What are 4 biomolecules?
Which ones are polymers, and which ones are macromolecules?
Lipids, protein, nucleic acids, carbs
Polymers: protein, nucleic acids, carbs
Macromolecules: all 4, including lipids
What are mitosis and meiosis?
Division of nucleus
Name domains and kingdoms
Bacteria - Bacteria
Archaea - Archaea
Eukarya - Protista, Plantae, Fungi, Animalia
An animal has two unlinked genes, one for head shape (Hh) and one for tail length (Tt). The animals genotype is TtHh. What is a possible genotype of the sperm (gamete)?
TH
Th
tH
th
Main differences between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
1. No nucleus
2. No membrane-bound organelles
3. Division: binary fision
The function of protein is determined by its....
As a result of denaturation, the protein becomes
primary structure
non-functional
Which of the following structures is shared by all LIVING cells?
Cell Membrane Chloroplast
Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus
Mitochondrion
Cell Membrane
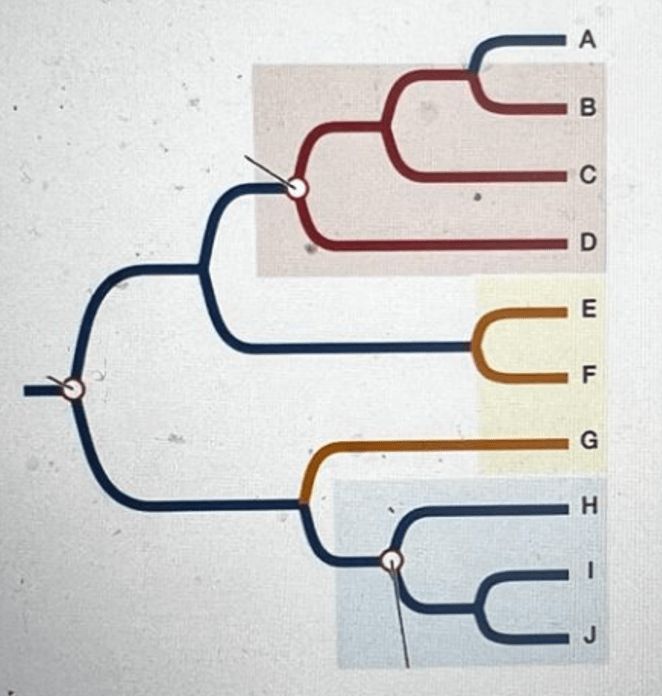
Identify monophyletic, polyphyletic, paraphyletic
Monophyletic,: H I J
Polyphyletic,: E F G
Paraphyletic,: B C D
When does independent assortment occur in meiosis?
Metaphase I
What prokaryotes were involved in evolution of mitochondria and chloroplast?
Mitochondria evolved from proteobacteria
Chloroplast evolved from cyanobacteria
Name the polymers and their monomers.
Nucleic acid - nucleotides
Protein - amino acids
Polysaccharide - monosaccharide
What is called cell's programmed death?
What is called cell's death as a result of being exposed to harmful substances?
Apoptosis
Necrosis
Two different cars are traveling at 60 mph. At a certain point, both cars slam on the brakes. The distance it takes for each car to stop is then measured.
Identify independent, dependent, constant variables
Independent: Car brand
Dependent: breaking distance
Constant: speed, road surface, weather
Synapsis and crossing over occur in ______ during ______________
Meiosis
Prophase I
Viruses: what are the proves they are living?
1. Interact with other organisms
2. Adapt through evolution
3. Respond to external changes – sensitivity (?)
No cell structure, no metabolism, no growth & reproduction, no homeostasis
What is the difference between polymers and macromolecules? Provide examples.
Polymers are long molecules consisting of many similar or identical monomers: proteins, carbs, nucleic acids
Macromolecules are giant molecules containing of thousands or more atoms, but not similar or identical monomers. All 4 biomolecules
Explain a process called nondisjunction.
What happens as a result? Use proper terminology.
Give one example.
When chromosomes fail to separate properly during cell division.
Aneuploidy.
Trisomy 21, Down Syndrome
Mary investigated the effect of different concentrations of "Miracle Substance" on the growth of tomato plants.
State a possible hypothesis for this experiment.
1. If "Miracle Substance" is added to the soil, the tomatoes will show extensive growth, because they get extra nutrition.
2. If "Miracle Substance" is added to the soil, the tomatoes will show slow growth, because the Substance is not healthy for tomato plants.
In sexual life cycles ________ are haploid
gametes
Classify Bacteria in three different ways. Explain what the classifications are based on.
1. Based on cell wall structure - ability to be colored by dye: gram-positive and gram-negative
2. Based on shape: coccus, bacillus, spirillum
3. Based on nutrition - Photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs; heterotrophs; decomposers
4. Antibiotic sensitivity - Biofilm forming
2 nucleic acids are...
What are 3 differences between them? (structure, function, composition)
DNA and RNA
1. Structure: DNA - double helix, RNA - single
2. Function: DNA carries genetic information, RNA - copies and translates it
3. Composition: DNA - A,T,G,C RNA - A,U,G,C
List all phases of the cell cycle
Interphase : G1, S, G2
Mitosis: Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Cytokinesis
What does the endosymbiotic theory explain?
Eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells through a symbiotic relationship where larger prokaryotes engulfed smaller ones. This led to the development of mitochondria and chloroplast.
It is theoretically possible for a gene from any organism to be transferred and remain functional in a completely different organism. Why is this possible?
All organisms have the same genetic code made of 4 nucleotides.
Structure of cyanobacteria: 3 types of cells, their function
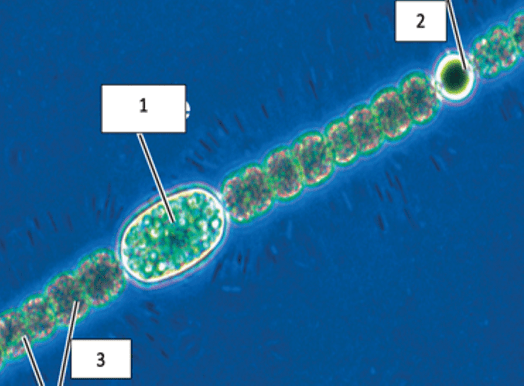
1. Spores are used as survival mechanism
2. Heterocyst are specialized for nitrogen fixation
3. Vegetative cells carry out photosynthesis