What does the octet rule state about the number of electrons in an atom's outermost shell?
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer shell of eight electrons (or two in the case of hydrogen and helium).
How are ionic compounds named?
Ionic compounds are named by writing the name of the cation (usually a metal) first and then the name of the anion (usually a non-metal) with "-ide" added to the end.
What is an ionic bond, and how does it form?
An ionic bond is formed when one atom transfers electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. These oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other and form a bond.
What are Lewis Dot Structures used for?
Lewis dot structures are used to represent the arrangement of valence electrons in an atom or molecule.
Define an ionic bond.
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that forms when one atom transfers electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). These oppositely charged ions are held together by electrostatic attraction.
Name an element that is an exception to the octet rule.
Hydrogen is an exception to the octet rule since it can only accommodate two electrons in its outer shell.
Provide the chemical formula for the ionic compound formed by calcium and chlorine.
Calcium chloride has the chemical formula CaCl2.
Give an example of a molecule with a covalent bond.
Water (H2O) has covalent bonds between its hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
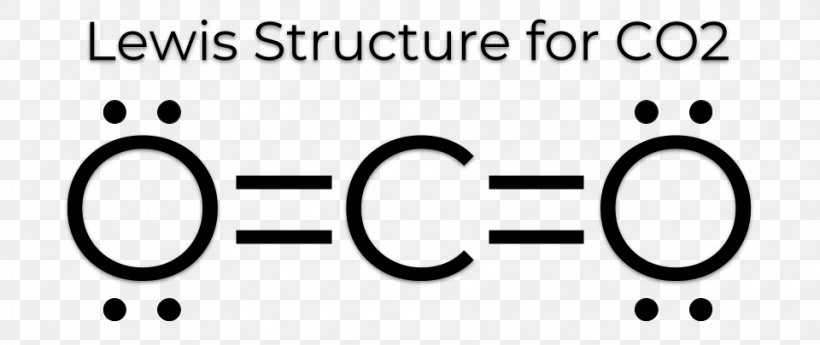
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for carbon dioxide (CO2).
Define a covalent bond.
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that forms when two atoms share electrons in order to achieve a full outer electron shell. Covalent bonds typically occur between non-metal atoms and result in the sharing of one or more pairs of electrons.
Give an example of an element that follows the octet rule when forming compounds.
Oxygen follows the octet rule when forming compounds. For example, in H2O, each oxygen atom has eight electrons in its valence shell.
How are covalent compounds named?
Covalent compounds are named using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms in each element. The second element typically ends in "-ide."
Name the three main types of chemical bonds.
The three main types of chemical bonds are ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds.
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for water.

Explain the concept of electronegativity in relation to chemical bonding.
Electronegativity is a measure of an element's ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. It is used to predict the nature of the bond between two atoms. When the electronegativities of two atoms differ significantly, a polar covalent bond or an ionic bond is more likely to form, as electrons are not shared equally.
Explain why some elements violate the octet rule when forming compounds.
Some elements have fewer or more than eight valence electrons, which makes them unable to achieve an octet. Elements in the third period and beyond can expand their valence shells, while elements in the second period can accommodate fewer electrons.
Provide the chemical formula for the covalent compound formed by carbon and oxygen.
Carbon dioxide has the chemical formula CO2.
What type of bond exists in a network covalent compound like a diamond?
Network covalent compounds, such as diamonds, are made up of a three-dimensional network of covalent bonds. Each carbon atom in a diamond is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms, forming a strong and rigid structure.
Explain how to determine the number of valence electrons in an element.
The number of valence electrons in an element can be determined by looking at its group number on the periodic table. Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. For example, elements in Group 1 have 1 valence electron, and elements in Group 17 have 7 valence electrons.
Define a metallic bond.
A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond that occurs in metals and alloys. It is characterized by the delocalized movement of electrons within a lattice of positively charged metal ions. This electron "sea" holds the metal atoms together and allows for high electrical and thermal conductivity.
How does the octet rule relate to the formation of chemical bonds?
The octet rule explains that atoms tend to form chemical bonds by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons to achieve a stable configuration with a full outer shell. This is the basis for understanding the formation of ionic and covalent bonds.
What is a polyatomic ion, and how does it affect the naming of ionic compounds?
A polyatomic ion is a group of atoms that carries a net charge. It affects the naming of ionic compounds because it is treated as a single unit and retains its name when forming compounds. It may also change the overall charge of the compound.
In metallic bonds, what is it that holds the metal atoms together?
In metallic bonds, a "sea" of delocalized electrons holds the metal atoms together by being shared among them. This electron "glue" allows metals to conduct electricity and have their characteristic properties.
Why do noble gases not readily form chemical bonds, and how does this relate to Lewis Dot Structures?
Noble gases do not readily form chemical bonds because they already have a full complement of valence electrons (an octet), making them very stable and unreactive. This relates to Lewis dot structures because noble gases have a full set of valence electrons, represented as dots around the element symbol, which is characteristic of a stable configuration.
Define the octet rule and its significance in chemical bonding.
The octet rule is a fundamental principle in chemistry that states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration with a full outer shell containing eight electrons (or two electrons in the case of hydrogen and helium). The significance of the octet rule is that it explains the formation of chemical bonds, particularly ionic and covalent bonds, as atoms seek to achieve this stable and low-energy configuration by interacting with other atoms.