What was the name of the myriad of territories that formed the Ancient Greek homeland, including high mountains and narrow valleys?
Hellas
What do we call the form of government in which power is controlled by citizens who have the power to elect leaders and vote on laws? Give an example from Ancient Greece and another from the world today.

Democracy
Athens
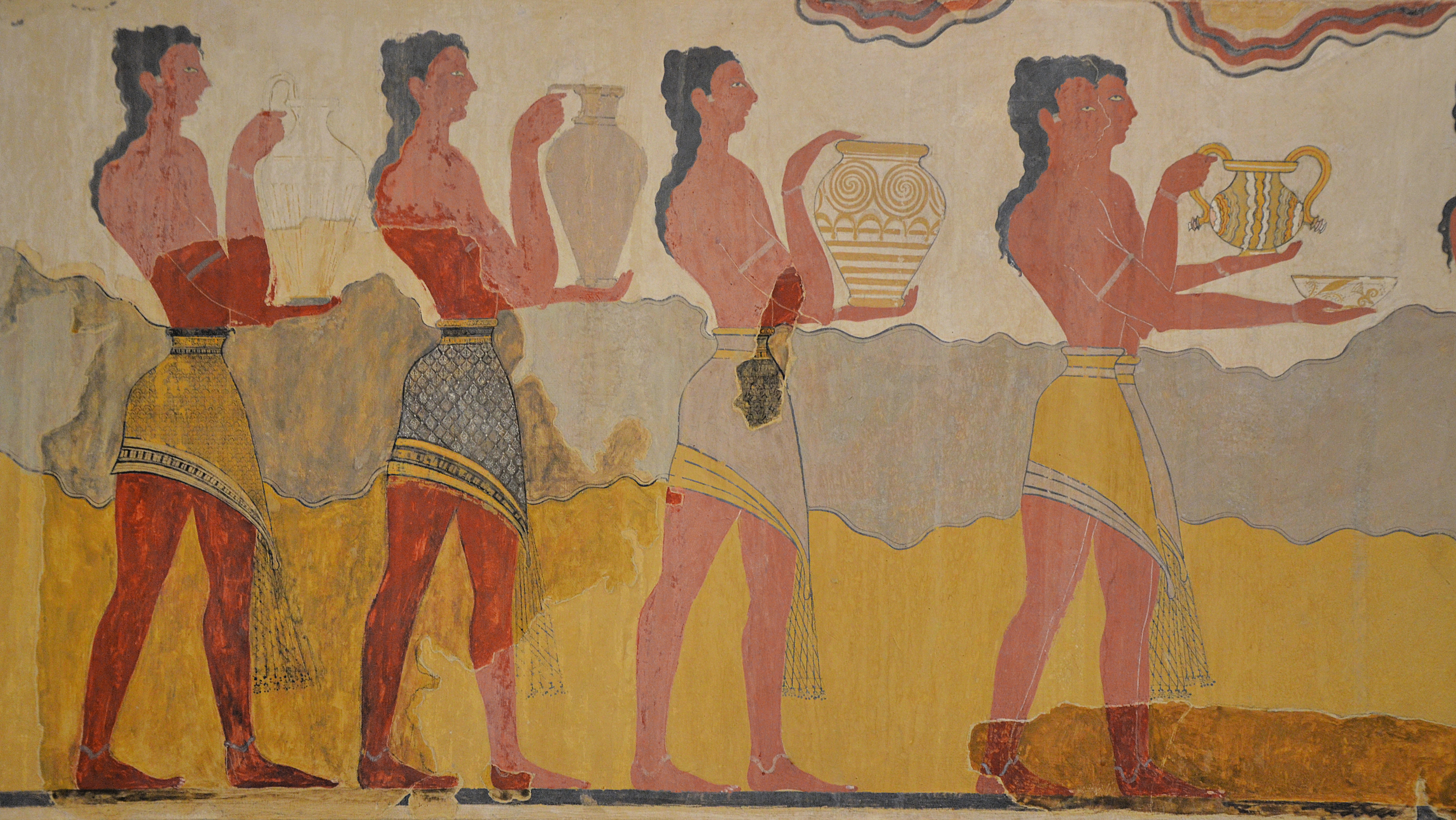
Describe the typical lifestyle of an Ancient Greek. What were their jobs like?


Many were farmers. They worked in livestock farming and agriculture--growing wheat, barley, grapes, and olives. The rest were artisans, merchants, or domestic workers.
Athenian citizens were required to uphold what duty and were provided with what right?

Duty: serve in the army
Right: participate in politics
To flee (v)

To escape, to run away
Ancient Greece was not unified into one single state but consisted of separate city-states which shared a common culture and language. What is the name we give for these separate city-states?

Poleis (singular: polis)
What do we call the form of government in which power is held by a single leader and inherited from the pervious generation? Give an example from Ancient Greece. Try to give an example from a modern nation for an extra point.

Monarchy
Macedonia
What were some of the places where the Greeks established colonies? Name at least two places

Southern Italy
Sicily (Magna Graecia)
The Iberian Peninsula (e.g. Emporion, Hemeroskopeion)
The Black Sea
North Africa (e.g. Cyrene, Naucratis)
What is an “ostracon”?

A piece of broken pottery where citizens wrote the name(s) of other citizens who were to be ostracized (banished from the city for 10 years).
What is a “sail”(n)?

A piece of fabric on a boat that catches the wind
What is the name of the great Bronze Age city found on the island of Crete from whose culture the Greeks felt they descended?
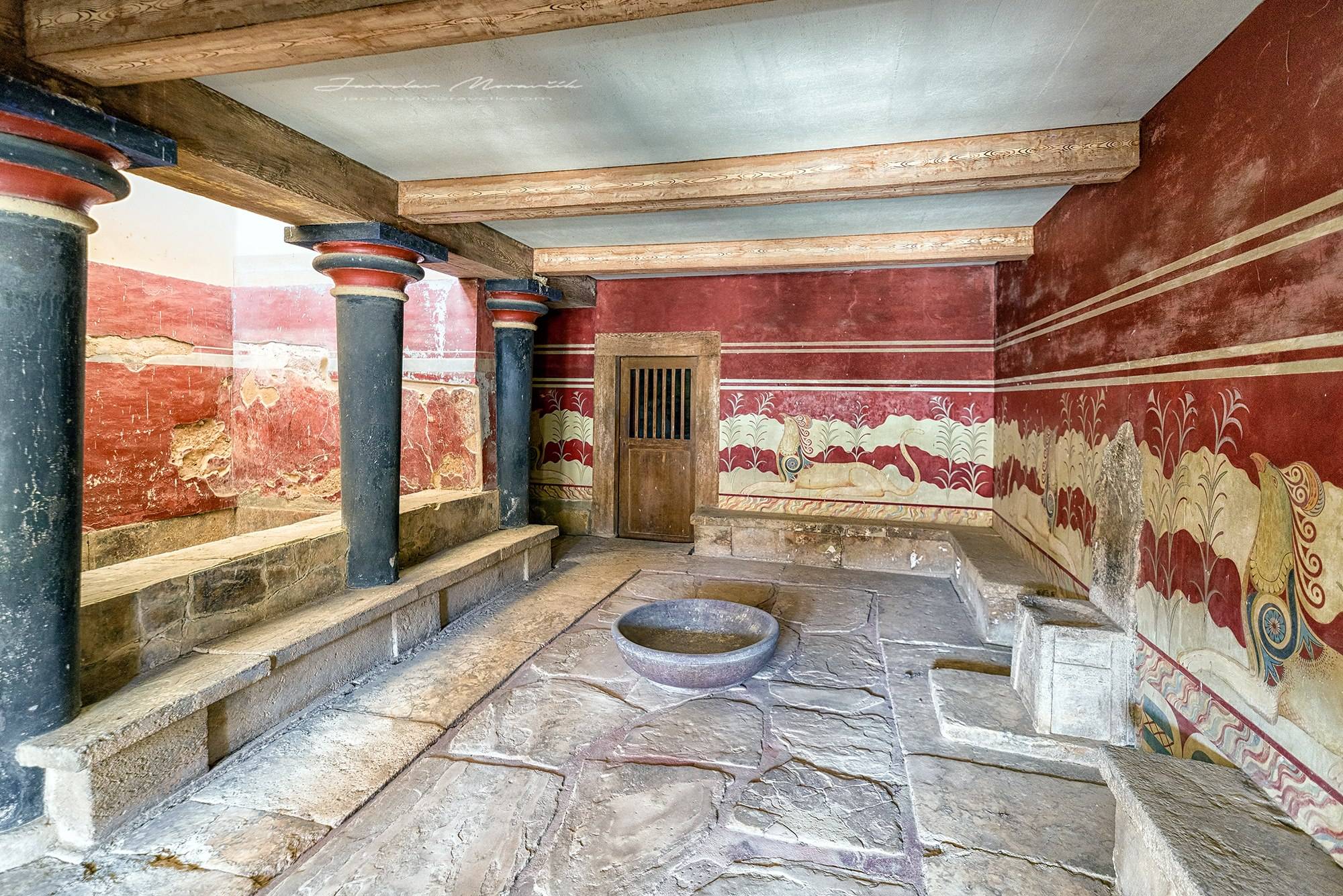

Knossos
What do we call the form of government in which power is held by a small group of elites (in the case of Ancient Greece, the aristoi--the best) who decide the laws? Give an example from Ancient Greece.

Oligarchy
Sparta
The Greeks modelled their colonial cities on "metropolises." What does the word "metropolis" mean in this context?

Metropolises were the cities in Hellas, the Greek homeland, which set the standard for Greek architecture and culture.
What was the minimum number of citizens required to vote in the ecclesia (assembly) for the decision of an election be considered valid?

6,000 citizens
What is “currency” (n)?

Money used in a particular place (eg Euro in Europe or USD in the US)
What are the names of the two epic poems by the Greek poet Homer which helped to unify the Hellenic culture and are still read today?


The Iliad and the Odyssey
What do we call the form of government in which power is taken by force by a single person who has the support of the military, a foreign power or the people? What is an example from Ancient Greece?

Tyranny
Corinth, 7th Century BCE
Why were Greek colonies located near the coast?

The Greeks were expert sailors who had always used the sea as a means of transport, communication, and trade.
What is the “Pnyx”?

The place where the ecclesia (assembly) was held four times a month—a hill in Athens.
What does “scarcity” (n) mean?
Not enough, insufficient
What were the four regions of Hellas and what do we call the people from each region?
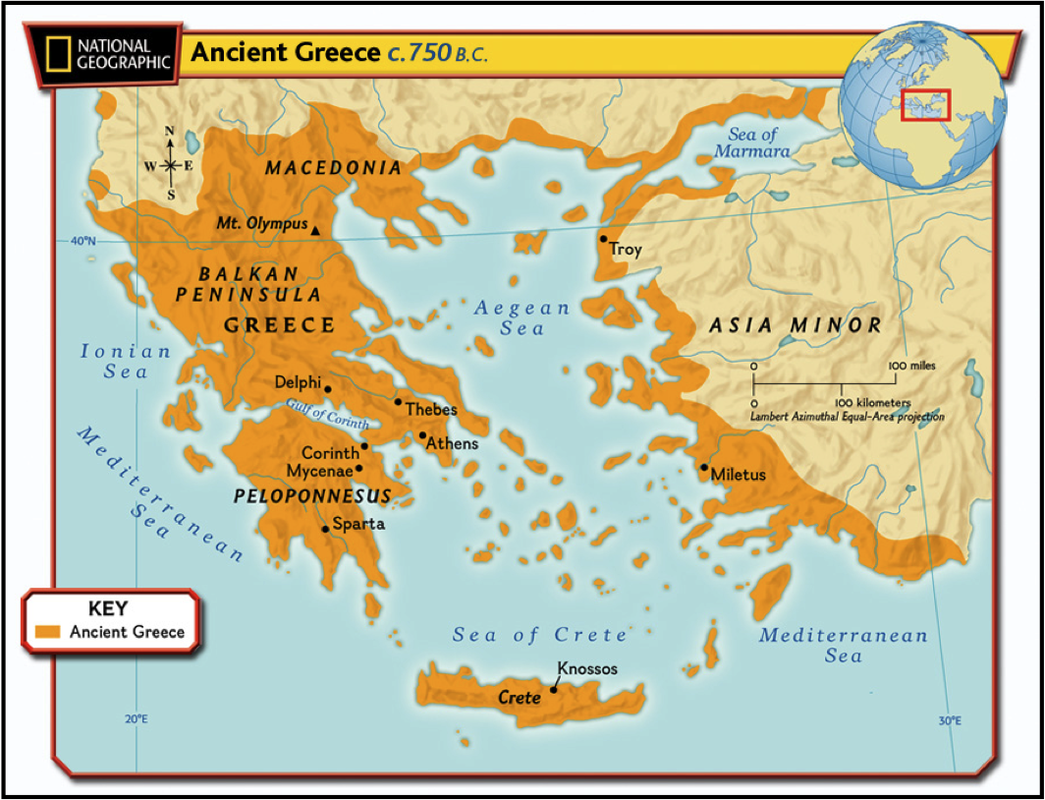
Asia Minor- Ionians
Crete- Minoans
Peloponnese- Mycenaeans
Northern/Continental Greece- Dorians
Describe the similarities in the structure of Greek poleis. Describe the two main parts of the polis.

The polis consists of the city and the surrounding farmland and villages. The two parts of the polis are as follows:
The upper part (the acropolis)- where main religious buildings are found and contains a citadel where the citizens go if the polis is attacked
The lower part- where houses and the agora (marketplace) are located. This is where public life takes place. It would contain the stadium and the theatre.
Describe at least three reasons a Greek may want to migrate from their homeland to a colony.

-a peasant looking for land
-citizen who could not pay his debt
-a person fleeing a tyrant
-a merchant who wants to expand his market
-a sailor with a desire for adventure
Who was allowed to vote in Athenian society and considered a citizen? Around what percentage of the people in the population were considered citizens?

Athenian men (born of two Athenian parents) who completed his military service could vote. They comprised around 15% of the society. Slaves were 36%, relatives of citizens were 35%, while metics and their families were 14%.
To flatter (v)
.jpg)
To compliment, to admire, often with insincere intentions to further one’s own interests

