forgetting can happen in which area(s) of this model
what is
sensory memory- forgotten due to lack of attention
STM- forgotten due to decay/displacement
LTM- forgotten due to interference or retrieval failures
Proactive-refers to the interference effect of previously learned materials on the acquisition and retrieval of newer materials
Retroactive-refers to conditions in which new learning interferes with old learning
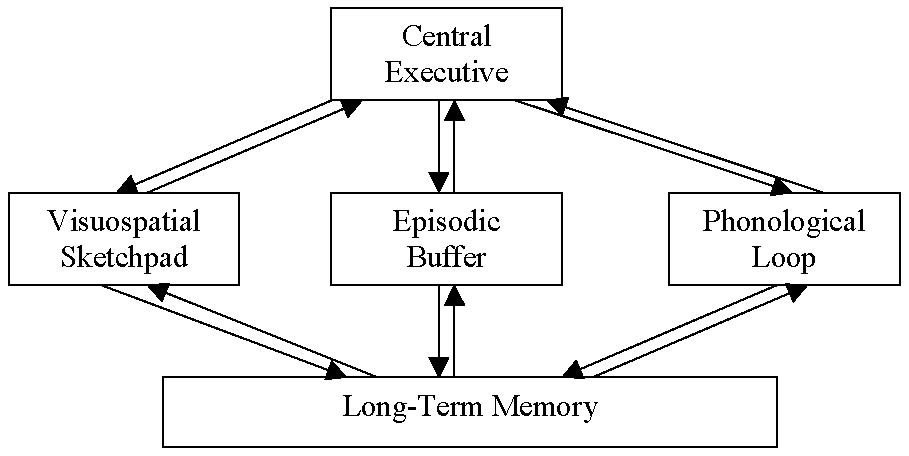
Processes spoken language, things we’ve written down, or information we get from speech
what is the phonological loop
Phonological store: inner ear à part that stores information based on speech for one or two seconds
Articulatory control process: inner voice à interprets and rehearses the new information from the phonological store and converts written material into phonological code so that it can be registered by the phonological store
Tendency of a person to recall the first and last items in a series best, and the middle items worst
what is the serial positioning effect (serial position curve)
basic components of language:
Phonology
Morphology
Syntax
Semantic
Pragmatics
what is (Phonology) how it sounds and patterns
what is (Morphology)construction of words
what is (Syntax) how words are arranged in sentences
what is (Semantic) what does it mean
what is (Pragmatics) use of natural language in communication
primary (basic) emotions
what are happiness, sadness, disgust, fear, anger, and surprise (we're still debating surprise)
Cold emotions: Experienced at a low level of arousal
Warm emotions: Experienced at a high level of arousal

Which cognitive bias causes individuals to pay more attention to negative information over positive information?
what is the Negativity bias
This bias means people tend to focus on negative experiences more than positive ones when making judgments or recalling events.
this model involves 3 primary sections of memory
what are sensory memory, short term memory, and long term memory
Processes visual and spatial information
what is the visuospatial sketch pad
Can be fed information directly, through perception, or indirectly through a visual image
Allows people to store images of objects and their locations à also used in navigation
Visual cache: store information pertaining to color and visual form
Inner scribe: rehearses information from the visual cache and transfers information from the visual cache to the central executive
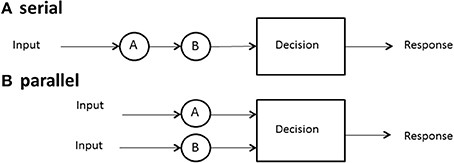
serial processing
parallel processing
what is when tasks are completed one at a time, in order. (The system finishes one task before moving to the next. This is like a single cashier at a store handling customers one by one).
what is when multiple tasks are handled simultaneously by different processors or cores. (store with multiple cashiers, each serving a different customer at the same time)
Parallel processing is much faster for complex computations, while serial processing is simpler and works well for tasks that must be done step by step.
skinner vs. Chomsky
what is BEEF
skinner said that language was a development by means of environmental influence and reinforcement
Chomsky said that children will never acquire the tools needed for processing an infinite number of sentences if the language acquisition mechanism was dependent on language input. He proposed the theory of Universal Grammar: an idea of innate, biological grammatical categories, such as noun, verb, and adjectives
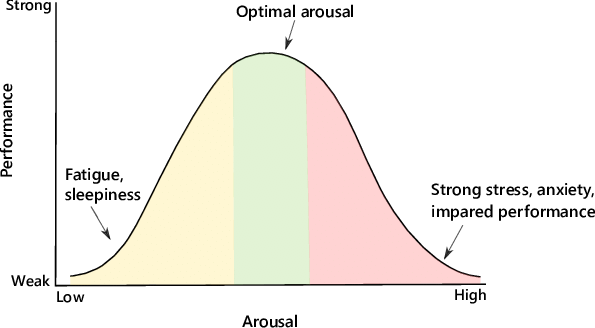
Performance increases with physiological or mental arousal (stress) but only up to a point. When the level of stress becomes too high, performance decreases
what is the Yerkes-Dodson Law
Which of the following best explains how emotional arousal affects working memory performance in complex cognitive tasks?
- Emotional arousal always enhances working memory capacity due to increased attentional focus.
- Emotional arousal disrupts working memory when cognitive load exceeds attentional resources.
- Emotional stimuli activate the central executive, improving cognitive flexibility.
- Emotional arousal reduces the engagement of the amygdala, leading to decreased task performance.
what is (2) Emotional arousal disrupts working memory when cognitive load exceeds attentional resources.
High emotional arousal can improve focus but may also deplete cognitive resources when dealing with complex tasks.
STM is maintained how?
What is rehearsal
Strategies:
- Rehearsal: The act of repeating information over and over to maintain it in short-term memory.
- Organizational Strategies: Techniques that involve organizing information into meaningful patterns or categories to facilitate easier recall.
- Chunking: Breaking down information into smaller, manageable chunks to improve encoding and recall.
- Mnemonic Devices: Memory aids that use acronyms, visualization, or other techniques to associate information with easily remembered cues.
- Elaboration: Connecting new information to existing knowledge or experiences, thereby deepening encoding and improving retention.
A place to temporarily integrate information gathered from the phonological loop, visuo-spatial sketchpad, and long-term memory
what is the episodic buffer
Controlled by the central executive, yet it transfers information into and out of the long-term memory
refers to perception that is driven by cognition. your brain uses information that is knows and applies it to what it expects to perceive
what is top-down processing
Top-down processing happens when our brain uses prior knowledge, experiences, and expectations to interpret new information.
(EX) Reading Words with Missing Letters. When you see a sentence with missing letters, your brain fills in the gaps based on context. For example, "Ths sntnc s msng sm lttrs" is still readable because you expect certain words to appear.
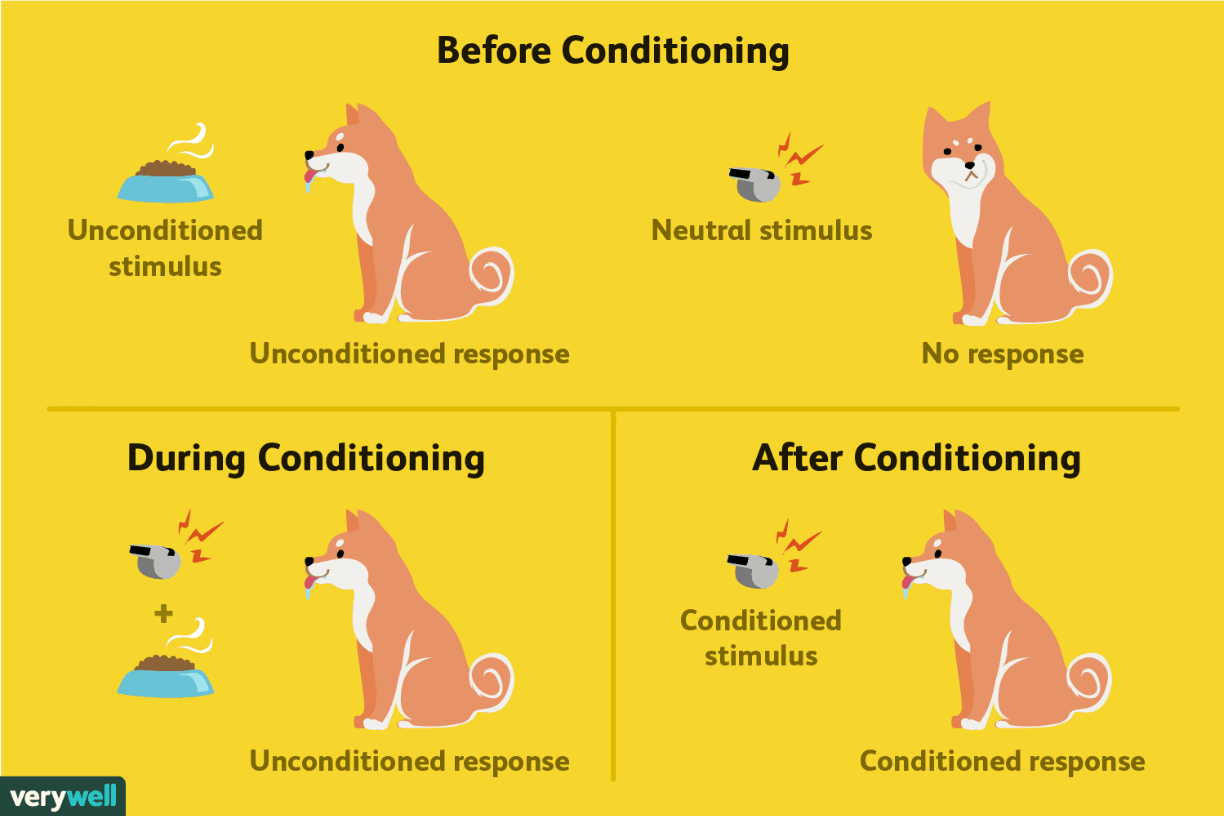
process of pairing unconditioned stimulus with a conditoned stimulus to form a conditioned response
what is classical condiitoning (founded by ivan pavlov & the DOGS)
Stimulus Generalization-tendency of a new stimulus to evoke responses or behaviors similar to those elicited by another stimulus
Stimulus Discrimination- learn to respond only to the original stimulus, and not to other similar stimuli
Backward Conditioning-an unconditioned stimulus is consistently presented before a neutral stimulus. Generally, this arrangement is not thought to produce a change in the effect of a neutral stimulus.
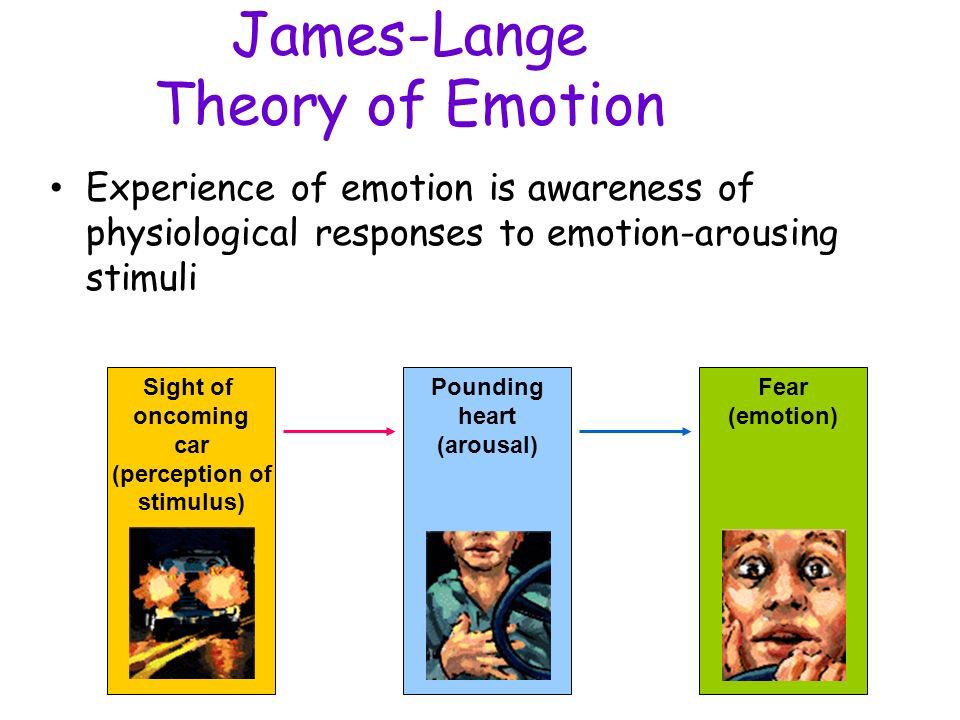
theory of emotions involving arousal, then physiological response, then emotion
what is the James-lang theory of emotion
__ occurs when learned behavior is demonstrated without any reinforcement or explicit teaching.
what is latent learning
Latent learning is a type of learning which is not apparent in the learner’s behavior at the time of learning, but which manifests later when a suitable motivation and circumstances appear. This shows that learning can occur without any reinforcement of a behavior.
the way information is changed so that it can be stored in the memory. (There are three main ways)
What is encoding
1. visual (picture)
2. acoustic (sound)
3. semantic (meaning)
incorporates information from the phonological loop, visuospatial sketchpad, episodic buffer, and from LTM
what is the central executive
Major functions- switching retrieval plans, time sharing in multitasking, selective attention, suppressing irrelevant information, daydreaming, and temporary activation of LTM
processing sensory information as it comes in. looks at small details and then builds a bigger picture
what is bottom-up processing
Bottom-up processing happens when we interpret information starting from raw sensory input, without relying on prior knowledge or expectations.
EX- Solving a puzzle. When working on a jigsaw puzzle, you examine each piece’s shape and color before seeing the full picture.
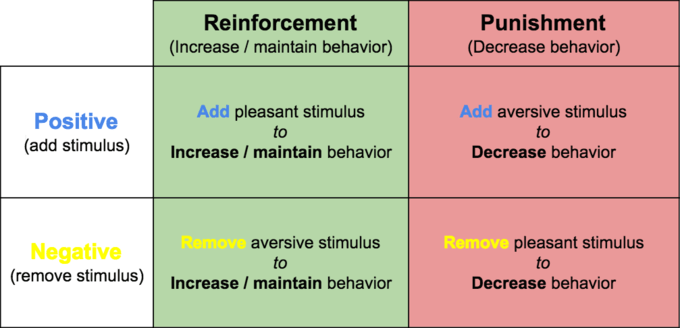
process of adding or removing stimuli to elicit behavior change
what is operant conditioning (founded by skinner)
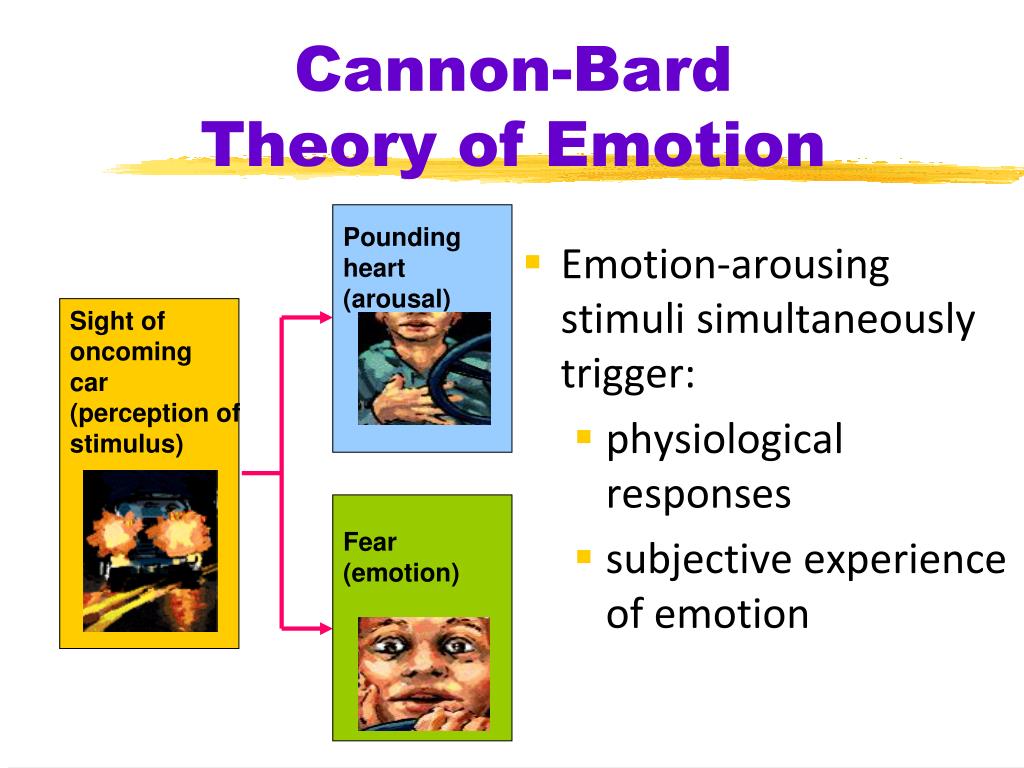
theory of emotion involving arousal following by simultaneous physiological response and emotion
what is the cannon-bard theory of emotion
What is one mechanism by which emotionally charged events can increase the likelihood of false memories?
- Heightened amygdala activity suppresses hippocampal encoding.
- Emotional valence reduces source monitoring accuracy.
- Negative emotions eliminate sensory-based memory consolidation.
- Dopaminergic activity in the striatum enhances retrieval fluency.
Answer: B) Emotional valence reduces source monitoring accuracy.
what is (2) emotional valence reduces source monitoring accuracy
Emotions, particularly strong ones, play a significant role in how we encode, store, and retrieve memories. When an event carries intense emotional weight—whether positive or negative—it often leads to:
- Enhanced memory vividness – The memory may feel highly detailed and real.
- Increased confidence in accuracy – People believe their recollection is correct, even if it's distorted.
- Greater susceptibility to misinformation – Emotionally arousing events can lead to reconstructive processes that alter memory content.
One major mechanism behind false memories is source monitoring errors, where individuals misattribute the origin of a memory. Emotional events exacerbate these errors because:
- High emotional arousal interferes with careful encoding, making it harder to distinguish between true and suggested memories.
- Post-event discussion or exposure (such as seeing emotionally charged images or hearing retellings) can blend with original memories, leading someone to falsely recall altered details.
- The amygdala and hippocampus, which are central to emotional memory processing, can sometimes emphasize certain elements of an event while neglecting others, causing distorted recall.
duration, capacity, and encoding abilities in each memory store
what are
Sensory memory-Duration ¼ to ½ second, Capacity all sensory experience (v. larger capacity), encoding is sense specific
STM-duration up to 30 seconds, capacity 7+/-2 chunks. mainly encodes information acoustically
LTM-Duration Unlimited, Capacity Unlimited, Encoding mainly Semantic (but can be visual and auditory)
a mental experience that’s remembered as factual but is either entirely false or significantly different from what actually occurred
what is the confabulation of false memories
-The distortion of the memory of the original event by the new information can be described as retroactive interference
-misleading/false information/ leading questions
-In 1974, Elizabeth Loftus and John C. Palmer conducted two experiments in which the participants viewed videos of automobile accidents and answered follow-up questions (Loftus & Palmer, 1974).
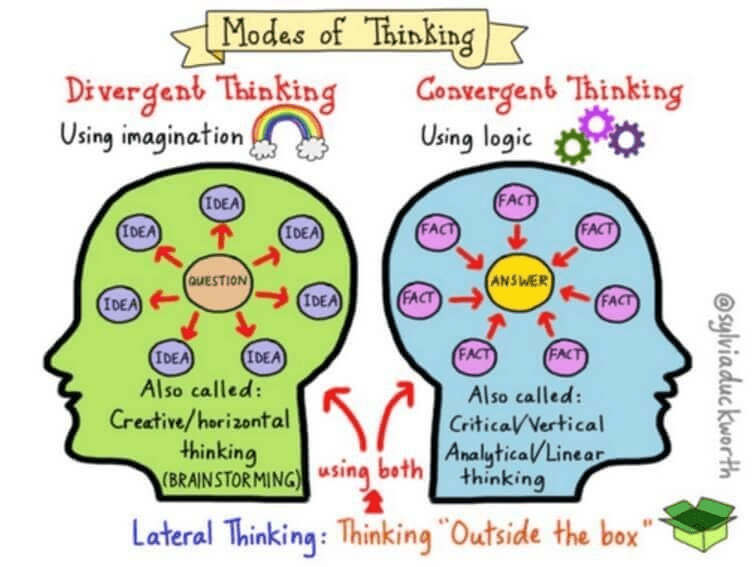
divergent thinking
convergent thinking
lateral thinking
DIV-what is a creative thought process where multiple possible solutions are explored freely and spontaneously. It encourages brainstorming and thinking outside the box to generate new ideas.
CON-what is the opposite of divergent thinking. It focuses on finding a single, correct solution to a problem using logic, structure, and existing knowledge. It’s often used in decision-making and problem-solving where there is a clear answer.
LAT- what is a problem-solving approach that involves looking at situations from unconventional angles. Instead of following a direct, logical path, lateral thinking encourages creativity and unexpected solutions.
conditioned fear by ringing a loud bell and presenting them with a bunny
what is the little albert experiment conducted by John Watson
He said that he could create any kind of child by manipulating the environment
Conditioned Taste Aversion: that the food is considered to be the cause of the illness
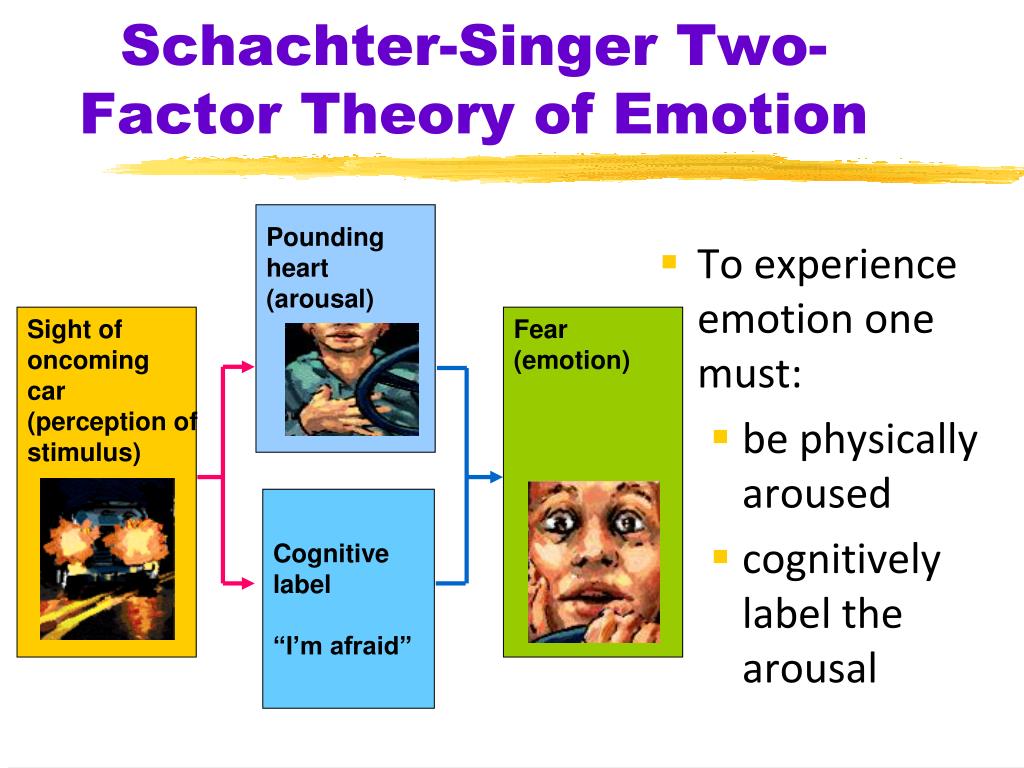
theory of emotion involving arousal, then simultaneous physiological response and cognitive label, then emotion
what is schachter-singer 2 factor theory of emotion
Which neurobiological mechanism best explains the role of the amygdala in emotionally enhanced memory encoding?
- The amygdala modulates hippocampal activity by increasing the release of norepinephrine during emotional experiences.
- The amygdala inhibits the prefrontal cortex, reducing cognitive control over memory consolidation.
- The amygdala directly encodes emotional information independently of the hippocampus.
- The amygdala suppresses attentional processing of emotionally salient stimuli, leading to memory distortion.
what is (1) The amygdala modulates hippocampal activity by increasing the release of norepinephrine during emotional experiences.
This heightened noradrenergic activation strengthens memory encoding, making emotional experiences more memorable.