To formally approve
Ratify
This article establishes the legislative branch of govenrment
Article I (1)
What was the first constitution in the United States?
Articles of Confederation
Someone who supported the Constitution
Federalists.
The amount of amendments added to the U.S. Constitution
27
Define Constitution.
A written plan for government.
The three parts of the Constitution (in order!)
Preamble, Articles, Amendments
The New Jersey plan favored ___ and representation was ___ for states.
Small states; equal (1 vote per state)
Someone who opposed the Constitution
This plan created a bicameral legislature and included aspects of both the NJ and VA plans
Great Compromise
Another word for representative.
Delegate
This article establishes the judicial branch of government
Article III (3)
What did the Virginia Plan state? What type of states did it favor?
-Favored larger states, number of votes for each state depends on the state’s population, smaller states opposed this plan
The __ branch of government interprets the Constitution.
Judicial
The idea that the power of government lies with the people
popular sovereignty
What is rule of law?
The principle that the law applies to everyone, even those who govern
This article sets up the executive branch of government
Article II (2)
Who proposed the Great Compromise?
Roger Sherman
One expressed power of Congress stated in the Constitution is the power to
a. coin money.
b. create treaties.
c. create schools.
d. establish prisons.
Define amendment.
A change to the Constitution
What is limited government?
The principle that a ruler or a government is not all-powerful; a government that can do only what the people allow it to do
What was the original purpose of the Constitutional Convention?
To fix the Articles of Confederation
Identify one "pro" and one "con" of the Articles of Confederation.

Define:
Enumerated powers
Reserved powers
Concurrent powers
Enumerated powers: powers outlined in the Constitution for federal government
Reserved powers: powers reserved to state governments
Concurrent powers: powers that both the federal and state governments have
What was the Three-Fifths Compromise?
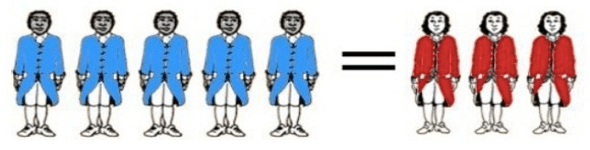 •North? Disagreed with counting enslaved
•North? Disagreed with counting enslaved
•Argue enslaved were legal property as they could not vote or share in gov’t
•Delegates of state agree that every five enslaved persons would equal three free persons