This is the location of protons and neutrons.
What is the nucleus?
The starting energy level for an electron before it absorbs energy.
What is the ground state?
The elements in Group 18, which are stable due to a full valence shell.
What are the Noble Gases?
This subatomic particle, found in the outermost shell, is responsible for chemical reactions.
What is the valence electron?
This experiment, performed by J.J. Thomson, led to the discovery of the electron, changing the atomic model from a solid sphere to the "Plum Pudding" model.
What is the Cathode Ray Tube experiment?
An atom is in this state when it has a completely filled outermost energy level, typically with eight electrons.
What is stable (or most stable)?
As wavelength increases, this property of light decreases, representing an inverse relationship.
What is frequency (or energy)?
The total number of electrons in the outermost shell, which determines the group number (for A-groups) and reactivity.
What are valence electrons?
A negative ion, formed when an atom gains electrons.
What is an anion?
Identify the following, label as covalent compounds or ionic compounds use the correct Jeopardy vernacular.
1. LiF
2. KCl
3. Na2S
4. NO2
1. What is ionic.
2. What is ionic.
3. What is ionic.
4. What is covalent.
This is the identity of an element and is determined by the number of protons.
What is the atomic number?
The color of visible light with the shortest wavelength, which also has the highest frequency and energy.
What is violet?
The atomic radius generally decreases as you move from left to right across this horizontal section of the periodic table.
What is a period?
The type of bond formed between a metal and a nonmetal through the transfer of electrons.
What is an ionic bond?
The reason the Oxygen atom in a water molecule has a partial negative charge $(\delta^-)$, which is the result of its strong ability to pull shared electrons toward itself.
What is high electronegativity?
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
What are isotopes?
When an electron falls from the excited state back down, it releases a particle of light energy called this.
What is a photon?
This trend is defined as an atom's ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond.
What is electronegativity?
DAILY DOUBLE!
The weak force of attraction between the partial negative charge on one polar molecule and the partial positive charge on a Hydrogen atom of an adjacent molecule.
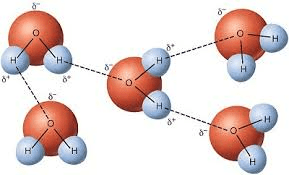 What is a hydrogen bond?
What is a hydrogen bond?
DAILY DOUBLE!!!
Draw the correct Lewis structure for Magnesium Chloride.
![]()
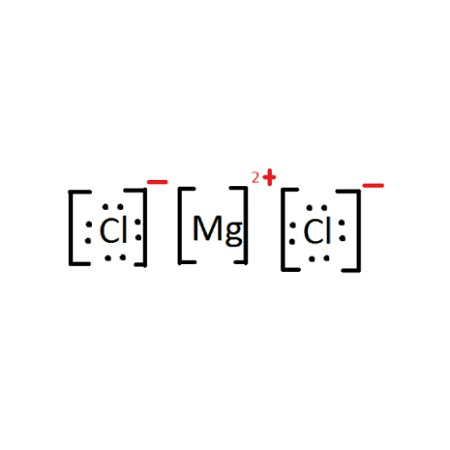
This scientist performed the Gold Foil Experiment, which led to the discovery of the dense, positively charged nucleus.
Who is Rutherford?
DAILY DOUBLE!
You friend has 4 firework, each containing the following elements calcium, barium, lithium and iron. He lights one, it takes off and it explodes emitting a green light. 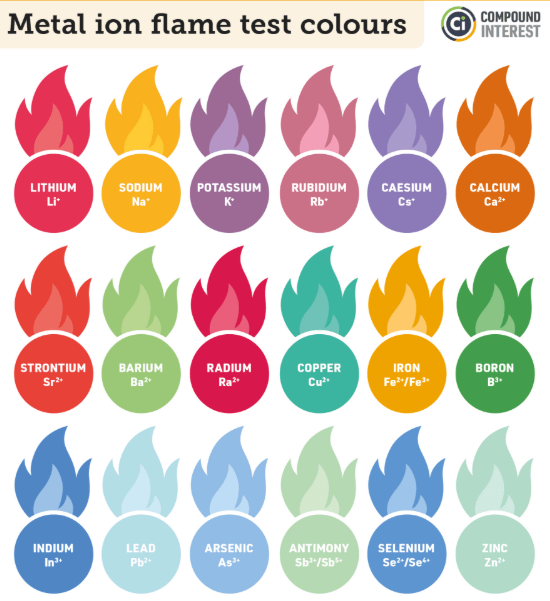
W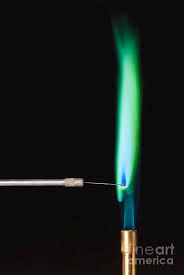 hat is barium?
hat is barium?
The two highly reactive groups of elements, Group 1 and Group 17, are known respectively as these.
What are the Alkali Metals and the Halogens?
The "skin" or force that causes the surface of a liquid, like water, to resist an external force due to cohesive forces between its molecules.
What is surface tension?
The unexpected result of Rutherford's Gold Foil experiment, where a small percentage of alpha particles bounced straight back, showed that the atom had this small, dense, and positively charged center.
What is the nucleus?