a single species that has a powerful influence on community structure where changes in its population size dramatically change the entire ecosystem
keystone species
what is found at the base/bottom of a food chain
producers
what is Nitrogen Fixation
nitrogen gas in atmosphere to ammonia (bacteria in soil, lightning)
when farmland turns into desert
desertification
what are the two types of energy/resources
renewable and nonrenewable
a cooperative relationship in which both species derive some benefit
mutualism
what is the difference between a food chain and food web
a food chain shows one possible path of energy flow, the food web shows all of the possible paths for energy flow
water evaporation from the leaves of plants
transpiration
Removal of an entire forest is called _______________________
The type of forest that can NOT grow back after logging.....
Deforestation......Tropical forests can not grow back
variety of environmental conditions within which it can survive and reproduce
Tolerance
Define resource partitioning
when the similar species coexist but each species only uses part of the available resources
what is the original source of energy for almost all ecosystems
the sun
these two processes go back in forth, one making energy and producing CO2, the other creating glucose and O2. also, which cycle is this a part of?
cellular respiration and photosynthesis
the Carbon Cycle
what percentage of earths water is fresh water? and where is most of it found
3% and it is mostly found in ice at the poles
76% of the atmosphere is this gas
Nitrogen
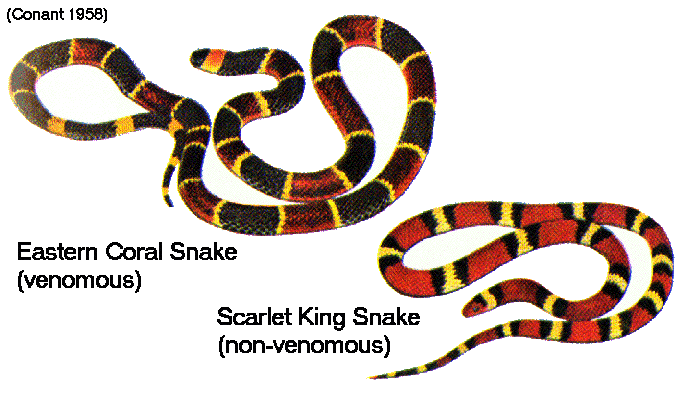 what is this an example of
what is this an example of
mimicry
only _________% of energy is moved up to the next trophic level
10%
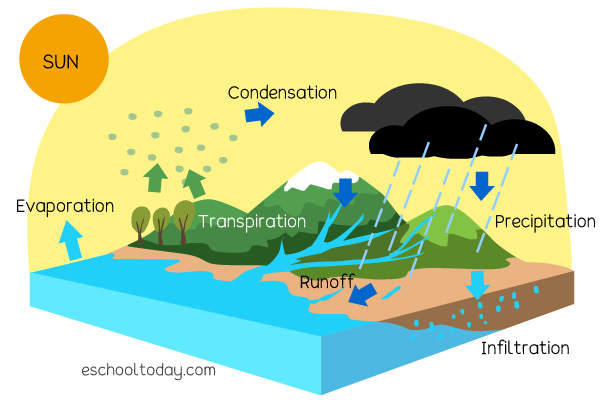
draw a labeled diagram of the water cycle
what are some negative affects of acid rain
kills plants, damages leaves, changes chemistry of the soil and surface water, erodes stone/rock
causes system to change further in the same direction
positive feedback loop
What are the 5 major types of species interactions
Predation, Parasitism, Competition, Mutualism, Commensalism
If there are 10,000 kilocalories in the grasses (producers) how many kilocalories would there be in the secondary consumer?
100 kilocalories
too much Nitrogen running off into water causing algae blooms resulting in die offs.
Eutrophication
what are 5 of the 8 threats to biodiversity
Habitat destruction/deforestation
introduced/invasive species
genetic pollution
over exploitation
hybridization
climate change
diseases
human over-population
what is the law of conservation of matter
and the 1st law of thermodynamics
mass/matter can not be created nor destroyed
Energy is neither created nor destroyed