What is a gas that follows the kinetic-molecular theory?
Ideal gas
What is the molar volume of any substance at STP?
22.4 L/mol
A handful of gas, which starts at 7.4 L and 23 oC, is heated to 51.2 oC at a constant pressure. What is the new volume?
8.1 L
What are the only intermolecular forces that work on nonpolar molecules?
London dispersion forces
What is a solid that splits or shatters into irregular fragments?
Amorphous solid
What is the ability of a gas to spread out uniformly to fill an entire volume over time?
Diffusion
What is the value of STP?
0 oC and 101.325 kPa
A 2.3 L sample of gas has a temperature of 74.2 oF. What is the volume is the temperature drops to 39 oF?
2.1 L
What is the temp and pressure at which a substance can exists in all three states of matter?
Triple point
Which gas law relates the pressure of a gas to its temperature in Kelvins?
What does Dalton's law of partial pressures state?
The total pressure of a mixture of gases equals the sum of the pressure of each individual gas
Between Chlorine gas and Oxygen gas, which one diffuses the fastest? By how much?
Oxygen is 1.47 times faster than Chlorine
What is the boiling point of ethylene glycol at 10 kPa?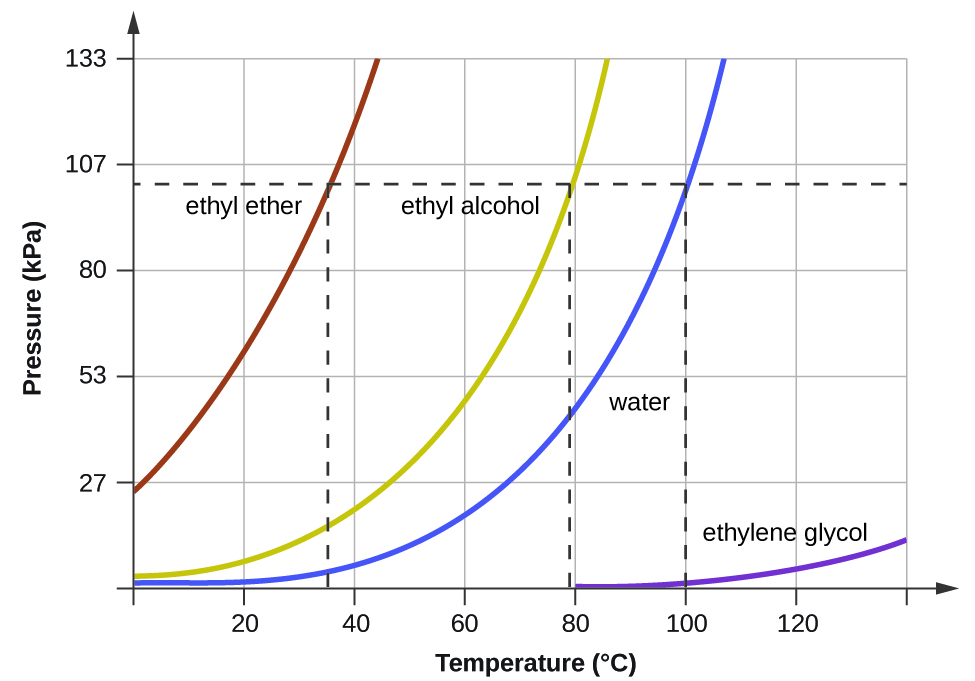
What is lattice energy?
The energy released when gaseous particles form crystals
Hydrogen bonds form between Hydrogen and which three elements?
N
O
F
State Boyle's law
The volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure, if temp is constant
What is the critical point of water?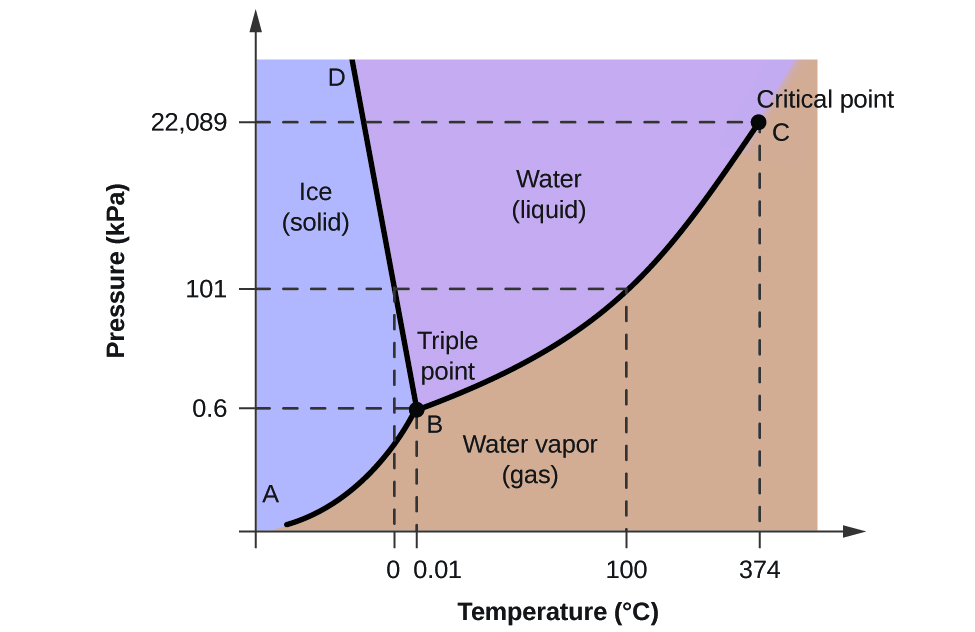
374 oC and 22089 kPa
38.2 g of hydrogen gas reacts with oxygen gas to produce water vapor. If this is happening at 200 K and at a pressure of 138.2 kPa. What is the volume of oxygen gas used?
28.7 mL
What is a meniscus and how does it form?
A meniscus is the curved surface of a liquid in a container. It forms because the attraction to the container exceeds the attraction to the liquid.
What is vapor pressure?
The pressure that is exerted by the evaporated particles over a liquid
List five characteristics of gases.
Consists of particles that are tiny compared with the great distances between them
Have particles that move in random direction at high velocities
Have particles that don't interact with each other except in momentary colisions
Whose collisions between particles are elastic (meaning they conserve energy)
Have an average kinetic energy that is proportional to its temp in Kelvins
A unknown gas has a molar density of 1.70 g/L. What is its molar mass? Which gas is it?
38.08 g/mol
Fluorine gas (F2)
A sample of 57.8 mL of Helium gas is collected over water at a temperature of 35.0 oC. Atmospheric pressure is 97.36 kPa. What is the volume of the sample at STP?
46.4 mL He
KCl, because dipole-dipole forces are stronger than london dispersion forces
The rate of effusion for a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the mass.