These are the outcomes (or sample space) for tossing a fair coin twice.
What is HH, HT, TH, and TT?
This is the probability of getting five heads when you toss five fair coins simultaneously.
What is 1/32?
Tossing five coins - sample space is 2^5 = 32
Probability of getting H H H H H is only 1 out of the 32 possible outcomes.
____________________ is the long-run average value of random variables. It also indicates the probability-weighted average of all possible values.
What is expected value?
The local paint store offers 28 basic colors, each of which can be prepared with one of 4 different textures. this is the number of different paint combinations that are available.
What is 112?
28 times 4 = 112.
The probability of rolling a fair die three times and getting in order 1, 2, 3.
What is 1/216?
Total outcomes for rolling a die 3 times is 6*6*6 = 216.
Getting a 1 the first time is 1/6. Getting a 2 the second time is 1/6. Getting a 3 the third time is 1/6.
1/6 * 1/6 * 1/6 = 1/216.
You have 100 dollars and can invest into a stock. The returns are volatile and you may get either $120 with probability of 0.4, or $90 with probability 0.6. You should or should not invest in this stock because the expected value is _______.
What is should invest in this stock because the expected value is $102.
E(X) = 0.4*120+0.6*90=48+54=102
If the probability of selecting a winning ticket is 1/100, this is the odds of not selecting a winning ticket.
What is 99 to 1?
P(winning ticket) = 1/100
P(not a winning ticket) = 99/100
O(not a winning ticket)= 99:1
The probability of rolling a sum of either 2,3, 4, or 5 on a roll of two dice.
What is 5/18?
Probability of rolling a sum of 2 is 1/36.
Probability of rolling a sum of 3 is 2/36.
Probability of rolling a sum of 4 is 3/36.
Probability of rolling a sum of 5 is 4/36.
1/36 + 2/36 + 3/36 + 4/36 = 10/36 = 5/18.
A local club plans to invest $10000 to host a baseball game. They expect to sell tickets worth $15000. But if it rains on the day of game, they won't sell any tickets and the club will lose all the money invested. If the weather forecast for the day of game is 20% possibility of rain, is this a good investment? The expected value is ___________.
What is yes, this is a good investment with an expected value of $2000.

Use the weighted average formula.
Expected Value=5000(0.8)−10000(0.2)=4000−2000=2000
This is the probability of drawing a red face card (red Jack, Queen, or King) from a standard deck of cards.
What is 3/26?
There are 6 red face cards in a deck of 62 cards (Jack of hearts, Jack of diamonds, Queen of hearts, Queen of diamonds, King of hearts, King of diamonds) which gives us 6/52. Reduce the fraction to get 3/26.
The probability of drawing no aces when you draw a card from a standard deck 4 times (replacing the card each time you draw), rounded to three decimal places.
What is 12/13 x 12/13x 12/13x 12/13 ?
A company makes electronic gadgets. One out of every 5050 gadgets is faulty, but the company doesn't know which ones are faulty until a buyer complains. Suppose the company makes a $3 profit on the sale of any working gadget, but suffers a loss of $80 for every faulty gadget because they have to repair the unit. The expected value for the company is __________.
What is $1.34?
E(X)=(49/50)(3)+(1/50)(−80)
=147/50−80/50
=67/50
=1.34
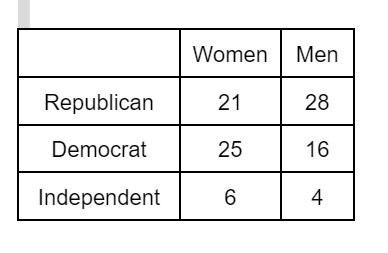 The table above gives the gender and political party of the 100 delegates at a political convention. Suppose you encounter a delegate at random. This fraction is the probability that you meet a Democrat.
The table above gives the gender and political party of the 100 delegates at a political convention. Suppose you encounter a delegate at random. This fraction is the probability that you meet a Democrat.
What is 41/100 or 0.41?
25/100 + 16/100 = 41/100.
The probability of drawing four spades in a row from a standard deck of cards when the card is not returned to the deck each time.
What is 11/4165?
P(1st card is a spade) 13/52 or 1/4.
P(2nd card is a spade) 12/51 or 4/17.
P(3rd card is a spade) 11/50.
P(4th card is a spade) 10/49.
(1/4)(4/17)(11/50)(10/49) = 11/4165.
You are a financial analyst in a development company. Your manager just asked you to assess the viability of future development projects and select the most promising one. According to estimates, Project A, upon completion, shows a probability of 0.4 to achieve a value of $2 million and a probability of 0.6 to achieve a value of $500,000. Project B shows a probability of 0.3 to be valued at $3 million and a probability of 0.7 to be valued at $200,000 upon completion. You should choose Project ___ with an expected value of _________.
What is Project A with an expected value of $1,100,000?

EV (Project A) = [0.4 × $2,000,000] + [0.6 × $500,000] = $1,100,000
EV (Project B) = [0.3 × $3,000,000] + [0.7 × $200,000] = $1,040,000
The EV of Project A is greater than the EV of Project B. Therefore, your company should select Project A.