Academic Year
The period of formal instruction usually late August/early September through late May/early June: may be divided into terms of varying lengths - semesters, trimesters or quarters.
Courses that students may choose to take for credit toward their intended degree, as distinguished from courses that they are required to take.
Core Requirements
The essential parts of a university program that are studied by all students in that program. Also called compulsory, mandatory or required courses.
Course
Regularly scheduled class sessions of one to five hours (or more) per week during the term. A degree program is made up of a specified number of required and elective courses which vary from institution to institution.
Lecture
Teaching method in which the teacher or professor presents information orally to the students who take notes or ask questions.
Degree
A qualification awarded on the basis of one or two years' successful study. It signifies the successful completion of three to four years of studies. Graduate/Masters and Doctorate degrees are awarded after further years of study.
Faculty
This word is used to indicate the teaching staff of a university. It is also an academic subdivision of a university that is a larger unit than a department.
Full-Time Student
Refers to the number of credit hours a student is taking in a year.
18 Or More Credits (3 Classes Per Semester) = Full Time
Less Than 18 Credits = Part Time
Semester
Half the academic year usually lasting between 15 and 18 weeks.
Syllabus
An out of topics covered, and the grading structure for academic courses.
Certificate
A qualification awarded upon successful completion of a university program which is usually one year in length.
Major
The subject in which a student wishes to concentrate for an undergraduate degree.
Program or course that a student is required to complete before being permitted to enrol in a more advanced programs or courses.
Undergraduate
A student enrolled in a bachelor or associate's degree program. An undergraduate program is a study program leading to the awarding of a bachelor or associate's degree.
Tuition
The money the institution charges for instruction and training (does not include the cost of books).
Bursary
A cash award to help students pay for their university education. Awarded on the basis of financial need and academic achievement.
Mature Student
A student who, because he or she has been out of school for a time, does not have to fulfill the usual admission requirements. Admission is generally decided on an individual basis and interested students should contact the university for more information.
Community College
A non-degree granting institution that offers technical or vocational post-secondary courses leading to a diploma or certificate. These courses can often be transferred to a university.
Honours Degree
This is in reference to the first (bachelor's) degree a student receives. The honour program is usually a year longer, requires a higher standing for admission and for the maintenance of honours status and the student specializes in a particular field.
Master's Degree
Postgradudate degree following the Bachelor's degree. This may be only 2 years, where the master's stands alone or it may be a degree attained whilst working towards a PhD. Academic master's degrees usually involve preparing a thesis as well as completing taught courses, whilst a processional master's degree (e.g. education, management, communications, etc.) may require directed practical training.
Co-requisite
Where a course is specified as a co-requisite course, it must be taken at the same time as (or prior) to the course requiring it as a co-requisite
Credits
Used to record the completion of courses (with passing grades) that are required to complete the degree. The catalogue will define the amounts and kinds of credits that are required for the university's degrees and will state the value of each course offered in terms of "credit hours"
Grade Point (GP) / Grade Point Average (GPA)
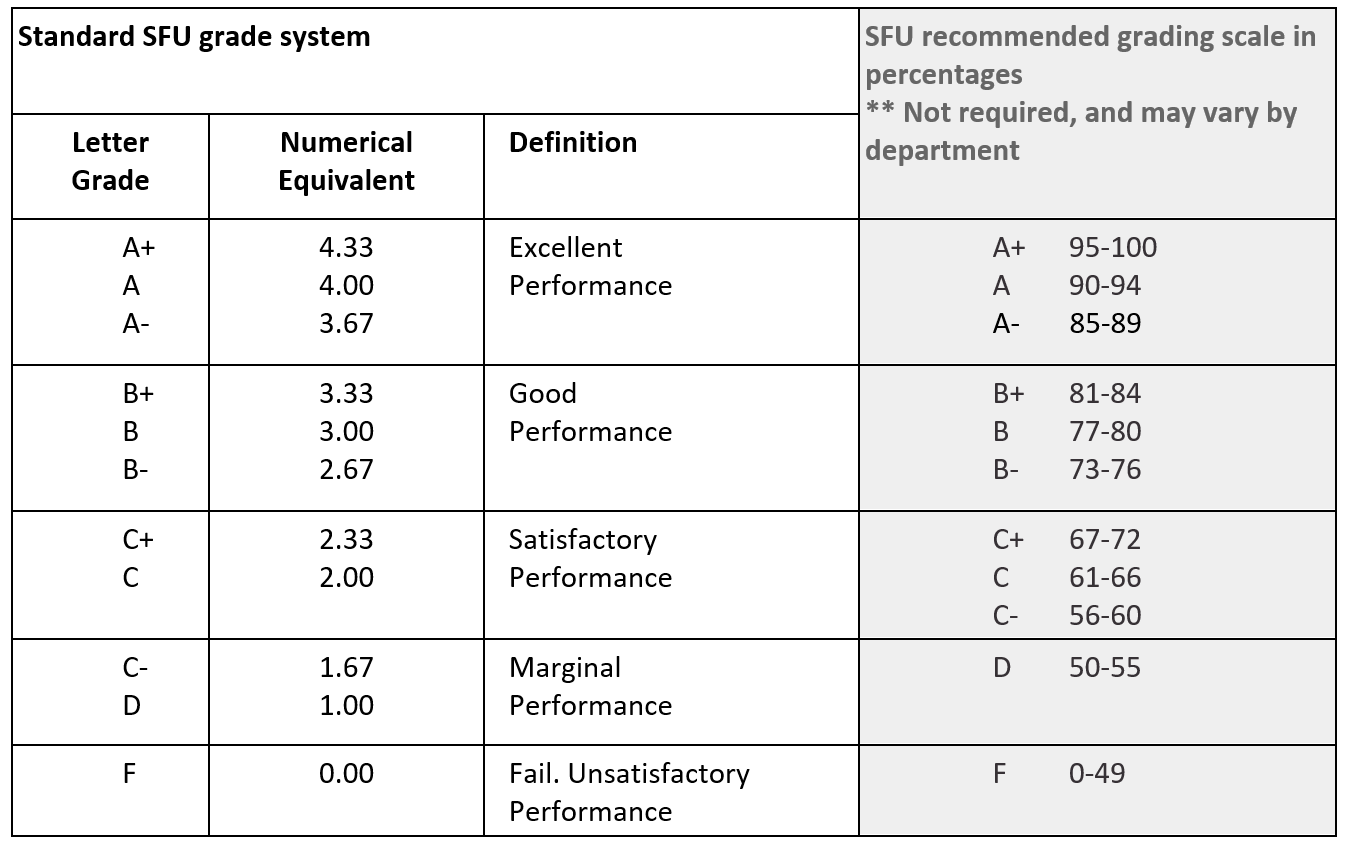
This refers to the system used for grading which most post-secondary institutions recognize. Usually based on a system with a max of 4.33 (but sometimes with a max of 4.0) where each letter grade is associated with a GP. GP is used for the final mark in a course. The average for a set of courses is used to calculate the GP received for each class and weighted according to the number of credit hours.
Intersession
A break between terms that generally serves as a vacation but in which courses may also be offered.
Registrar
A university official concerned with