The most common reagent used in a clinical chemistry laboratory
What is water (deionized, or reagent grade)
Violation of this Westgard Rule is observed in this image
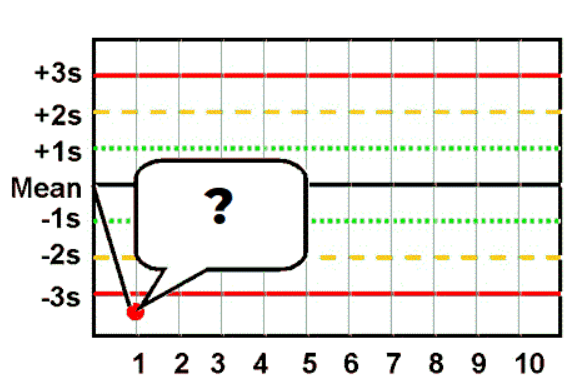
What is a 13s error
This equation is used to calculate the concentration of an unknown solution based upon its spectral absorbance at a given wavelength
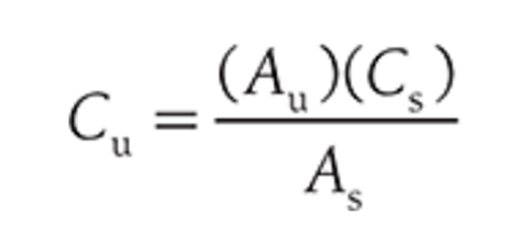
What is Beer's law (Beer-Lambert law)
The most common route of toxin exposure in humans
What is ingestion
This enzyme has a wide distribution in cardiac, muscle, and cellular tissues in the body and will separate into 5 isoenzymes upon electrophoresis
What is lactate dehydrogenase (LD)
A serum specimen is mislabeled during collection. this is an example of what type of laboratory error?
What is pre-analytical
The accuracy of a test result may be assessed by screening for this type of error (random or systematic)
This component of a spectrophotometer is responsible for recognizing the amount of light that is transmitted through a sample
What is a photodetector?
Tetrahydrocannabinol is the principle psychoactive compound in which drug?
What is THC (marijuana)
This isoenzyme of creatine kinase (CK) will be markedly elevated following myocardial infarction
What is CK-MB
The most common type of sample used for testing in the clinical chemistry laboratory
What is serum
The accuracy of a test result may be assessed by screening for this type of error (random or systematic)
What is random
This component of a spectrophotometer is responsible for providing isolation of a single wavelength of radiant energy (light)
What is a monochromator
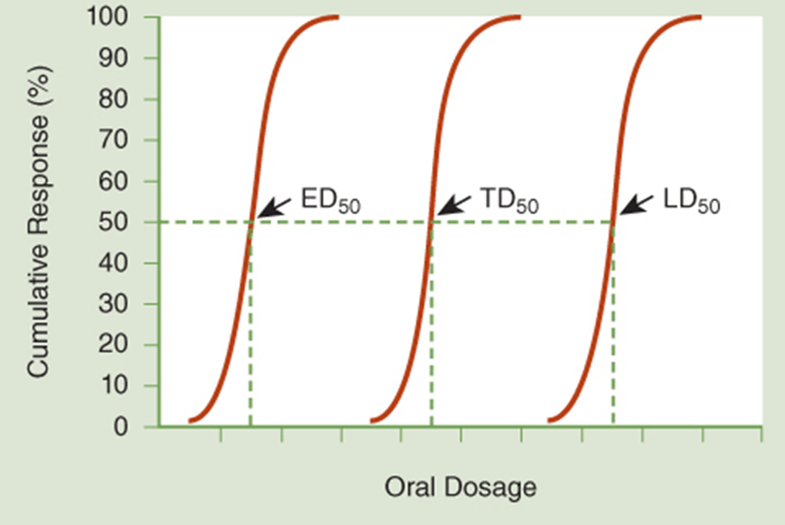
The dosage of a substance at which 50% of the population experiences mortality
What is the lethal dose (LD50)
Alanine amino transferase (ALT) is believed to be specific for this organ
What is the liver
Upon centrifugation of a serum specimen a milky appearance is noted

What is lipemia
2 consecutive control runs exceed 2SD on one side of the mean, this is a violation of which Westgard rule
22s
This type of spectrophotometer (shown below) does not require the use of a sample blank between testing different samples
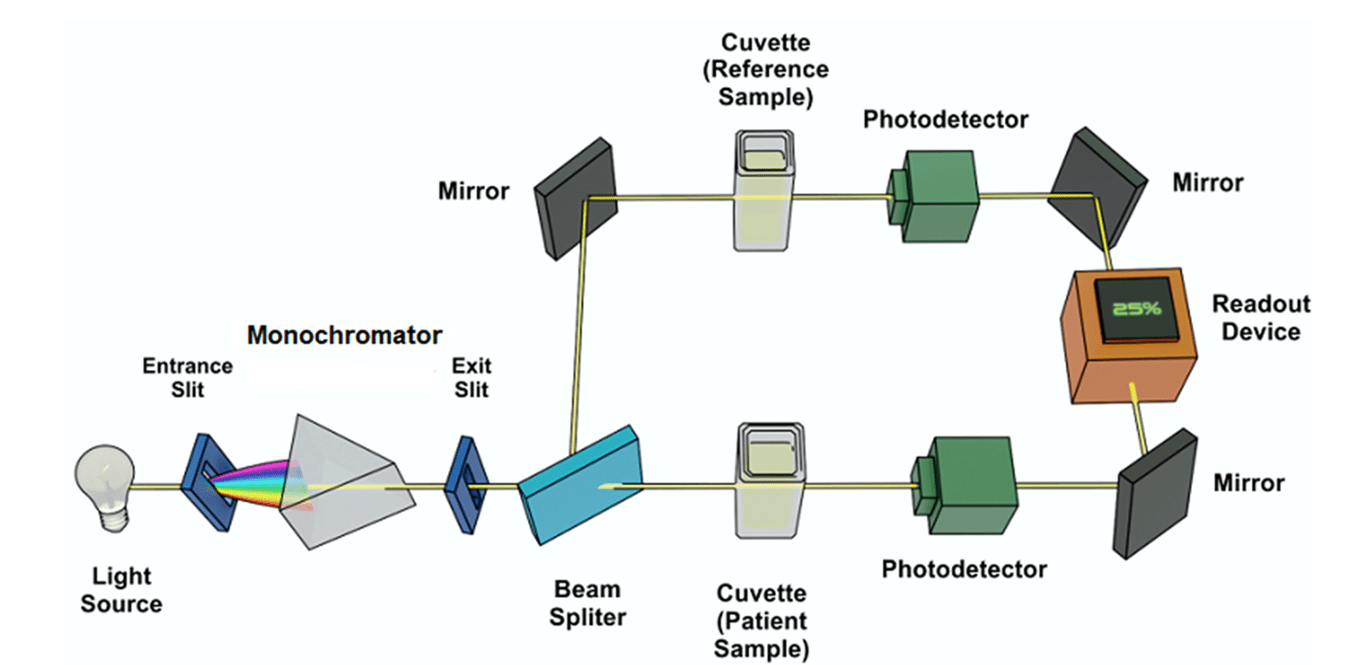
What is a double beam spectrophotometer
Reye's syndrome is associated with what toxic levels of which commonly taken therapeutic drug?
What are salicylates (aspirin)
The most specific enzymatic indicator of acute pancreatitis
What is amylase (AMY)
This protein is absent from serum specimens, but present in plasma samples
What is fibrinogen
This percentage of test results should fall within 1SD of the mean in otherwise normal circumstances
What is 68%
Absorbance values cannot be measured directly via spectrophotometry and must be calculated based upon the amount of radiant energy transmitted using what formula
What is: A= 2 -log(%T)
Impaired hemoglobin synthesis and altered vitamin D metabolism are commonly observed in patients suffering from exposure to this toxin
What is lead
DAILY DOUBLE
State the order of LD isoenzymes as observed in a "flipped" pattern frequently seen following myocardial infarction