Which theory best explains paramagnetism?
Molecular orbital theory
If the difference between two element's electronegativity is high, the polarity is (Less/greater).
Greater
Is H3O+ polar or nonpolar?
Polar
What is the expected angle of a tetrahedral?
109.5o
Which theory focuses on the location of high electron densities surrounding the central atom and with electrons repelling each other?
VSEPR theory
What shape is O3?
Bent
Which theory states that both atoms acquire another valence electron that fills the vacancy in that particular orbital?
Valence bond theory
What is the expected bond angle of a trigonal pyramidal?
109.5o
What is molecular resonance?
The use of multiple molecular structures at once
What is a free radical?
A substance with unpaired electrons
Which theory would state that orbitals can be promoted?
Orbital hybridization
What is the expected bond angle of a trigonal planar molecule?
120o
How many bonds (sigma and pi) are in ethene (C2H4)
Six sigma and four pi bonds
or CH2O:
1. Draw the Lewis structure
2. Molecular shape
3. Bond angle
4. Dipole moment
5. Polar/nonpolar
1. 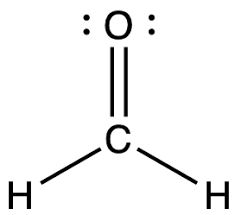
2. Trigonal planar.
3. 120o
4. 
5. Polar
What is the difference between sigma bonds and pi bonds?
Sigma bonds - form when orbitals overlap along the bond axis that connects two nuclei
Pi bonds - a side-to-side overlap
What is the expected bond angle of a linear molecule?
180o
Give three instances in which the octet rule is not applicable.
The presence of an odd number of valence electrons (Ex. NO2)
When there is an electron deficiency (Like with boron)
When there is an expanded octet.
For SO42-:
1. Draw the Lewis structure
2. Molecular shape
3. Bond angle
4. Dipole moment
5. Polar/nonpolar
1. 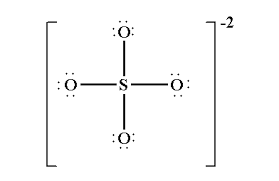
2. tetrahedral
3. 109.5o
4. N/A
5. Nonpolar
For O3:
1. Draw the Lewis structure
2. Molecular shape
3. Bond angle
4. Dipole moment
5. Polar/nonpolar
1. 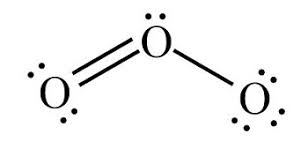
2. Bent
3. 120o
4. Points towards the negative
5. Polar