What are the four classes of primary pharmacologic therapy for patients with HFrEF?
ACEi/ARB/ARNI
Beta Blockers
MRAs
SGLT2i
These are the 3 classifications of Oncological emergencies.
(must have all 3)
1. pressure or obstruction caused by a space occupying lesion,
2. metabolic or hormonal problems (ie. paraneoplastic syndromes
3. treatment related complications
Name this arrhythmia
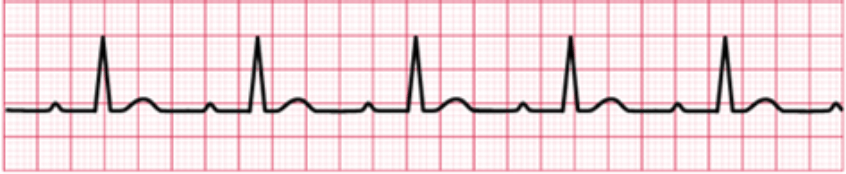
First degree AV block
Antibiotic regimen for febrile patients with prolonged neutropenia
What is:
(1) Cefepime (or Ceftazidime)
(2) piperacillin/tazobactam
OR
(3) imipenem/cilastatin or meropenem
These are the two distinct forms of esophageal cancer and their locations
(all parts needed to get the points)
1) squamous cell; upper 2/3
2) adenocarcinoma; lower 1/3
A friendly, giant green guy lives in a swamp and has some serious anger management issues."
What is Shrek?
Protocol used for treadmill stress test
What is the Bruce Protocol
After reduction of comorbidities, what are the TWO therapies for treatment of HFpEF?
+500 Bonus points if someone knows the third class of agents that have shown promise and the TRIAL that shows this
- SGLT2i - (EMPEROR and DELIVER Trials)
- Spirinolactone (TOPCAT)
- TIRZEPATIDE (SUMMIT trial) - B
This treatment related complication is commonly seen as result of treating rapidly proliferating lymphomas and some chronic leukemias; characterized by hyperuricemia, hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, and hypocalcemia
What is Tumor Lysis Syndrome?
What is the technical term for the failure of heart rate to increase with exercise
Chronotropic Incompetence
This drug is implicated in the most common cause of chemotherapy induced lung disease.
What is Bleomycin?
This GI Neoplasia Syndrome is characterized by Hamartomatous polyps, mucocutaneous pigmentation; and tumors of the ovary, breast, pancreas, endometrium
What is Peutz-Jeghers syndrome?
A teenage boy gets really excited about a car that doesn't belong to him.
What is Back to the Future?
Which (3) beta blockers have been shown to decrease mortality, HF sx, and increase LVEF in HFrEF patients?
Metoprolol succinate, carvedilol, bisoprolol
What are the four classifications of Heart Failure by LVEF per the 2022 ACC Guidelines? (Must have name and EF correct)
HFrEF - LVEF ≤40%
HFimpEF - Previous LVEF ≤40% and a follow-up measurement of LVEF >40%
HFmrEF - LVEF 41%–49%
HFpEF - LVEF ≥50%
Name the diagnosis: this complication usually results from Malignant tumors
Pt with neck and facial swelling (especially around the eyes), dyspnea, and cough.
PE: dilated neck veins; an increased number of collateral veins covering the anterior chest wall; cyanosis; and edema of the face, arms, and chest.
What is Superior Vena Cava Syndrome?
This rhythm is a variant of polymorphic VT that is typically preceded by a prolonged QT interval in sinus rhythm
What is Torsades
Hodgkin’s disease are prone to persistent infections by this organisms, often affecting a vascular site.
(Hint: it's not related to chickens)
Salmonella
The stomach is the most frequent primary site of this lymphatic cancer generally associated with H.pylori infections.
What is MALT lymphoma?
A guy spends hours trying to fix his life while riding a motorcycle and wearing a very tight leather suit.
What is the Matrix?
This condition is characterized by acute LV dysfunction in the setting of physiologic stress, mimics acute MI with ST elevation and elevated biomarkers. Dilation and akinesis of LV/apex. Resolves within weeks of supportive care
What is takotsubo cardiomyopathy
Name one of the three indications for PRIMARY prevention with implantation of an ICD in patients with HF (per the 2022 ACC Guidelines)
- Ischemic heart disease at least 40 days post-myocardial infarction (MI) with a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 35% or less and New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class II or III symptoms on guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT)
- Nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) with an LVEF of 35% or less and NYHA Class II or III symptoms on GDMT.[1-2]
- Ischemic heart disease at least 40 days post-MI with an LVEF of 30% or less and NYHA Class I symptoms on GDMT
Hemorrhagic cystitis is characterized by diffuse bladder mucosal bleeding that develops secondary to chemotherapy.
Name the most common culprit and its antidote
(both answers to get credit)
What is:
Drug: Cyclophosphamide
Antidote: Mesna
Name the underlying rhythm

AV DISASSOCIATION IN V1 --> VT
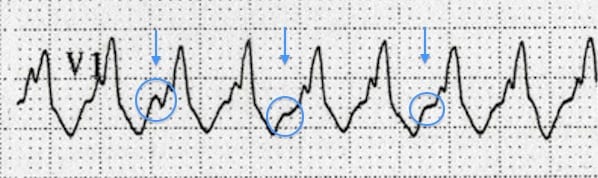
This virus has been documented in the urine of bone marrow transplant recipients and may be associated with hemorrhagic cystitis
BK virus
DNA analysis for “microsatellite instability” or immunohistochemical staining for deficiency in mismatch repair proteins in patients with colorectal cancer can help identify this cancer related syndrome
What is Lynch Syndrome?
A man fights his own father while trying to find his place in the galaxy
What is Star Wars: Episode V – The Empire Strikes Back?
Name the drug: used for refractory angina, MOA selective inhibitor of late Na sodium channel in myocardium
What is Ranolazine
Name Three out of Four Secondary Therapies for Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction
- Isosorbide dinitrate plus hydralazine
- Ivabradine (HR > 70 BPM on MAX BB Therapy; SHIFT trial)
- Vericiguat
- Digoxin
This anti-neoplastic drug is most commonly associated with hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS).
(will accept 1 of 2 answers)
What is Gemcitabine or Mitomycin?
- most often in patients with gastric, lung, colorectal, pancreatic, and breast carcinoma.
- usual onset 4-8 weeks after the last dose of chemotherapy
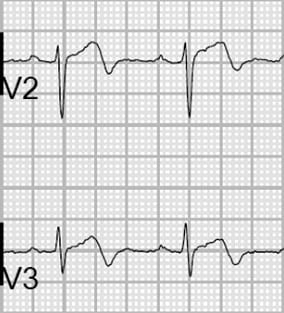
Read the following EKG and answer these three questions (ALL must be right)
- Activate lab or wait
- Name the pattern (be specific)
- What artery would there stenosis in, if any?
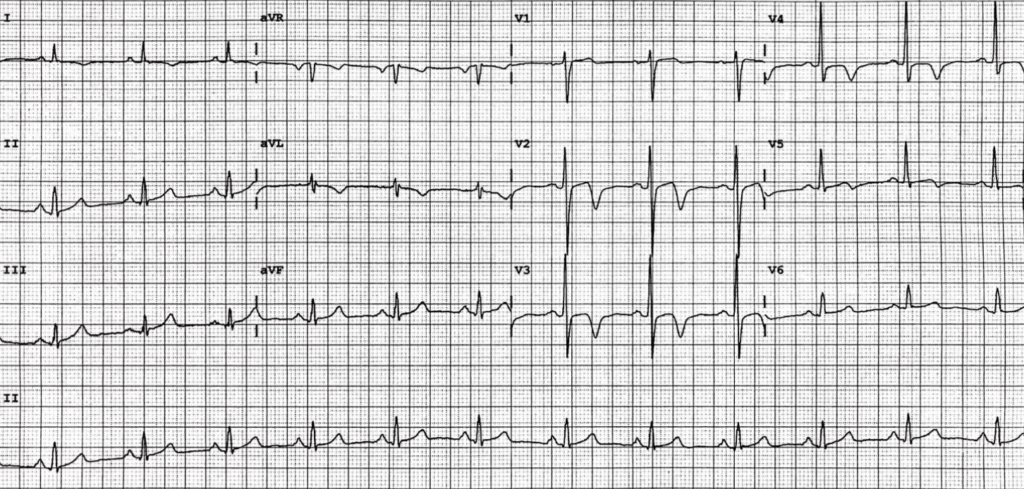
Wellens Syndrome is a clinical syndrome characterised by biphasic or deeply inverted T waves in V2-3, plus a history of recent chest pain now resolved -highly specific for critical stenosis of the left anterior descending artery (LAD)

Disease characterized by red or bluish-red solid lesions or nodules, accompanied by high fevers and an elevated ESR

What is Sweet syndrome, or febrile neutrophilic dermatosis?
Patients with this gene mutation are considered for prophylactic gastrectomy because it increases the risk for the diffuse cell (signet cell) gastric cancer
(Hint: well-known Team Health patient)
What is CDH1 mutation?
A bunch of people in a snow-covered landscape get trapped by a big, angry bear.
(HINT- this actor won a long coveted award for his performance)
What is The Revenant?
Who should receive infective endocarditis prophylaxis? (4 conditions)
-Prosthetic valve
-Previous infective endocarditis
-Congenital heart disease - unrepaired cyanotic, repaired with prosthetic material or device during the first 6 months after the procedure, repaired with residual defects
-Valvulopathy following cardiac transplantation.