The first line medication for a symptomatic patient with the below rhythm?
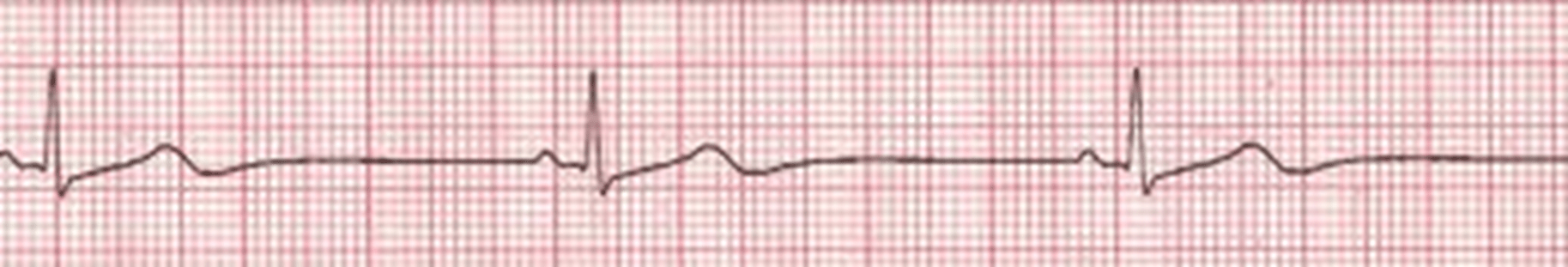
Atropine 1mg
Can repeat every 3-5 minutes up to 3mg
What medication cab be given every 3-5 minutes and what is the dose?
Epinephrine 1:10,000
Adult- 1mg
What are the first things we do when obtaining ROSC?
Obtain Vitals
The only times when you would stop CPR during a code
1. Defibrillation
2. Pulse check
3. Advanced airway placement
A sinus rhythm where the PRI is >.20
1st Degree block
A rhythm at 62 where the PR interval continually becomes longer then a QRS drops
2nd degree Type 1 (Wenckebach or Mobitz Type I)
When do we give Amiodarone?
Dosages?
Refractory Vfib/PVtach
Adult- 300mg, 150mg
A pulse and rhythm change is noted during active CPR
Is not an accurate assessment of either, likely related to compressions
A patient presents with near syncope. The patient is found to have a third degree heart block and is hypotensive. What are your next interventions?
Transcutaneous Pacing
An organized wide v-shaped pulseless rhythm
Treatment?
PVtach
Shock-defibrillate at 200J
Fast narrow rhythm >150bpm
Treatment?
SVT
Compensated- vagal maneuvers, adenosine
Uncompensated- synchronized cardioversion
Narcan dosages
Adult: 1mg
Peds: .1mg/kg
After obtaining ROSC, pt BP- 74/56. What are the two medications you would give?
NS bolus and Epi drip/push dose epi
After 2 minutes of CPR you check a pulse and rhythm noting a pulseless NSR rhythm. What ACLS algorithm are you in and what are your next actions?
PEA (Pulseless Electrical Activity)
Resume CPR, consider next medication dosing and possible causes.
A slow pulseless organized rhythm at a rate of 46?
Treatment?
PEA- continue compressions
The following rhythm is either shockable or not shockable:
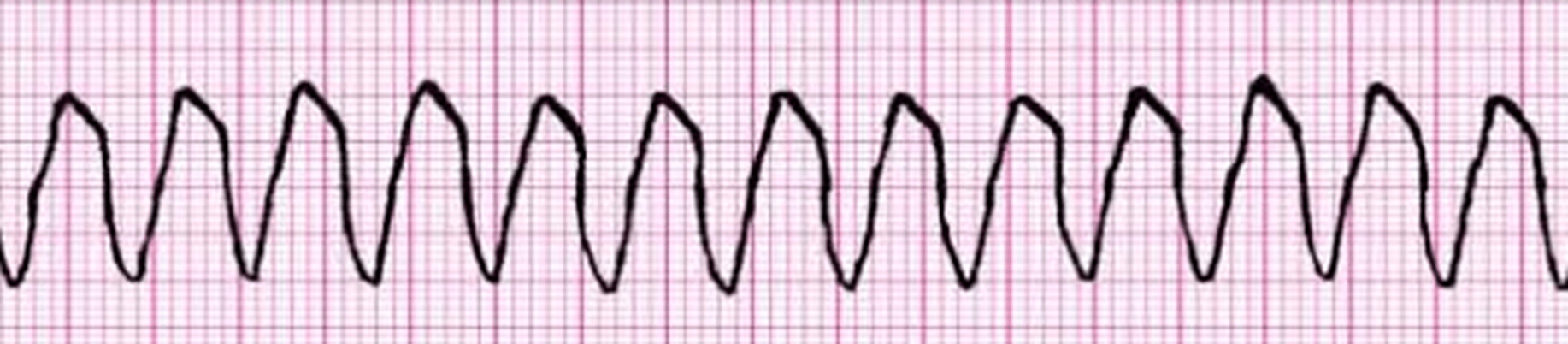
Shockable- Ventricular Fibrillation
When do we give adenosine?
Dosages?
SVT (Supraventricular Tachycardia)
Adult: 6mg, 12mg
Peds: .1mg/kg, .2mg/kg
After obtaining ROSC you notice a bradycardic rhythm, what is your next action?
Start pacing
What are the Hs and Ts
Hypovolemia, Hypoxia, Hydrogen Ions, Hypothermia
Tension Pneumo, Tamponade, Toxins, Thrombosis (pulmonary, coronary)
bradycardic rhythm that has a pwave for each qrs execpt for the qrs that occasionally drops. What rhythm?
A wide multifocal tachycardic pulseless rhythm is called what?
Treatment?
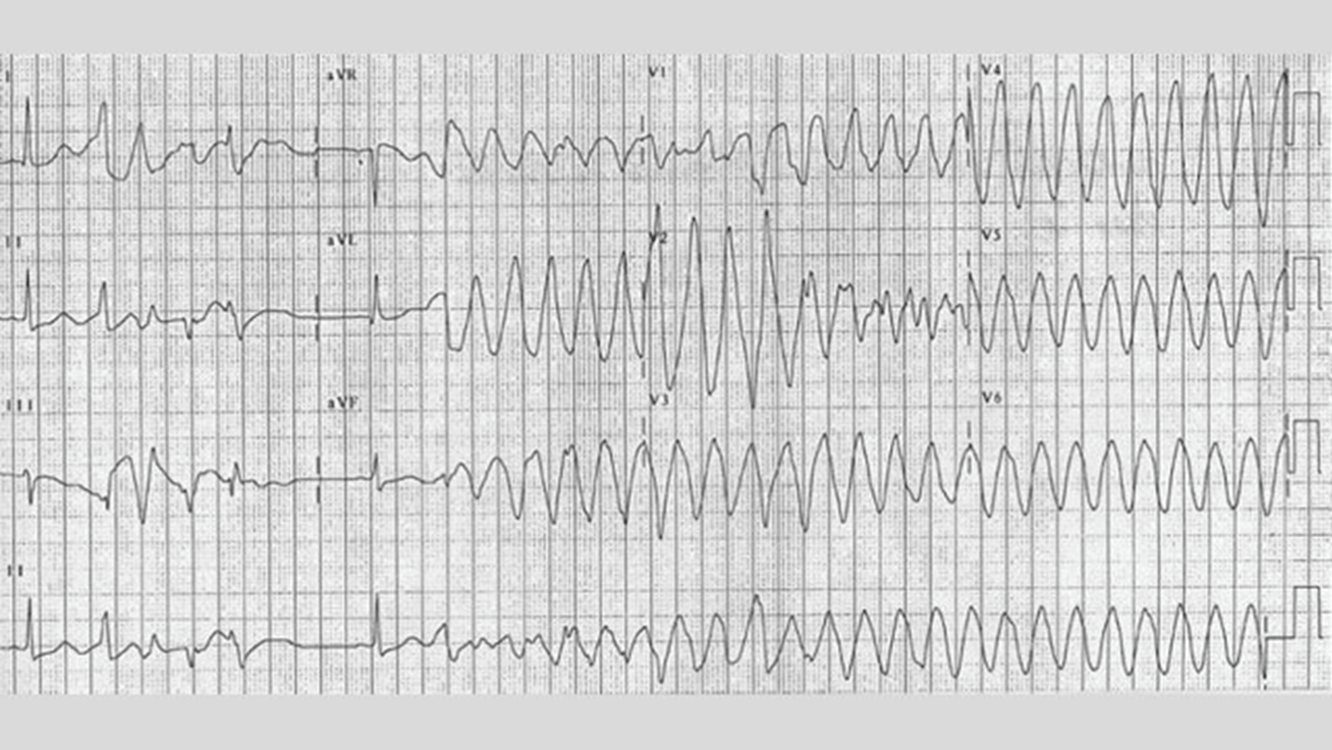
Torsades des Pointes
Defibrilation, 2g Mag sulfate in 10cc
End Tidal C02 range of 10-20mmHg
The end tidal range to confirm adequate CPR compression and resuscitation efforts
Normal ET C02 range is 35-45mmHg
After obtaining ROSC, pt is in an organized wide tachycardic rhythm. What are your next actions?
Synchronize cardioversion and 150mg Amiodarone drip
You have a 22 y.o. patient found to be in SVT. They are alert and conversant, with a blood pressure of 105/70. What is your first step in managing this rhythm?
Attempt a Valsalva maneuver
You see a pulse of 32 on the monitor and notice the rhythm has pwaves and qrs's but there are more pwaves and they are disassociated from each other. What rhythm is this?
3rd degree block