How many valence electrons does carbon have AND how many bonds can it form?
What are the trends for atomic radius (size) going top to bottom and left to right on the periodic table?
Increases top to bottom, decreases left to right.
What types of elements form covalent bonds?
Nonmetals
CH4 (in 3D)

Molecular geometry and bond angles in CH4
Tetrahedral, 109.5o
How many valence electrons does hydrogen have and how many bonds can it form?
1 and 1
What are the trends for electronegativity going top to bottom and left to right on the periodic table?
Decreases top to bottom and increases left to right.
Give an example of a nonpolar covalent bond and one of a polar covalent bond.
H-H (nonpolar)
C-O (polar)
C3H4 (in 3D)
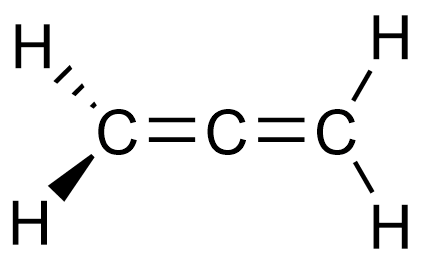 OR
OR 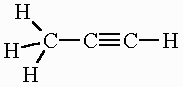
All molecular geometries and bond angles in C3H4
Allene: Trigonal planar (120o) and linear (180o)
Propyne: Tetrahedral (109.5o) and linear (180o)
How many lone pairs of electrons does oxygen have, and how many bonds can it form?
2 and 2
Explain WHY carbon has a larger atomic radius than hydrogen.
Carbon has more energy levels, so it's valence electrons are farther from the nucleus, resulting in a larger atomic radius.
What type of bond is C-H? Why is it classified this way?
Nonpolar. The difference in electronegativity between C and H is small.
Draw the Lewis structure of a 5-membered ring of carbons. Give its chemical formula.
C5H10
Draw an organic molecule that includes a bent shape.
What are the electron configurations of C, N, O, and F?
C: 1s22s22p2
N: 1s22s22p3
O: 1s22s22p4
H: 1s1
Which is more electronegative: oxygen or nitrogen? Explain why.
Oxygen is more electronegative. Oxygen has one more proton than nitrogen, so electrons are drawn more strongly towards its nucleus.
Draw a molecule with a polar covalent bond and draw any dipoles, labeling the partial positive and partial negative charges.
(See drawings)
CH3CONH2 (in 3D, include all lone pairs of electrons)
Draw an organic molecule that contains 3 different geometries. Label each with their bond angles.
(Answers vary)