass of KClO3
122.5 amu
% composition of Al2O3
52.925% Al
47.075% O
NO2
nitrogen dioxide
Draw the Lewis Structure for CHCl3

Draw the atoms in a metallic bond.
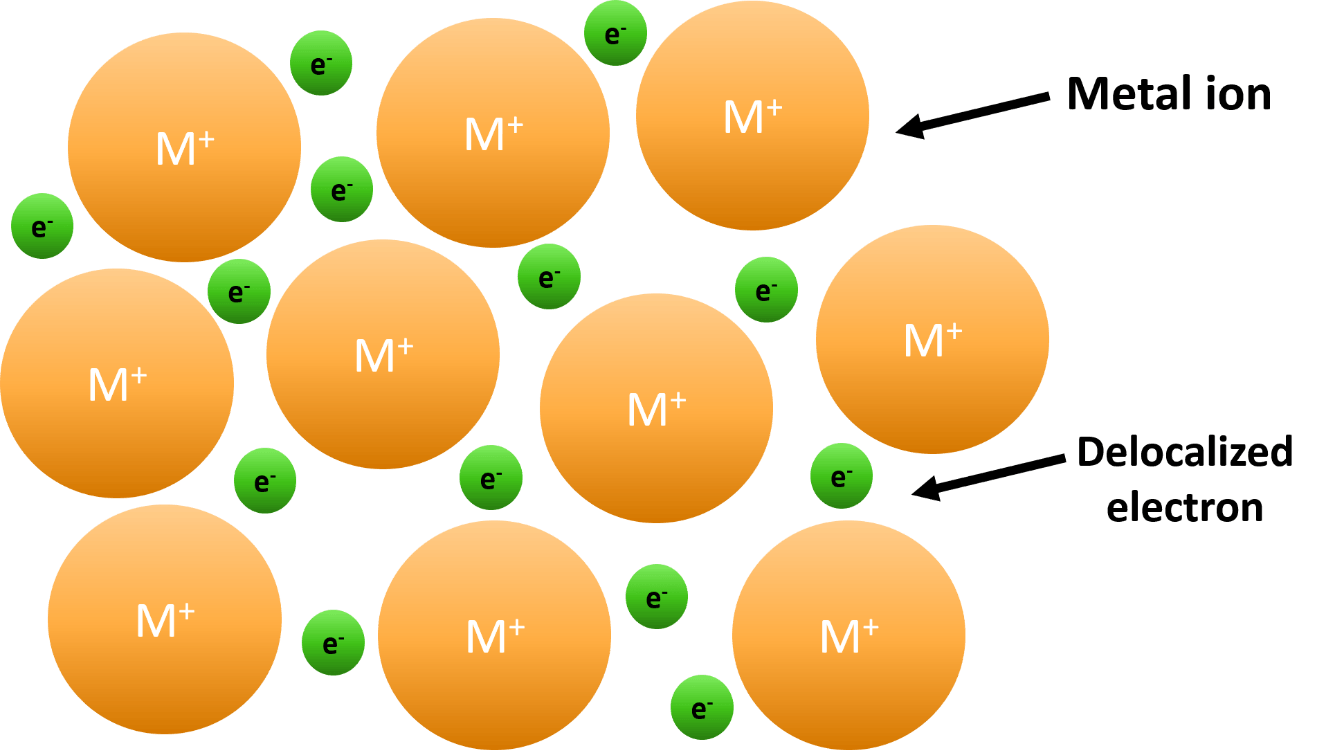
Name 2 properties of ionic compounds and 2 properties of covalent compounds
Ionic: hard, brittle solids; high melting points; conducts electricity in water (electrolytes)
Covalent: low melting and boiling points
chromium (III) chloride
Molar mass of ammonium oxalate
124 g/mol
% composition of Fe(C2H3O2)2
32.107% Fe
27.621% C
3.477% H
36.794% O
diphosphorus pentoxide
P2O5
Draw the Lewis structure for CO2. Give its molecular geometry
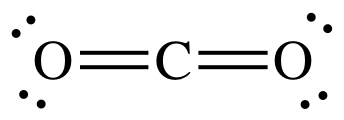
linear
Give a definition of intermolecular forces.
Forces of attraction between molecules.
Write the chemical sentence to show the ionic bond formed from Magnesium + Oxygen
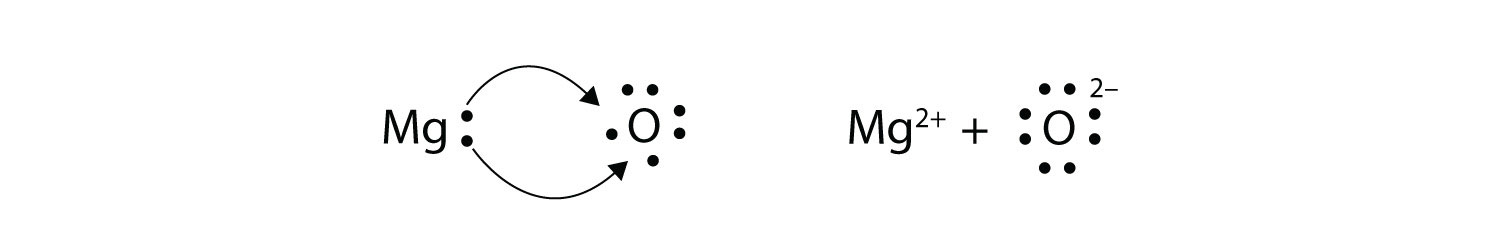
iron (IV) nitrate
Fe(NO3)4
The number of grams in 5.6 moles of BaCl2
1200 g BaCl2
Empirical formula of a compound containing 20.235% Al and 79.765% Cl
AlCl3
hydrochloric acid
HCl
Draw a structure with trigonal pyramidal geometry. How many bonds and lone pairs does it have?
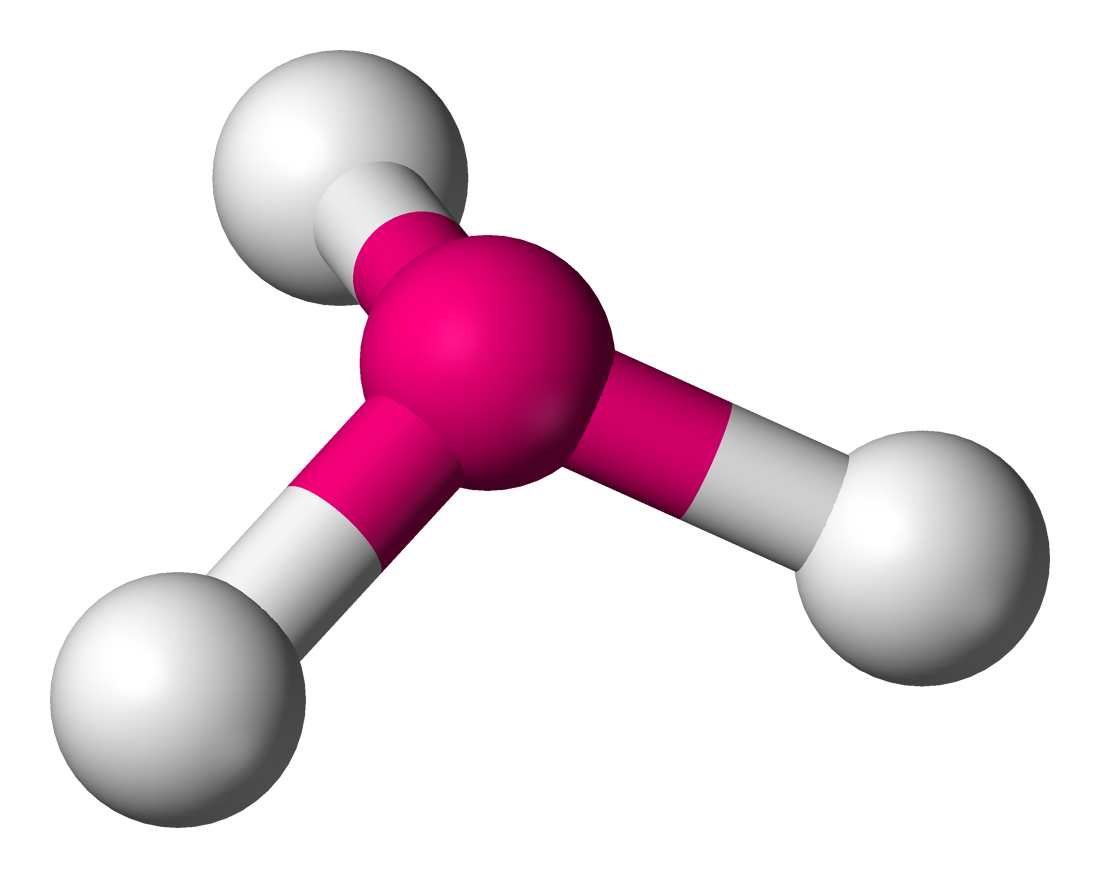 3 bonds, 1 lone pair
3 bonds, 1 lone pair
What type(s) of intermolecular forces are found in propane?
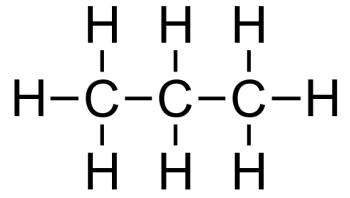
London dispersion
Explain how covalent and ionic bonds form. Give at least 1 similarity and 1 difference.
Covalent bonds form when nonmetals share pairs of electrons. Ionic bonds form when a metal gives valence electrons to a nonmetal. Both happen so that all atoms have a full octet.
NiC2H3O2
nickel (I) acetate
The number of formula units in 125 g of silver nitrate.
4.43 x 1023 formula units AgNO3
Empirical formula of a compound that is 60.001% C, 4.476% H, and 35.523% O
C9H8O4
HNO3
nitric acid
What are the bond angles for:
Linear geometry?
Trigonal planar?
Tetrahedral?
Trigonal bipyramidal?
Octahedral?
Linear: 180o
Trigonal planar: 120o
Tetrahedral: 109.5o
Trigonal bipyramidal: 120o and 90o
Octahedral: 90o
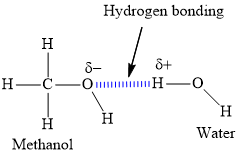
Draw the Lewis structures for CH3OH and H2O. Draw the hydrogen bond between the two molecules.
Write the chemical sentence for the compound that forms from Scandium(III) + Fluorine
Assign oxidation numbers for each element in the compound.

manganese (VI) peroxide
Mn(O2)3
The number of oxygen atoms in 1.000 g sucrose (C12H22O11)
1.935 x 1022 atoms O
Empirical and molecular formulas of caffeine (49.48% C, 5.19% H, 16.48% O, 28.85% N)
Molar mass = 194.19 g/mol
Empirical: C4H5N2O
Molecular: C8H10N4O2
sulfuric acid
H2SO4
Draw all of the resonance structures of SO2. What is its molecular geometry?

bent
Rank the following from highest to lowest boiling point. Give a brief explanation.
CH4, C2H5OH, C2H6, C2H5Br
C2H5OH > C2H5Br > C2H6 > CH4
Boiling point decreases as IMFs get weaker.