This is normally transparent but it is red in this picture.

What is the conjunctiva.
Bacterial conjunctivitis has a "_______" discharge.
What is purulent?
(As opposed to a watery discharge for viral conjunctivitis)
This is the typical cause of viral conjunctivitis.
What is adenovirus?
This is one of the 4 treatments for dry eye.
warm compresses, eyelid scrubs, artificial tears, topical cyclosporine
This is most likely showing (bacterial or viral?) conjunctivitis.
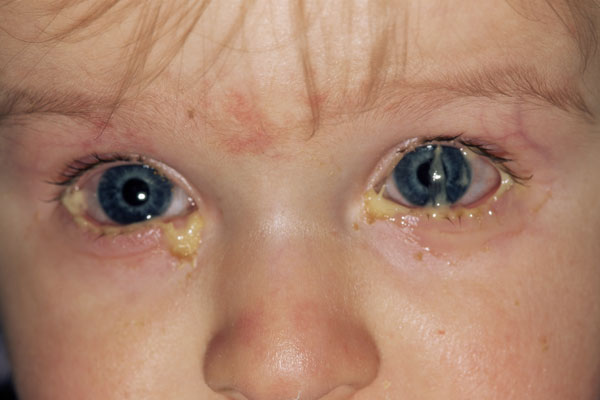
What is bacterial conjunctivitis?
This is the most common cause of blindness in the world.
What are cataracts?
Patients with conjunctivitis complain that their eyes are "______ _______" when they wake up.
What is "stuck shut"?
*This does not determine bacterial vs. viral
This type of glaucoma is typically asymptomatic.
What is open-angle glaucoma?
As opposed to angle-closure glaucoma (symptoms include loss of visual acuity, pain, conjunctival erythema, and corneal edema)
This is used to treat cataracts.
What is surgery?
This species of bacteria can cause hyperacute bacterial conjunctivitis that is severe and sight-threatening.
What is Neisseria (N. Gonorrhea).
- Characterized by a profuse purulent discharge present within 12 hours of inoculation
This is the color of conjunctiva in a healthy person.
What is transparent?
Angle-closure glaucoma affects this chamber of the eye.
What is the anterior chamber.
This medication is first line for open-angle glaucoma.
What is beta blockers?
- Recent studies have shown prostaglandins may be more effective.
- Laser therapy is also effective in reducing IOP
This is a treatment for bacterial conjunctivitis.
Soft contact lens wearers have a high risk of this type of keratitis, especially with use of extended-wear lenses.
What is pseudomonas?
- causes acute red eye and discharge in association with an ulcerative keratitis (can cause perforation within 24 hours).
This is believed to be the reason for age-related dry eyes in most cases.
These are 2 viruses that can cause uveitis.
Herpes, CMV, west nile, ebola, zika
When a person is developing cataracts, this typically increases before there is any cloudiness seen.
Nearsightedness ("myopic shift")
Three of these will definitely be treated with antibiotics:
Viral conjunctivitis, Bacterial conjunctivitis, Allergic conjunctivitis, Corneal ulcer or abrasion, iritis/uveitis, episcleritis, corneal ulcer, corneal abrasion, dry eye
bacterial conjunctivitis, corneal ulcer/abrasion, corneal ulcer
These are 2 red flag warning signs in a patient with a complaint of a red eye.
- Reduction of visual acuity --> infectious keratitis, iritis, angle closure glaucoma
- Ciliary flush: the redness is most pronounced in a ring at the limbus (transition zone between the cornea and the sclera) --> infectious keratitis, iritis, angle closure glaucoma
- Photophobia --> concerns about infectious keratitis, iritis
- Severe foreign body sensation that prevents the patient from keeping the eye open --> concerns about infectious keratitis
- Corneal opacity --> concerns about infectious keratitis
- Fixed pupil --> concerns about angle-closure glaucoma
- Severe headache with nausea --> concerns about angle closure glaucoma
These tend to be round on fluorescein staining but are typically evident as a white or opaque spot with a penlight or direct inspection.
What is a corneal ulcer

After removal of an object with iron in it, there is typically a rust ring left which should be removed with this.
It should not be removed as it will go away on its own.
These 2 systemic diseases are most commonly associated with uveitis.
What are spondyloarthropathies (ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis), sarcoidosis
One of these three needs aggressive treatment with topical antibiotics and a referral to ophthamology:
bacterial conjunctivitis, corneal ulcer/abrasion, corneal ulcer
What is a corneal ulcer?
If you have a patient with angle-closure glaucoma who can not see an ophthamologist within an hour, you should give the patient pressure lowering eye drops and this drug IV.
What is acetazolamide?
A possible regimen would be one drop each, one minute apart, of: timolol, apraclonidine, and pilocarpine