A phase change from a solid to a liquid.
What is melting?
The first scientist credited with theorizing the existence of "the smallest possible" part of matter.
Who is Dalton?
Found by rounding the atomic mass from your periodic table to the nearest whole number.
What is the mass number?
Atomic radius increases as you go down a group due to the increasing number of these.
What are electron shells/levels?
The name of the compound with chemical formula Na2CO3.
What is sodium carbonate?
The way that covalent compounds are formed.
What is electron sharing?
A substance that contains more than one element or compound and its parts are clearly visible.
What is a heterogeneous mixture?
The scientist that theorized the existence of energy levels using evidence from passing electric currents through different gases and observing the light created.
Who is Neils Bohr?
What is zinc?
Metals in these groups are more reactive than metals in group 3.
What are groups 1 & 2?
The chemical name of this compound.
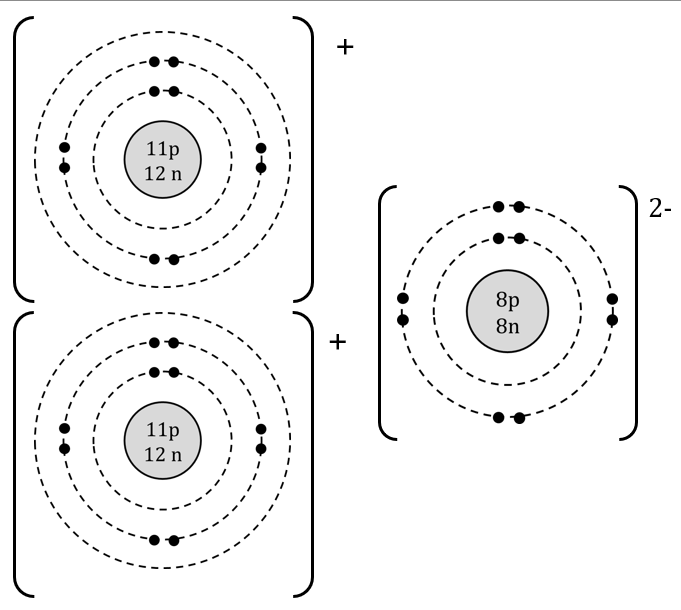
What is sodium oxide?
The formula of the compound dinitrogen monoxide.
A property that can be observed or studied without changing the chemical structure of a compound.
What is a physical property?
The model of the atom created by Thomson.
What is the "raisin bun" model?
An ion with 20 protons and 18 electrons.
What is Ca2+?
What is decreasing?
The chemical formula of cobalt (II) phosphate.
What is Co3(PO4)2
The name of this compound.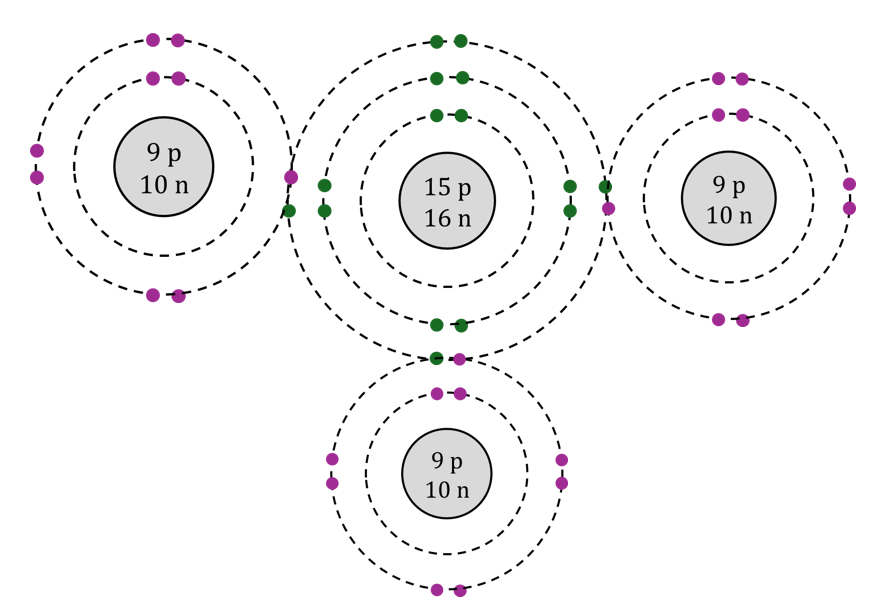
What is phosphorous trifluoride?
The state of matter with no fixed shape and no fixed volume.
What is a gas?
The new addition to the structure of the atom theorized by Ernest Rutherford.
What is the nucleus?
The number of neutrons in an atom of chromium.
You will find metals that are more reactive than than barium in this period.
What is period 6?
The way an ionic compound is created.
What is electron stealing?
The chemical formula for the compound dichlorine heptoxide.
What is Cl2O7?
The three state changes that involve atoms beginning to move faster and further apart - gaining energy.
What are melting, evaporation, and sublimation?
The two types of subatomic particles that are equal in a neutral atom.
What are protons and electrons?
The charge on an atom of mercury with 79 electrons.
What is 1+?
Atomic radius decreases across a period due to this force.
What is attraction between nucleus and electrons?
The name of the compound with formula PtS2
What is platinum (IV) sulphide?
The name for the compound with the formula CH4
What is carbon tetrahydride?
Temperature change, colour change, bubble formation, precipitate formation, or light/sound production.
What is the evidence of a chemical change?
The two subatomic particles that account for almost all of the mass of an atom.
What are protons and neutrons?
How sulphur becomes an ion.
What is losing 2 electrons?
The reason that noble gases are the most stable and non-reactive group of elements on the periodic table.
What are full valence shells?
The name of the compound with formula Nb2Se5
What is niobium (V) selenide?
The name for the compound with formula TeBr2
What is tellurium dibromide?