An interaction between two different organisms living in close physical association
What is Symbiosis?
The first level of any trophic level are _______ and produce energy through_____
What are producers and photosynthesis?
The idea that moderate levels of disturbance contribute to greater species diversity
What is the Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis?
The _______ and _______ of an island affect the species richness on that island.
What are the size and distance from the mainland?
Pathogens cause
What is disease?
The relationship between a tapeworm and a dog
What is parasitism?
Herbivores are classified as ______ consumers
What is primary?
The _______ and _______ of a species affect the diversity within communities.
What are numbers and relative abundance?
Images 2-5 can be considered __________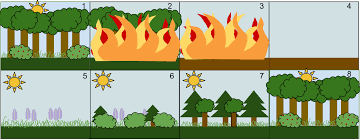
What is Secondary Succession?
Pathogens affect oceanic ecosystems, terrestrial ecosystems and ______
What is humans?
A hermit crab taking up residence in an empty seashell fall under this symbiotic relationship
What is commensalism?
As energy moves up the pyramid ___% is lost as ____ energy.
What are 90% and heat?
Two things commonly found in a highly diverse community are
What are high productivity, ability to withstand and recover environmental stresses, high biomass productivity, higher resistance to invasive species, etc.?
An 800-acre plot of land was found to have over 50 species of ants while a 200-acre of land had only 25 this falls under the __________ pattern of species richness.
What is the Species-Area Curve?
Example of disease caused by pathogen used in the powerpoint
What is Swine Flu?
The gut flora (bacteria) which live in the human gut and humans have a __________ relationship
What is Mutualism or Commensalism?
Consider a food web with the tertiary consumer being an otter. A decrease in the otter population causes an increase in the secondary consumers' population. This is classified as a ______ control system.
What is a Top-Down Control system?
Size and distance from mainland affect rates. Small: _____ immigration, _____ extinction. Closer islands have _____ immigration, _____ extinction.
What is lower, higher; higher, lower?
List at least 4 human activities that disturb the diversity of an ecosystem
What are overfishing, agricultural practices, genetic modifications, clear-cutting, mining, deforestation, etc.
Viroids and prions are infectious ________ and ______, respectively
What is RNA molecules and proteins?
Predation and mutualism both differ in their effects on species because
What is predation only benefits the predator while the prey is hurt (+/-) and mutualism benefits both (+/+)?
Secondary consumers on a 5 level pyramid receive ___% of energy.
What is 1%?
Two factors that would explain why species diversity is greater in tropical regions are
What are tropical regions have had a long time to evolve, large solar energy inputs, larger water availability, and large amount of precipitation?
High and levels of disturbance reduce species diversity by
What is kill off many of the species and leave behind few tolerant?
A disease-causing agent that is transmitted to humans from other animals
What is Zoonotic Pathogens?