Is a cation positive, negative, or neutral?
Positive
Covalent bonds occur between these two classes of element:
Non-metals and non-metals
Write the chemical formula for the compound formed between magnesium (Mg) and oxygen (O).
MgO
What kind of bond is represented by this model:

Ionic Bond
Bonus: What is the chemical formula? (100pt)
Metallic bonds are special because of their ____ of electrons.
Sea of electrons
Ionic bonds occur between these two types of element:
Metals and Non-metals
Which one of these covalent bonds is NOT polar:
C-F, O-O, H-Cl, S-O
O-O
Write the chemical formula for the compound formed between rubidium (Rb) and selenium (Se).
Rb2Se
Name the compound and type of bond for this molecule:

NH3, covalent
Bonus: Which side of a polar water molecule would be attracted to nitrogen's lone pair of electrons? (Hydrogen or oxygen side) (100pts)
Which one of these is NOT a characteristic of metallic bonds:
High conductivity, High malleability, High Solubility
High solubility (metals don't dissolve easily in water)
Bonus: What does "ductility" mean in reference to properties of metals? (200pts)
Which of these is an ionic bond:
Na-Fe, C-O, H-H, K-Br, F-C, Cu-Cu
K-Br
What kind of covalent bond involves the unequal sharing of electrons?
Polar covalent
Write the chemical formula for the compound formed between boron (B) and oxygen (O).
B2O3
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for CaBr2

List the five shapes that we learned about in the VSEPR model of molecular bonds.
Linear, bent, tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal, trigonal planar
Define: Polyatomic ion (and give one example).
A covalently bonded compound with an overall charge. Examples: OH-, SO4-2, NO2-
Single, Double, Triple bonds: give an example molecule for each type of covalent bond
Single: F2
Double: O2
Triple: N2
Bonus: Which type of bond can rotate? (200pts)
Write down a representative chemical formula for each type of bond: ionic, covalent, metallic
(Too many examples)
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for CBr2F2
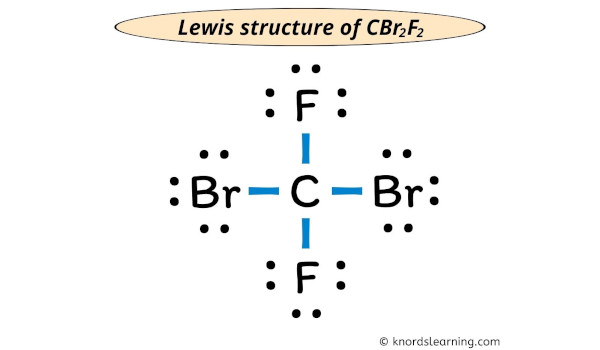 Bonus: Is this a polar or non-polar molecule? (100pt)
Bonus: Is this a polar or non-polar molecule? (100pt)
Draw a particle diagram to show the compound MgCl2 dissolved in water. Show at least 4 water molecules correctly oriented.
Your diagram should have 1 Mg+2 and 2 Cl- ions. Water molecules would surround the ions as below:

List three physical properties of ionic compounds.
Examples: High solubility, electrolytes, not malleable (shatters when hit), not conductive as a solid, high melting point
XeF4 is one of the only covalent compounds formed by a noble gas. Using vocab terms, explain why xenon doesn't normally form bonds, but why it can form bonds with fluorine.
Xenon is a noble gas with 8 valence electrons, so it does not need to form bonds. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, so it is strong enough to pull electrons away from xenon for a bond.
Iron (Fe) can form +1, +2, and +3 ions. Write the formulas for the three forms of iron oxide (ionic compound of iron and oxygen).
Fe2O, FeO, Fe2O3
Bonus: What family of elements does iron belong to? (100pt)
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for HCN (hydrogen cyanide).

Determine the shape and polarity of a molecule of PI3
Trigonal pyramidal, polar