This refers to the amount of heat needed to raise a substance 1 degree Celsius.
What is the most basic unit of MATTER?
Atom
The chemicals that are produced by a reaction are called _______.
products
Macromolecule which gives the body energy
Carbohydrate (starch)
True/False: The structure of a protein has no affect on its function.
False
Is this considered to be a monomer or polymer? 
Polymer - Polysaccharide
Which bond holds together a DNA molecule?
Hydrogen bonds
What charge does an electron have?
Negative (-)
When a solution has a pH of below 7 it is considered an _______.
Acid
What is the monomer for a carbohydrate called?
Monosaccharide
What is the function of a protein?
Instructions for arranging amino acids
What is the monomer of nucleic acids called?
nucleotide
What term do we use to refer to an uneven distribution of electrons resulting in a charge? How is water an example of this?
Polarity
Oxygen is slightly negative and Hydrogen is slightly positive due to their arrangement of electrons. The molecule overall is neutral.
What are the 3 subatomic particles that comprise an atom?
Neutron
Proton
Electron
Almost all enzymes are considered to be which macromolecule?
This macromolecule forms long chains and functions to help form membranes.
Lipids
Amino Acid
What is the polymer of a protein called?
Oxygen -1
Hydrogen- 2
Which subatomic particles (2) is housed within the nucleus of the atom?
protons and neutrons
A substance that speeds up the rate of a reaction.
Catalyst
Which type of lipid forms double bonds?
Unsaturated fats
Hemoglobin is a type of protein found in red blood cells. What molecules are transported via red blood cells?
oxygen
What macromolecule is shown below? Is this a monomer or polymer?
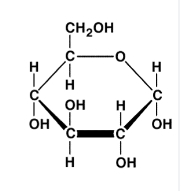
Carbohydrate (starch)
It is a monosaccharide (monomer).
The ____________ is the substance being dissolved, while the __________ is the substance doing the dissolving.
solute
solvent
What is 1 example of an element?
Results may vary
Hydrogen, oxygen, sodium, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, chlorine, carbon, helium, gold, silver, etc.
Hydrolysis
What sugar is an example of a monosaccharide?
glucose
The directions to build a protein orginally come from where?
Your DNA.
What macromolecule is being shown below? Is this image of a monomer or polymer?
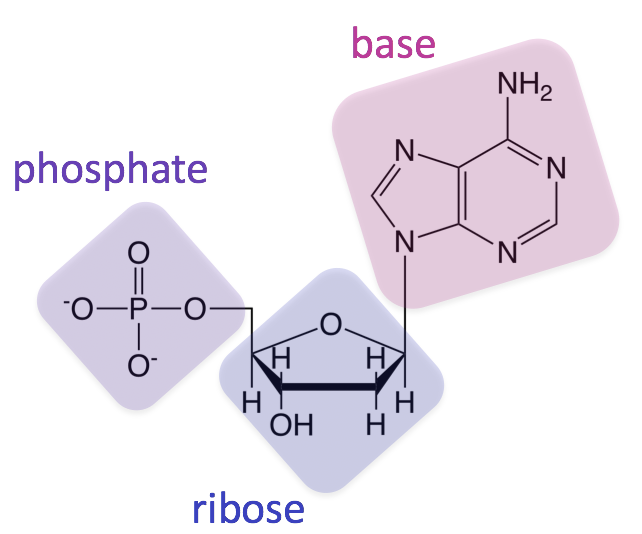
Nucleic Acid
This molecule is a monomer (only having 1 building block).
The attraction between molecules of the same substance.
cohesion
A substance consisting of 2 or more atoms of an element.
Compound
Which type of metabolism is nonspontaneous and absorbs energy (builds polymers)?
Anabolic Metabolism
Which macromolecule is comprised of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen (CHON)?
Which protein shape is a complete 3D arrangement of a polypeptide chain?
Tertiary Structure
I have a pond next to my house that I want to go swimming in. Before I jump in, I test the water quality of the pond for safety purposes. When my results come back, I found that the water has a pH of 4. Is the water safe to swim in? Why or Why not?
No! The water is acidic!
0 - 6.9 = Acidic
7.1 - 14 = Basic
7 = Neutral