The bushy, branching fibers of a neuron that receive information and conduct it toward the cell body
What is dendrite?
Physicians who specialize in the treatment of psychological disorders
What is psychiatrist?
A type of conditioning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events
What is classical conditioning?
A generalized (sometimes accurate but often overgeneralized) belief about a group of people
What is stereotype?
The tendency for people to perceive past events as more predictable than they actually were; also known as the I-knew-it-all-along phenomenon
What is hindsight bias?
The neurotransmitter that affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal; sunlight triggers its production in the brain; undersupply linked to depression
What is serotonin?
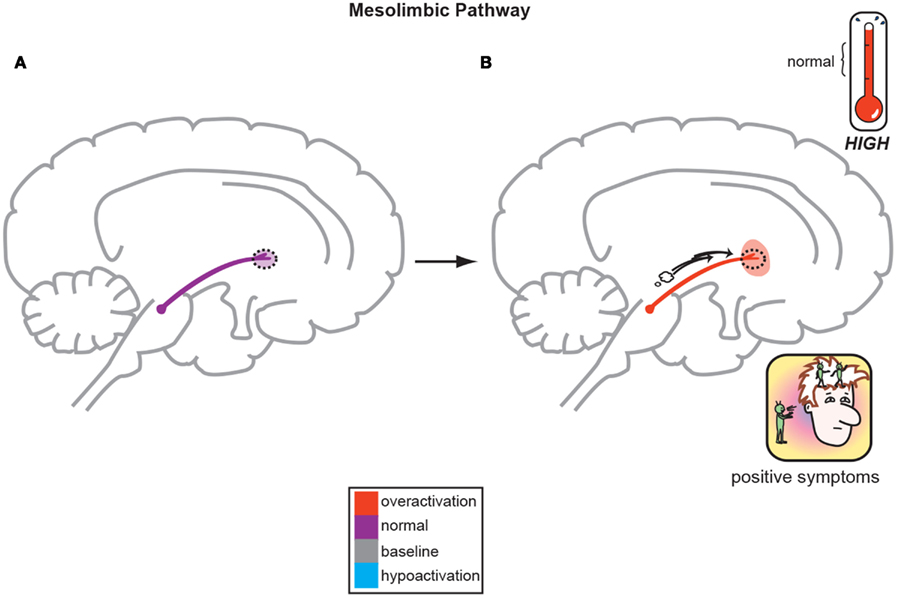 Psychological disorder characterized by dopamine overactivity; symptoms include delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, etc
Psychological disorder characterized by dopamine overactivity; symptoms include delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, etc
What is schizophrenia?
The eerie sense that “I’ve experienced this before;” cues from the current situation may unconsciously trigger retrieval of an earlier experience
What is déjà vu?
 The tendency for any given bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present
The tendency for any given bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present
What is bystander effect?
The tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share our beliefs and our behaviors
What is false consensus effect?
The part of the limbic system that lies below the thalamus and controls heart rate, body temperature, hunger, etc
What is hypothalamus?
A mood disorder in which a person experiences, in the absence of drugs or another medical condition, two or more weeks with five or more symptoms, at least one of which must be either depressed mood/pleasure or loss of interest or pleasure
What is major depressive disorder? (accept MDD, depression, or clinical depression)
A clear memory of an emotionally significant moment or event
The planned two-week experiment led by Zimbardo that only lasted for 6 days in 1971; participants acted to be either a prisoner or prison guard; this very controversial experiment had to be finished earlier than planned due because it became very dangerous
What is Stanford prison experiment?
The general term for an organism’s decreasing response to a stimulus with repeated exposure to it
What is habituation?
Axon fibers that connect the two cerebral hemispheres
What is corpus callosum?
Formerly called manic-depressive disorder, a mood disorder in which a person alternates between the hopelessness and the overexcited state of mania
What is bipolar disorder?
According to Freud, this is the underlying meaning of a dream
What is latent content?
The tendency for people to believe the world is just and that people therefore get what they deserve and deserve what they get
What is just-world phenomenon?
A concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
What is schema?
The gland(s) on top of the kidneys that release epinephrine, norepinephrine, and cortisol; increases heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar, causing the fight-or-flight response
What is adrenal gland?
Carl Rogers developed this widely used humanistic therapy that focuses on the person's conscious self-perceptions
What is client-centered therapy? (also known as person-centered therapy or Rogerian therapy)
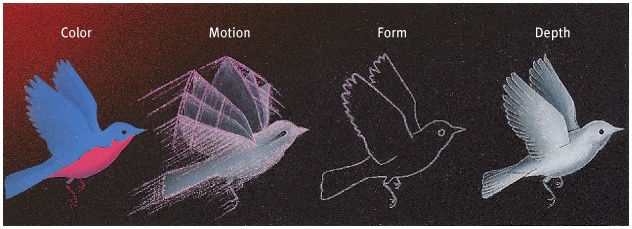 The processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously; the brain’s natural mode of information processing for many functions; contrasts with the step-by-step (serial) processing of most computers and of conscious problem solving
The processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously; the brain’s natural mode of information processing for many functions; contrasts with the step-by-step (serial) processing of most computers and of conscious problem solving
What is parallel processing?
Developed by Fritz Heider, the tendency to give causal explanations for someone’s behavior, often by crediting either the situation or the person’s disposition
What is attribution theory?
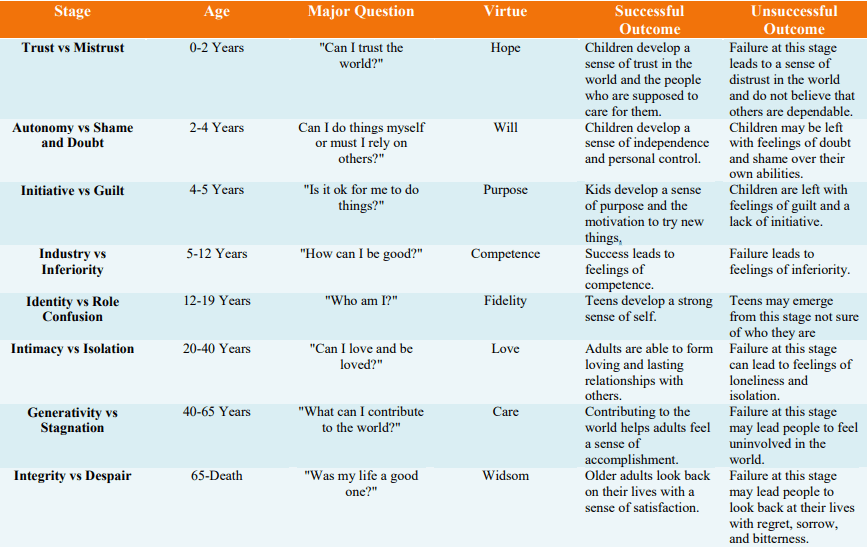 Psychologist that developed the stages of psychosocial development
Psychologist that developed the stages of psychosocial development
Who is Erik Erikson?