Name 3 things that a Surface Analysis Chart will provide to a pilot.
What is Surface wind direction and speed, Temp, Dewpoint, Position of Fronts, areas of high/low pressure, obstructions to vision
Every physical process of weather is accompanied by, or a result of a ____________ ___________.
What is heat exchange?
This is the meaning of the following symbol:
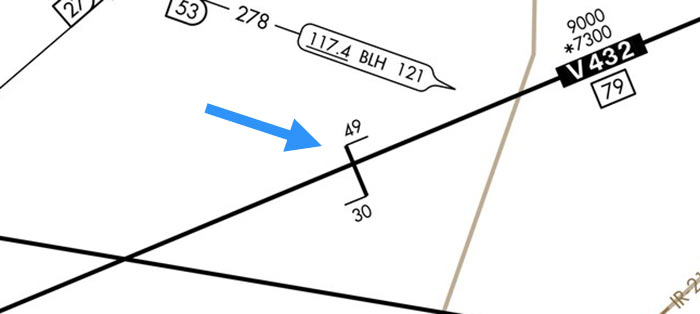
What is a Change Over Point? Change tracking from one vor to another on an airway.
This is a combination of a heading indicator and a VOR/ILS indicator.
What is an HSI (Horizontal Situation Indicator)?
These two things are required if a pilot wants to operate under special VFR rules at night.
What is pilot must be IFR rated and the aircraft is IFR rated?
This depiction denotes lines of equal pressure.
What are Isobars?
___________ ____________ deflects wind to the right in the Northern Hemisphere.
What is Coriolis Force?
Look at the numbers listed on the following symbol. Define each one and what each one provides
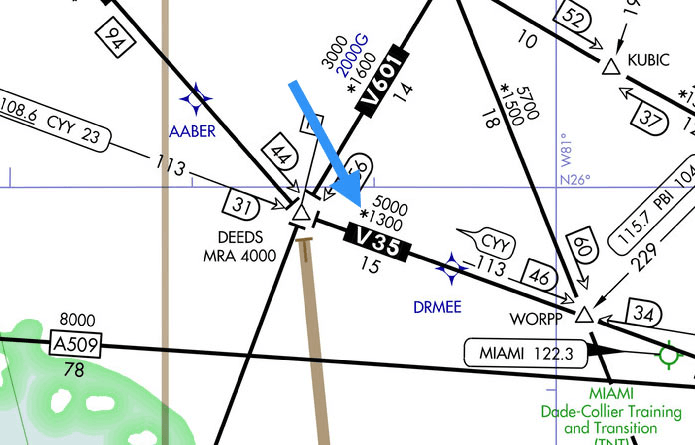
What are the MEA and the MOCA?
MEA - Radio Reception and obstacle clearance entire route.
MOCA - designated with * Obstacle clearance entire route. Radio reception within 22nm.
If there is a one-fifth deflection on a VOR receiver, this is how many degrees off course you are.
What is 2 degrees - or 2NM at 60NM from station?
This is where Class E airspace begins in the picture below: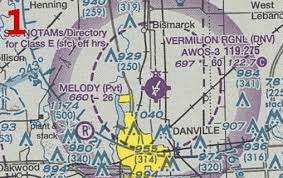
What is 700 Feet AGL?
The following information in a TAF. Explain its meaning:
PROB40 2203 +TSRA
What is a 40% chance of Heavy rain and Thuderstorms between 2200z and 0300z?
Name the general circulation of air in a high pressure area in the Northern Hemisphere (three things).
What is outward, downward, and clockwise?
On a precision approach, this is the final approach fix (FAF).
What is Glide Slope Intersept?
Explain how you track a VOR Radial Outbound ( in regards to OBS, heading and CDI)
What is set OBS to outbound radial (top), make heading corrections towards CDI.
When operating in Class C Airspace, a pilot must have this visibility and remain how far from clouds?
What is 3 SM visibility and 1,000 above, 500 below, and 2,000 horizontal?
Name three things that a convective sigmet may be issued for.
What are Tornadoes, Lines of Thunderstorms, Embedded Thunderstorms, Thunderstorm areas greater than or equal to thunderstorm intensitiy level 4 with coverage of 40% or more, and hail greater than 3/4 inch in diameter.
This happens to the jetstream during the winter months.
What is shifts south and the wind speed increases?
The minimum safe altitude is depicted on which part of the IFR approach plate. It is what altitude on the following picture?
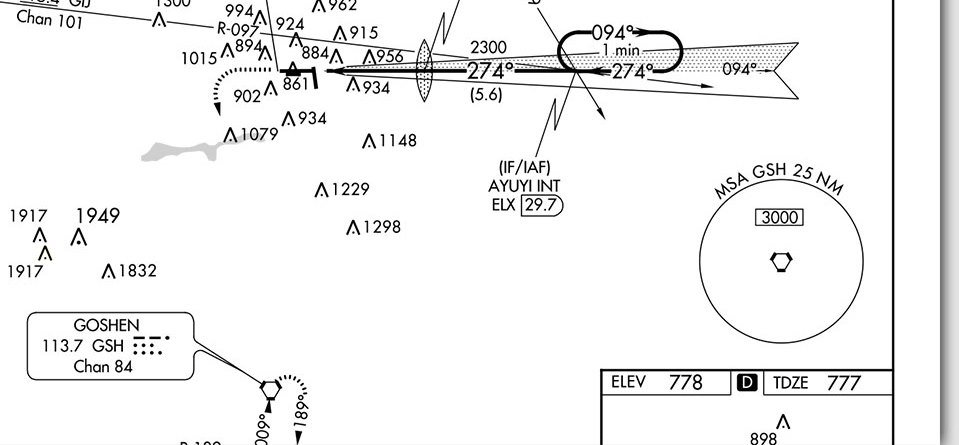
What is 3,000?
Name three things a pilot should do when flying by means of GPS Navigation.
What are determine - GPS is approved for planned route, understand how to make proper entries, program and review plan, ensure track flown is approved by ATC
This is the type of airspace that Federal Airways are designated as.
What is Class E?
This is considered a sudden increase in windspeed of at least 16 knots to a sustained speed of 22 knots or more and lasting for at least 1 minute.
What is a squall?
This is the approximate base of the cumulus clouds if the temperature at 2,000 ft MSL is 10 degrees C and the dewpoint is 1 degree C.
What is 5,600 feet MSL?
Converge at 2.5 degrees C. Spread is 9 (10-1) so they will converge at 3,500 feet AGL (9/2.5 = 3.6) the base of the cumulus clouds is approx. 5,600 feet MSL (3600 + 2000)
You have flown 52 miles and are 6 miles off course. You still have 118 miles to fly. To converge on your destination this is the total angle correction
10 degrees
nm off/nm flown X 60
6NM/52NM X 60 = 6.92
to converge:
NM off / NM Remaining X 60 =
6NM/118NM X 60 = 3.05
6.92 + 3.05 = approx 10 degrees
Name two operational pitfalls pilots can experience when using GPS navigation.
What are losing proficiency in performing manual calculations on courses, times, distances, headings, and emergency situations.
This is the required visibility and cloud clearances in Class G airspace when operating at Night below 1,200 feet AGL.
What is 3 SM 1,000 above, 500 below, and 2,000 horizontal?