What is the term for a substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical means?
Atoms
What is the heat of fusion of water?
334 J/g
What are the three subatomic particles of an atom?
protons, neutrons, electrons
What is the ideal gas law?
(P1V1)/(T1) = (P2V2)/(T2)
Which period is Sodium in?
Period 3
These are the two types of pure substances
Elements and Compounds
Which heat equation would you use for a question that involves changing temperature?
q = mcΔT
Define isotope
An isotope of an atom has the SAME number of protons and a different number of neutrons.
Which decay particle has the largest mass?
alpha particles
18
Evaporation is a type of ____________ change
Physical change
Explain what happens to the kinetic energy as a phase change is happening.
Kinetic energy stays the same
What are the Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment's two conclusions.
Discovered that the atom was mostly empty space and had a small, dense, positive center called the nucleus.
If the temperature of a gas increases, what happens to its volume?
It also increases.
Across a period (left to right), what trend is seen in electronegativity
It increases
This is an example of a _______________________.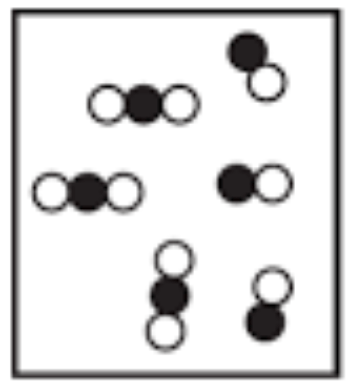
Heterogeneous mixture
Which heat constant would you use when calculating the heat for a condensation of water vapor to liquid water?
Heat of vaporization.
DOUBLE POINTS!
What happens when an atom:
1. gains a neutron
2. gains an electron
3. gains a proton
1. forms an isotope
2. forms an anion
3. forms a new element
1/32
Non-metals prefer to hold on to their valence electrons
Explain the difference between a compound and a mixture.
A compound is a substance that is formed when two elements chemically combine in a fixed ratio.
A mixture is formed when substances are physically combined in variable ratios.
Describe the difference between potential and kinetic energy in a heat curve.
Kinetic energy changes while in one phase of matter, but remains constant during a phase change.
Potential energy remains the same during one phase of matter but changes during a phase change.
What information does the Bohr model of the atom tell us?
The number of protons and neutrons, as well as the number of electrons and how they are distributed
Describe the process of nuclear fusion and where it naturally occurs.
When two smaller nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus and produce a lot of energy. It occurs in the sun
Explain in terms of electron shells why atomic radius increases as you go down a group
Each new shell is further away from the nucleus. This increased distance means that the outermost electrons are located farther from the nucleus.