The landmarks for a Ventrogluteal IM injection
-Greater Trocanter
-Iliac crest
-Anterior superior iliac spine
SOB, fatigue with exertion, white or pink tinged sputum, crackles on lung auscultation
What is Heart Failure
The process of extracting blood from a vessel
What is Phlebotomy
Longer, longer, longer, lack
What is Wenckebach or 2nd degree type 1 AV block
Pt presents to ER 1 day after greenstick arm fracture and casting. Pt now complains of tingling to thumb and index finger. Describe your priority assessment and diagnosis.
CSMT of limb due to compression of the radial artery
I both react to and regulate light
What is the Pupil
Valsava maneuver is best indicated for
What is SVT
-Blow into a syringe for 10-15sec (long as you can) in a sitting position with legs stretched out in front of you
-Instantly lay the patient down after blowing into the syringe and raise the feet to 45 degrees
Patient presents to ER immediately after GLF. Assessment details include: Hypertension, AFIB, SOB, Osteoarthritis. What would be my priority Lab?
What is INR
-Target range 2-3
Inpatient x5 days post PCI for NSTEMI is now complaining of chest pain 4/10 when walking to the bathroom. What is my primary nursing assessments?
-Vitals
-ECG
-PRN medication
Which of the following statements about shivering is correct?
- A. Shivering is a response controlled by the brainstem.
- B. Shivering can occur in the absence of hypothermia.
- C. Shivering is effectively treated with small doses of naloxone.
- D. Shivering is an uncomfortable, though harmless, effect of anesthesia.
What is B - can occur in the absence of hypothermia
Shivering can also appear after surgery. This is known as postanesthetic shivering. Postoperative shivering is a common complication of anesthesia. Shivering is believed to increase oxygen consumption, increase the risk of hypoxemia, induce lactic acidosis, and catecholamine release. Therefore, it might increase postoperative complications, especially in high-risk patients. Moreover, shivering is one of the leading causes of discomfort for postsurgical patients.
The dermatomes of male genitalia rash
What is S2, S3
Name the Tri-leaflet valves
What is Tricuspid, pulmonic, and aortic
*DAILY DOUBLE*
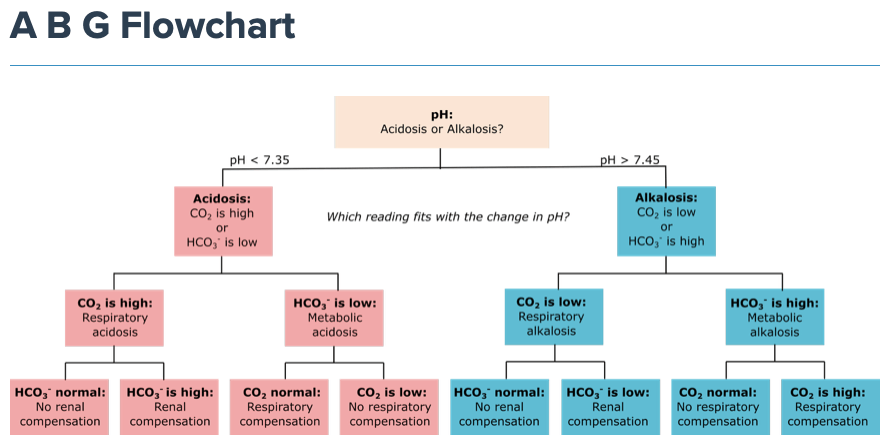
pH - 7.29
PaO2 - 65
PCO2 - 31
HCO3 - 21
What is Metabolic Acidosis, uncompensated
In an cardiac cycle the ST segment and the T-wave represents what
What is Ventricular Repolarization
The nursery nurse is putting erythromycin ointment in the newborn’s eyes to prevent infection. She places it in which of the following area of the eye:
- A. Under the eyelid.
- B. On the cornea.
- C. In the lower conjunctival sac.
- D. By the optic disc.
What is C - Lower conjunctival sac
Nasogastric tube location when feeding a patient with gastric enteral nutrition intolerance
What is post pyloric or duodenum
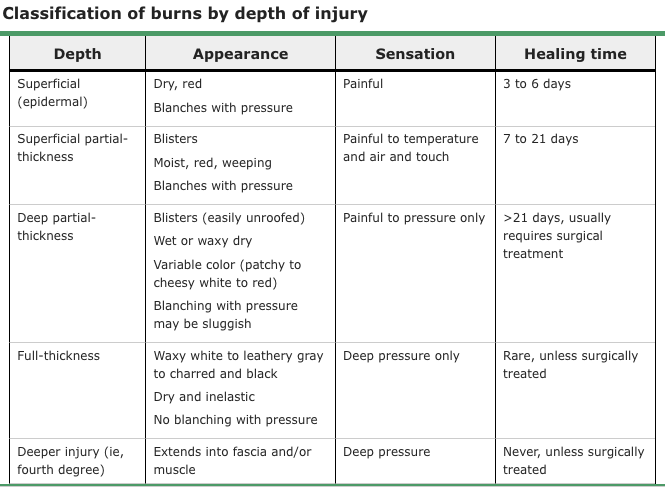
Burn classification with noted Blisters, Pain to pressure only, and a healing time of >3 weeks
What is Deep Partial Thickness
I have a rapid onset fever >38 deg, hypotension and SpO2 <90% and the Dr ordered what
What is CBC, Blood Cultures, VBG/ABG
-CBC with indicate WBC, neutrophil, etc.
-Blood Cx are looking for source
-VBG/ABG will provide a pH, HCO3,O2,CO2,Lactate
Pt presents with MI symptoms. Dr orders a 12 lead ECG. Once reviewed the Dr immediately orders a 15 lead ECG, WHY?
What is Confirmation of Posterior MI. (Differentiation between Inferior and Posterior)
Unpredictable and irregular prodromal uterual pains noted in the 2nd or 3rd trimester, with no etiology
What are Braxton Hicks contractions
I regulate electrical impulses with an intrinsic rate of 40-60 bpm
What is the Atrioventricular node (AV)
Adult Pt present to ER with decreased LOC and abdomen pain. Lab values show:
Hgb-125, Crea-75, Gfr-75, Na-133, K+-3.2, CO2-16, Gap-21, pH-7.21, Glucose-16.6. Pt also has a distinct smell and a Left Lower Leg wound. What is the Diagnosis?
What is DKA
Labs:
HGB 119, WBC 11.2, Na 133, K+ 3.2, Crea 75, GFR 75, CO2 16, GAP 20, Glucose 16.6, pH 7.21. Patient presents with abdo pain, drowse and with a distinct smell
What is DKA
Patient presents in a 3rd Degree Heart Block. Pt is pale, diaphoretic, hypotensive, bradycardic. What is the priority nursing intervention?
Defibrillation pads placed and prepare for Transcutaneous pacing
A reentry circuit within the atria generating a loop that discharges impulses at a rate of 250-350 / minute. Most often the AV junction passes every second or every fourth impulse(2:1 or 4:1 response) through to the ventricles. Noted characteristics include irregular or regular ventricle depolarization and a atrial saw tooth pattern
What is Atrial Flutter
The anatomical aspect and definition of a Nurse Maid Elbow
Radial head dislocation
-reduced at bedside with flexion, extension, supination and pronation
67yr old female presents to ER with tearing/ripping epi-gastric pain that radiates to groin and back and states, "this feels like a bladder infection". Pt VS show a HR of 75 and NIBP's that differ between Left and Right arms. What are our priority assessments and interventions? What do you think is going on?
1. Chest/abdo xray
2. Labs for a Cardiac set
3. ECG
The differentials include: AAA, MI
Pt presents to ER via EMS after being found down on the ground for >12hr. Pt is noted to have decreased LOC and brown urine. What is diagnosis and confirming lab value?
What is Rhabdomyolysis and CK
*DAILY DOUBLE*
HOCM
What is Hypertrophic Obstructed Cardiomyopathy
Early signs and symptoms of local anesthetic toxicity include all but one of the following. Indicate the exception:
- A. Tinnitus
- B. Perioral numbness
- C. Dizziness
- D. Hypertension
What is D - Hypertension
Manifestations of local anesthetic toxicity typically appear 1-5 minutes after the injection, but onset may range from 30 seconds to as long as 60 minutes. Initial manifestations may also vary widely. Classically, patients experience symptoms of central nervous system (CNS) excitement such as the following: Circumoral and/or tongue numbness, metallic taste, lightheadedness, dizziness, visual and auditory disturbances (difficulty focusing and tinnitus), disorientation and drowsiness.