2 findings on urine dipstick suggestive of UTI
what are Leukocytes and nitrites?
The most common bacterial cause of prostatitis
What is E. coli ?
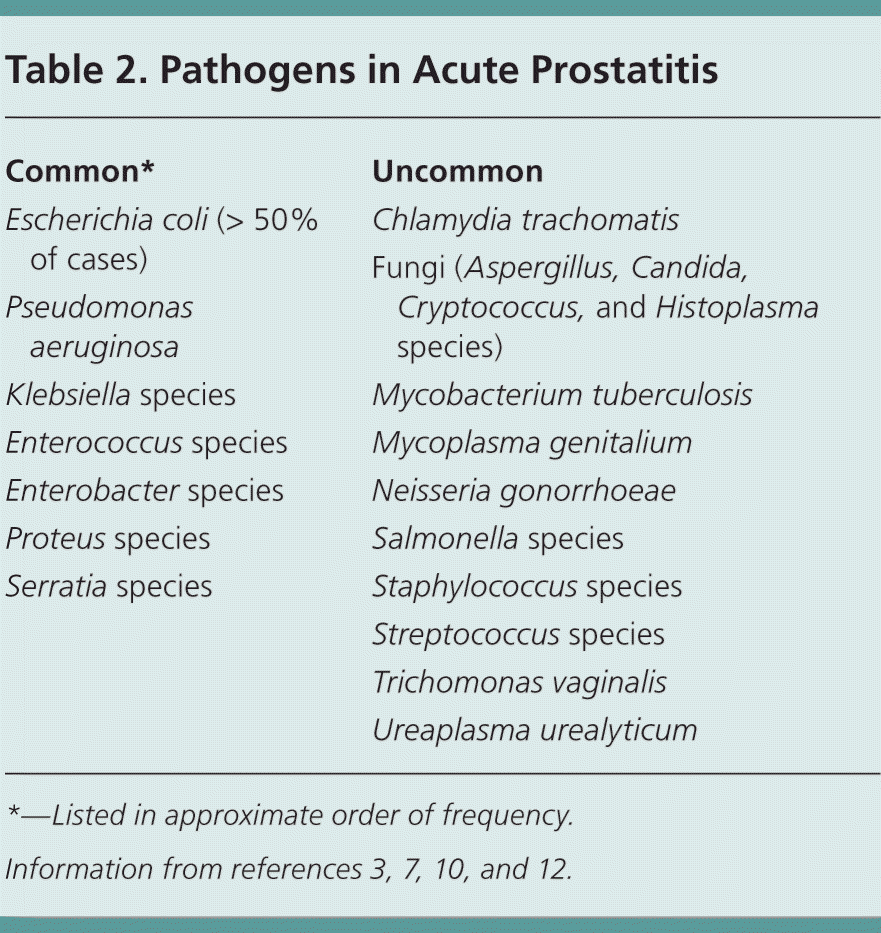
List the types of incontinence
What are stress, urge, overflow, functional, and mixed?
Most common cause of painless hematuria
what is Bladder cancer ?
3 most common symptoms of BPH
What is increased frequency/urgency, nocturia, difficulty initiating urine stream or weak stream?
List 2 features that differentiate a simple and complicated UTI
fever/chills, flank pain, costovertebral angle tenderness, and nausea/vomiting; symptoms beyond the bladder 
Common physical exam finding in prostatitis
What is a distended bladder, CVA tenderness, tender/enlarged/boggy prostate?
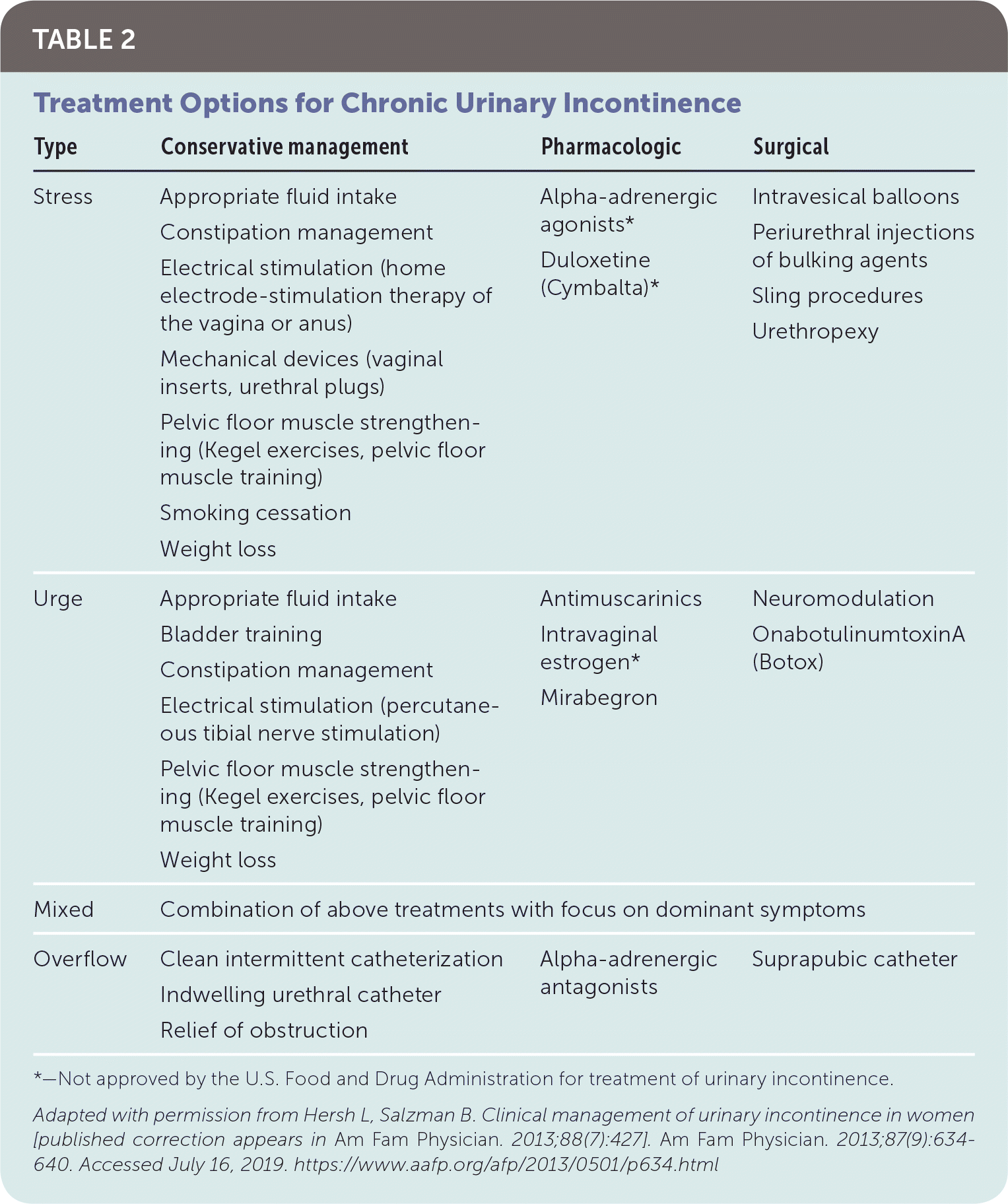
Patient presents for follow up of sudden, intense feelings of needing to urinate, and occasional leaking of urine. You recommended her to try the following for conservative managment
What is bladder training, appropriate fluid intake and starting pelvic floor PT?
This is urge incontinence. Medical management can include Antimuscarinics or mirabegron. Surgical procedure could include botox injections
Name two common causes of painful hematuria
What is UTI, trauma, kidney stone?
List 2 Lifestyle interventions for BPH
What is Limiting fluids prior to bedtime & Limiting diuretics like caffeine/alcohol ?
Patient is diagnosed with a UTI, urine culture grows >500k e. coli. List 2 possible antibiotics for outpatient management
What is Nitrofurantoin or TMP-SMX?
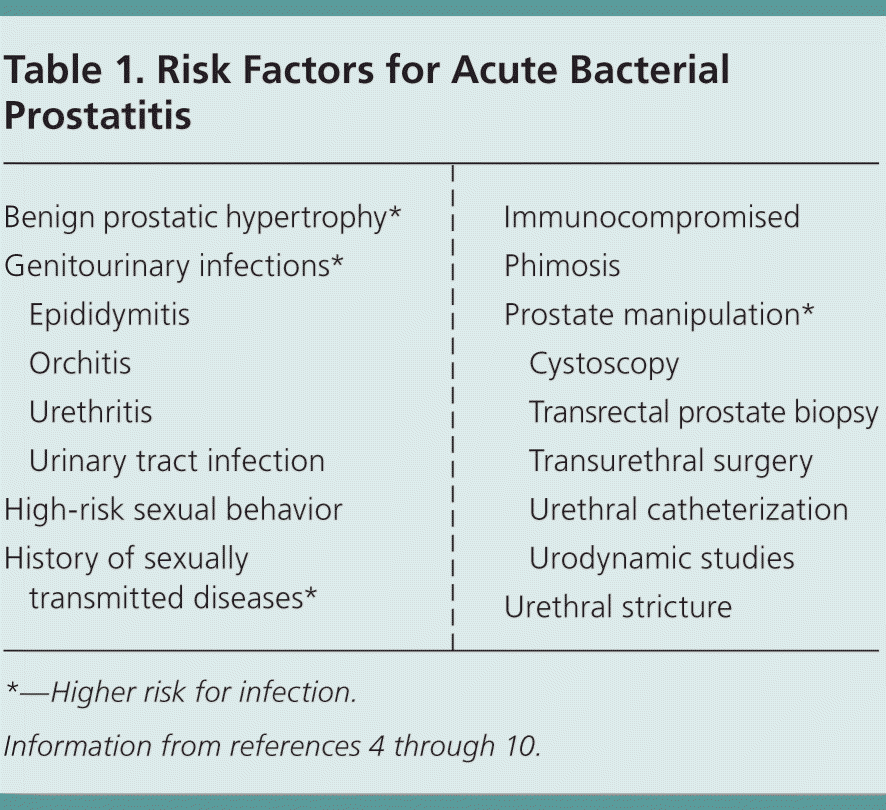
List 3 risk factors for acute bacterial prostatitis
What is having BPH, GU infection (UTI, urethritis, orchitis, epididymitis), hx of high risk sexual behavior or STI, immunocompromised, recent procedure (catheterization, cystoscopy, prostate biopsy)?
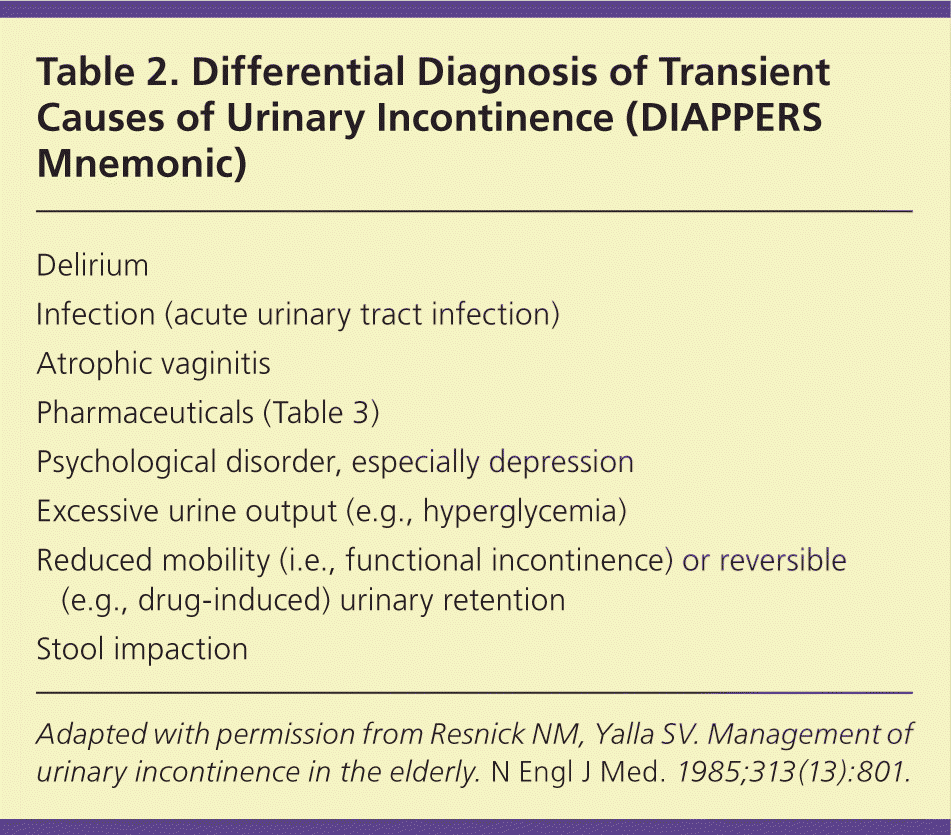
List 3 transient causes of urinary incontinence
What is delirium, infection (UTI), atrophic vaginitis, stool impaction, reduced mobility, meds, psych disorders (depression) ?
Name the first line test when working up hematuria
What is Urinalysis with microscopy?
Name a class of medication and an example that is used to treat BPH symptoms
What is Alpha blockers (tamsulosin, doxazosin) or 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (finasteride) or anticholinergics (oxybutynin)?
88 yo F with PMHx of poorly controlled diabetes and a chronic indwelling catheter, coming from a nursing facility, presents to the ER meeting sepsis criteria and is acutely altered. UA was consistent with infection and thought to be the source. List the antibiotics the ER should start her on before admitting to medicine
What is Cefepime or Zosyn and Vancomycin?
This patient has several risk factors for both pseudomonas and MRSA UTI due to the indwelling catheter, diabetes, and coming from a facility
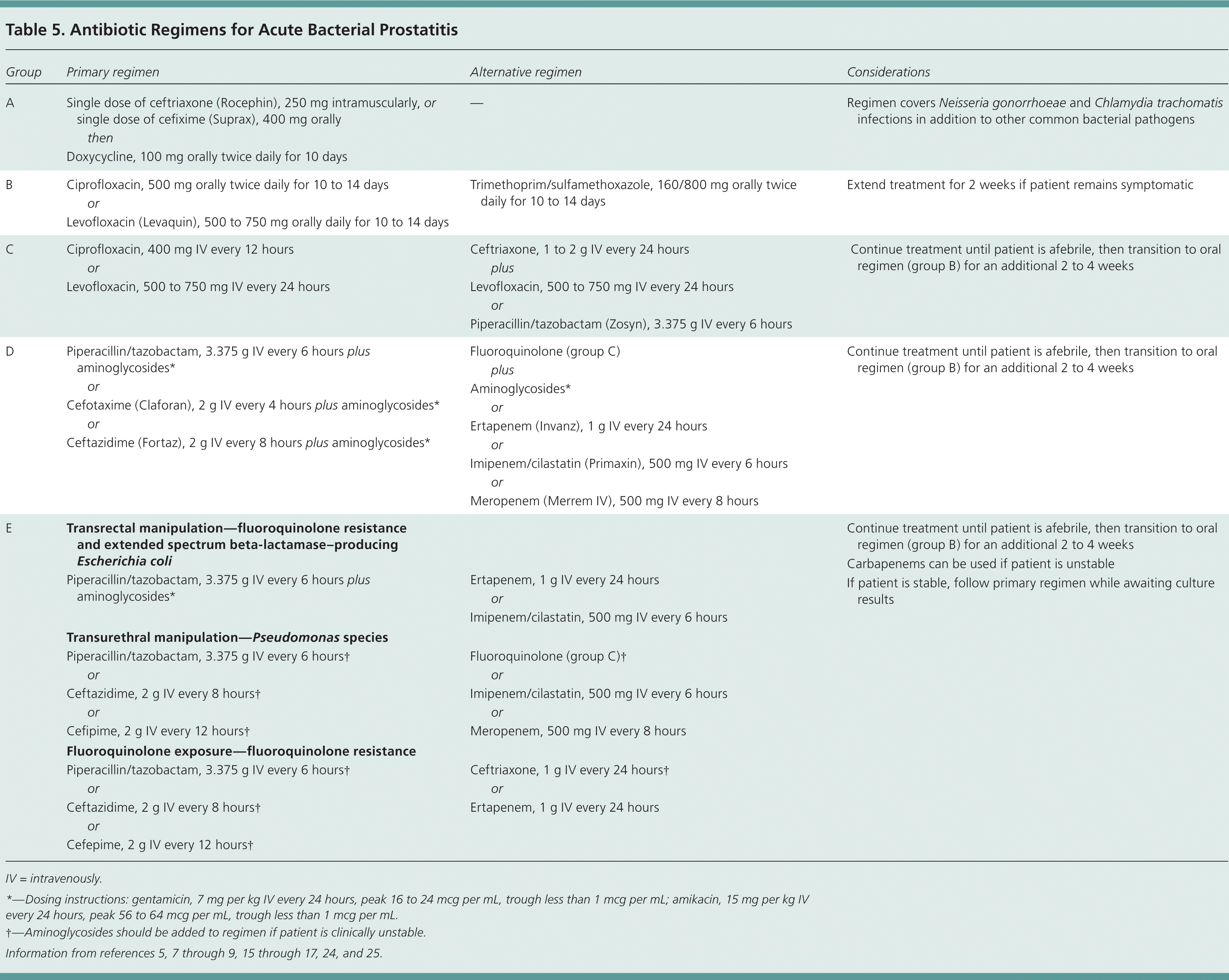
List 3 common antibiotics used to treat acute bacterial prostatitis as an outpatient
What is TMP-SMX, Doxycycline and Ciprofloxacin? Can use a dose of IM Ceftriaxone depending on risk factors
Patient presents for a follow up appointment regarding complaints of leaking urine with coughing, laughing or sneezing. At her last appointment you recommended pelvic floor PT, monitoring fluid intake, and managing constipation. She has done these and has noticed some improvement but would like to discuss other options. Possible next steps include
What are vaginal insert (pessary) or surgical intervention such as a sling procedure or urethropexy?
This is stress incontinence.
Definition of hematuria on UA (# of RBC)
What is >3?
Name 2 classes of medications that can cause lower urinary tract symptoms in men
What are antihistamines, decongestants, diuretics, opioids, TCAs?
Medical conditions include: bladder cancer, prostate cancer, CHF, diabetes, Parkinson's disease
List two situations you consider screening for & treating asymptomatic bacteriuria
Pregnancy, urologic procedures that are expected to result in mucosal bleeding, and recent renal transplantation are situations in which it may be reasonable to screen for and treat asymptomatic bacteriuria
Threshold is >100k on two separate occasions outside of the above populations
A patient was treated for bacterial prostatitis with Cipro 500 mg BID x 10 days. They present back to the office after completion and are still reporting symptoms of urinary frequency and suprapubic pain. The next best step is
What is extending the antibiotic course for 14 more days?
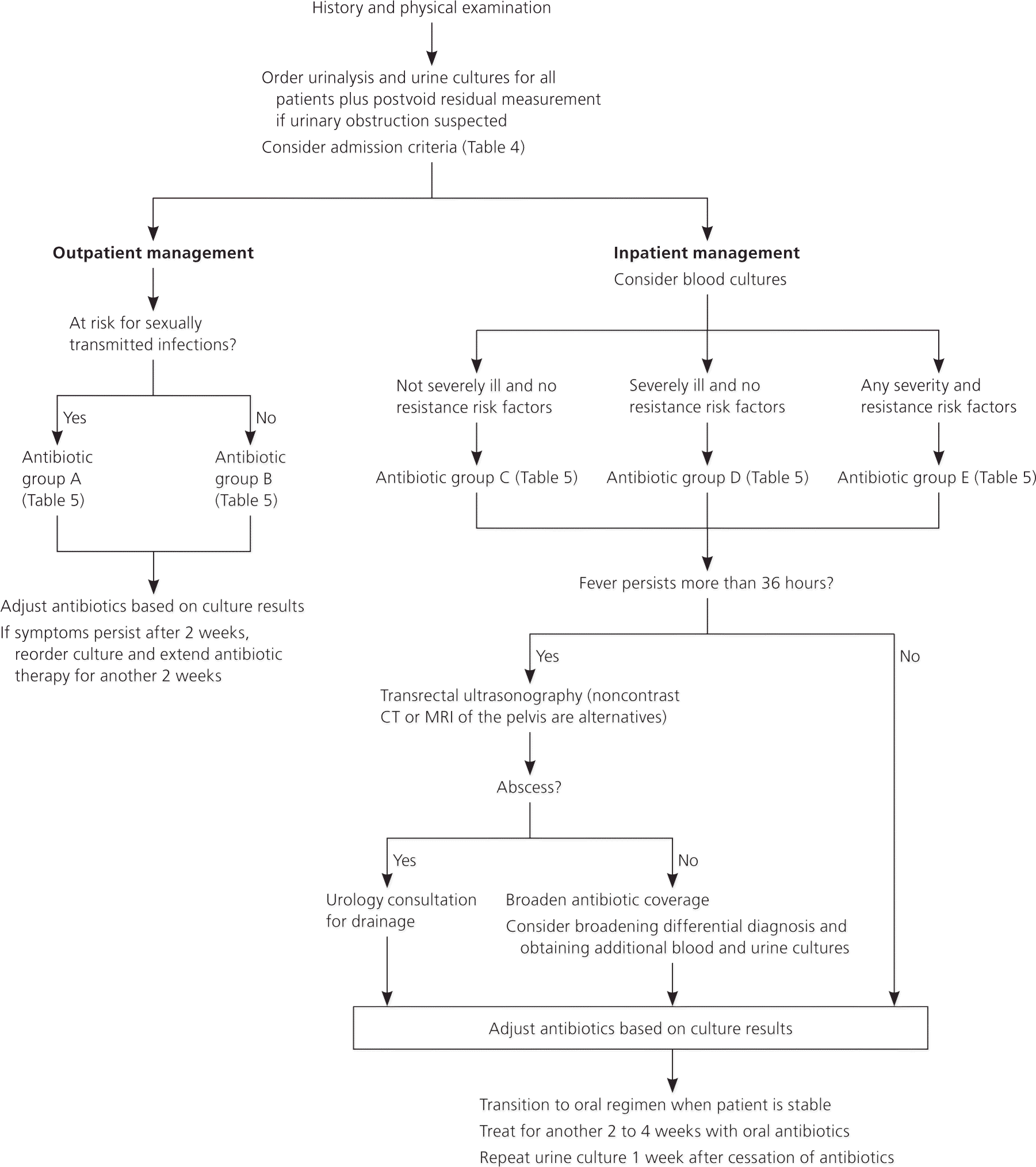
The duration of antibiotic therapy for mild infections is typically 10 to 14 days (with a two-week extension if the patient remains symptomatic), or four weeks for severe infections. Febrile patients should generally become afebrile within 36 hours of starting antibiotic therapy. Otherwise, imaging with transrectal ultrasonography, CT, or MRI is required to rule out prostatic abscess. (From AAFP article Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: Diagnosis and managment)
Name 3 commonly used classes of medications that can contribute to urinary incontinence
What are ACEi, diuretics, CCB, alpha blockers, opioids, muscle relaxers, antidepressants, sedatives, antihistamines, anticholinergics?

A patient has gross hematuria and UA and culture are consistent with infection. After treating the UTI, list the next best step
What is repeating a UA with micro at 6 weeks?

75 yo male with hx of BPH that has been managed with tamsulosin and finasteride presents to the office with persistent symptoms despite maximizing medical therapy options. He has now been hospitalized twice for urinary retention. The next best step in management is... (Bonus points available)
What is referral for surgical intervention?
Bonus points for knowing TURPS.
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is considered the benchmark for surgical therapies
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2008/0515/p1403.html#afp20080515p1403-t4