In this kind of reaction, the forward process absorbs heat; raising the temperature pushes equilibrium toward products.
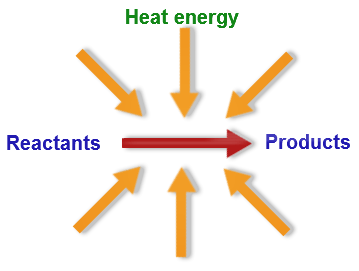
Response: What is an endothermic reaction?
State the structural feature shared by aldehydes and ketones.
Answer: A carbonyl (C=O) group.
Sucrose, Lactose and Maltose
What are Disaccharides
When you add a reactant to a system at equilibrium, it shifts this way to consume it.

Response: What is to the right/forward direction?
Which compound is more soluble in water:
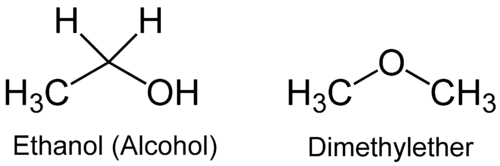
Answer: Ethanol.
The enzyme mechanism where the active site adjusts shape to fit the substrate
What is Induced Fit Theory?
For A + B ⇌ C + D + heat, decreasing [A] drives the equilibrium this way.
Response: What is to the left/toward reactants?
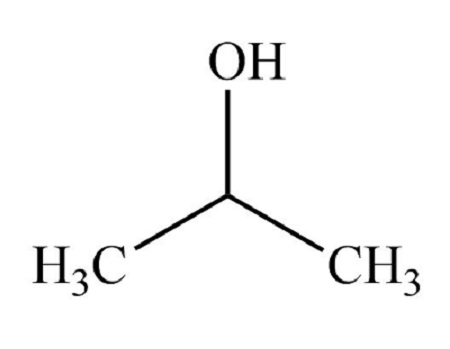
classification of alcohol
Secondary alcohol
Double Bond Location:
CH3–CH2–CH=CH–CH3
C 2
For A + B ⇌ C + D + heat, increasing temperature shifts equilibrium this way.
Response: What is to the left/toward reactants?
Hydrogen bonds between amide hydrogens and carbonyl oxygens hold this protein level together
Secondary
Which of the following has the highest normal boiling point: methane, octane, nonane, or decane?
decane
Identify the class of organic compounds represented by CH₃CH₂OH
Answer: Alcohols.
A molecule that blocks an enzyme's active site and reduces activity.
(What is an inhibitor?)
Identify the saturated compound among: heptane, cyclopropene, 2-hexene, and 3-heptyne.
Answer: heptane.