What supplies do you need for a chest tube dressing change?
DOUBLE:
Explain how you would change the chest tube dressing.
vaseline gauze
4X4
Silk/foam tape
What is a pneumothorax?
air in the pleural space
What is flail chest?
Defined as the fracture of two or more sequential ribs in two or more locations that results in a flail section.
What is a clamshell thoracotomy?
a double thoracotomy
What is a blunt cardiac injury?
Includes myocardial contusion, injury to the ventricular septum, coronary arteries, or cardiac valves.
Occurs from a direct impact or compression of the thoracic cavity.
What things do you assess for?
Fluctuation, Output, Color of drainage, and Air leak present
What is a hemothorax?
caused by blood accumulating in the pleural space
Signs / symptoms of flail chest
Dyspnea
Diminished breath sounds
Chest wall pain
Chest wall contusions
Paradoxical movement of the chest
How many joules are used to internally defibrillate.
30-50 j
Post-resuscitation care
Adequate ventilation and oxygenation
Monitoring vital signs
Chest tube management if indicated
ABG, labs
EKG
Scans - xray
What's a normal amount of output for a chest tube?
1-1.5L initially
150-200 per hour X2-4hrs
Blood loss increases
Pt. arrives to your unit. They are anxious, HR is 130s, went from 2L to NRB, and abdomen is hard and rigid. Xray is at the door. Is this a priority?
Yes
Hemothorax can result from liver or spleen lacerations; rapid accumulation of blood in the pleural space can occur.
This pt could be experiencing hepatic hydrothorax; accumulation of fluid in the pleural space due to a liver laceration.
Interventions for flail chest
Support adequate oxygenation and ventilation
Administer analgesics
Prepare for possible intubation
Possible surgical intervention
What are the indications for a thoracotomy
Relief of cardiac tamponade
support cardiac output (internal massage)
cross-clamp the descending aorta (to preserve blood flow to the brain and thoracic)
Defibrillator the heart internally (more effective than external
Limit hemorrhage from the heart or great vessels
What labs can you expect for a patient with a sternum fx.
elevated trops
How do you troubleshoot a chest tube?
Displaced tube, Obstruction, Pneumo/hemo present, Equipment failure
Will you anticipate a larger bore chest tube for a hemo or pneumothorax? why?
Hemothorax; blood is thick and has the capability to clot in smaller diameter tubes
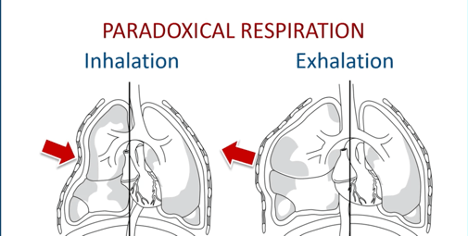
What is paradoxical respiration?
Can nurses cardiac massage?
HELL NO!!
What is tracheobronchial injury
DOUBLE:
S/S
blunt or penetrating trauma to neck or chest, occurs from direct blows to the neck, a branch is used for intubation to visualize the ET tube going past the area of injury
Can indicate emergent cricothyrotomy
Signs and Symptom
- dyspnea or tachypnea
- hoarseness
- subcutaneous emphysema in the neck, face, or upper thorax
- Pneumothorax
- Hemoptysis
- Decreased or absent breath sound
- Airway obstruction
 Is suction on?
Is suction on?
No
What is the assessment findings for a tension pneumothorax and hemothorax?
If left untreated, will the pt most likely code??
Anxiety and restlessness
Chest pain
Respiratory distress
Diminished or absent breath sounds on affected sides
Tachycardia
Distended neck vein
tracheal deviation
Cyanosis
yes, Tension pneumothorax is one of the Hs and Ts
How would you teach a patient to use an incentive spirometer?
Teach us!
Where do you find the internal defibrillator paddles.
ED and OR
Complications of blunt cardiac injury
CHF, hemoperricardium with cardiac tamponade, cardiac rupture, valvular rupture, intraventricular thrombi, coronary artery occlusion, ventricular aneurysms, dysrhythmias, conduction abnormalities
You go into the patients room and notice the patient is sitting up, covered in blood, and chest tube dressing soaked in blood. What do you do?
Make sure pt. is positioned safely
Assess pt. vitals
Take dressing down and assess site
place temporary occlusive dressing
contact physician
What issues can occur with a retained hemothorax?
This occurs when blood remains in the pleural cavity after initial drainage attempts via chest tube.
Complications can include empyema (infection in pleural space) and fibrothorax (scarring of the lung tissue)
Complications of flail chest
Pain that causes patient to have rapid and shallow respirations
Deformity of the chest wall that results in loss of tidal volume, atelectasis, and inability to clear secretions
Underlying injury to thoracic organs, including parenchymal laceration, pulmonary contusion, pneumothorax or hemothorax
A pt was booked over that was a clamshell in R9 and taken to the OR. CRNA is calling report and states the pt. is an open abd and open chest. How should you prep the room prior to the pt. arriving?
SUCTION!!!!!!
S/S of cardiac tamponade and treatment
Becks triad: hypotension, distended neck veins, muffled heart sounds
Chest pain
Tachycardia or pulses electrical activity
Dyspnea
Cyanosis
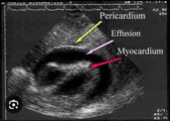
Treatment: Pericardial decompression - surgical pericardectomy or pericardiocentesis
What is the most common size chest tube?
28F
Sternum fractures are often associated with what injuries
Blunt cardiac injury
pneumothorax
Why are they admitting a 87 year old meemaw to the ICU with the only injuries being 4 rib fractures?
Rib fractures could cause pulmonary contusions and the onset of those symptoms might not show for 72 hours
If pain is not adequately managed it could affect the pt's ability to ventilate and cough effectively; therefore leading to decreased respiratory drive, shallow breathing and possibly pneumonia
With Cardiac trauma what can happen electrically?
Dysrhythmias
What happens when diaphragm rupture occurs?
When the diaphragm ruptures, the abdominal contents can herniate into the thoracic cavity, compressing the lungs and obstructing the patient's ability to take a breath
Pt. needs emergent bedside chest tube. Go!
FIND YOUR SUPPLIES!
First and second rib fractures are often associated with what injury
great vessel injuries
brachial plexus injuries
head and spinal cord injuries
What is a pulmonary contusion?
a bruised lung
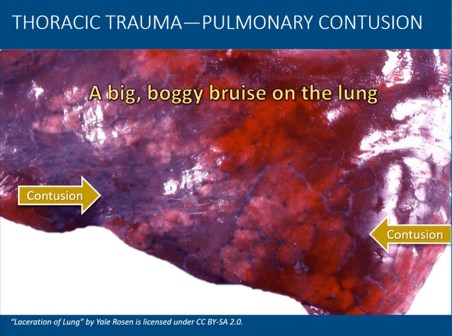
S/S: Dyspnea, ineffective cough, increased work of breathing, hypoxia, chest pain, hemoptysis
Is a clamshell done in the ED sterile?
They "try"
Aortic disruption related to blunt trauma
Most injured site of the aorta occurs to the distal left subclavian artery and adjacent to the ligamentum arteriosum - the injury occurs when this ligament is pulled during the trauma
How often do you change the chest tube dressing?
Initial change should be 48hr unless stated by physician, only reinforce first 24hrs
Daily
After removal change 48hrs
Multiple rib fractures and flail chest are often associated with what injury
pulmonary contusion
pneumothorax
hemothorax
Signs / symptoms of rib and sternum fractures
Dyspnea
Localized pain during movement, palpitation, or inspiration
Splinting chest
Paradoxical chest wall movement
Chest wall contusions
Bony crepitus or deformity
Do you do chest compressions if the patient has a open chest?
Ask your physician
Assessment finding for an aortic disruption
Cardiac murmurs
back or chest pain
Unequal extremity pulse strength or blood pressure
Hypotension
Tachycardia
Diaphoresis
Pallor
Paraplegia - disruption of spinal perfusion
Widening mediastinum
Right-sided tracheal deviation
Left hemothorax
Where do you find pigtail chest tubes?
IR
Lower rib fractures (7-12) are often associated with what injuries
liver
spleen
What other injuries could be associated with sternum fractures?
Pulmonary contusions
Thoracic spinal fractures
What is cardiac tamponade?
A collection of blood in the pericardial sac, that compresses that heart and decreases the ability of the ventricles to fill, causing decreased cardiac output and decreased stroke volume.
Signs and symptoms of a ruptured diaphragm
Bowel sound auscultated in the lung fields
Decreased breath sounds
Dyspnea or orthopnea
Dsphagia
Abdominal pain
Left shoulder pain - splenic injury, stems from diaphragmatic irritation