Describe the pathway of the electrical impulse that creates a heartbeat.
sa node, av node, bundle of his, bundle branches, purkinje fibers
Leads V3 and V4 correlate with what part of the heart?
What is anterior?
Leads V1 and V2 correlate with what part of the heart?
What is septal?
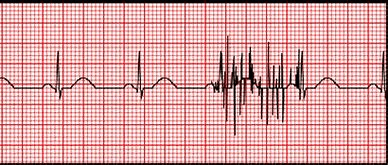
What is NSR with artifact?
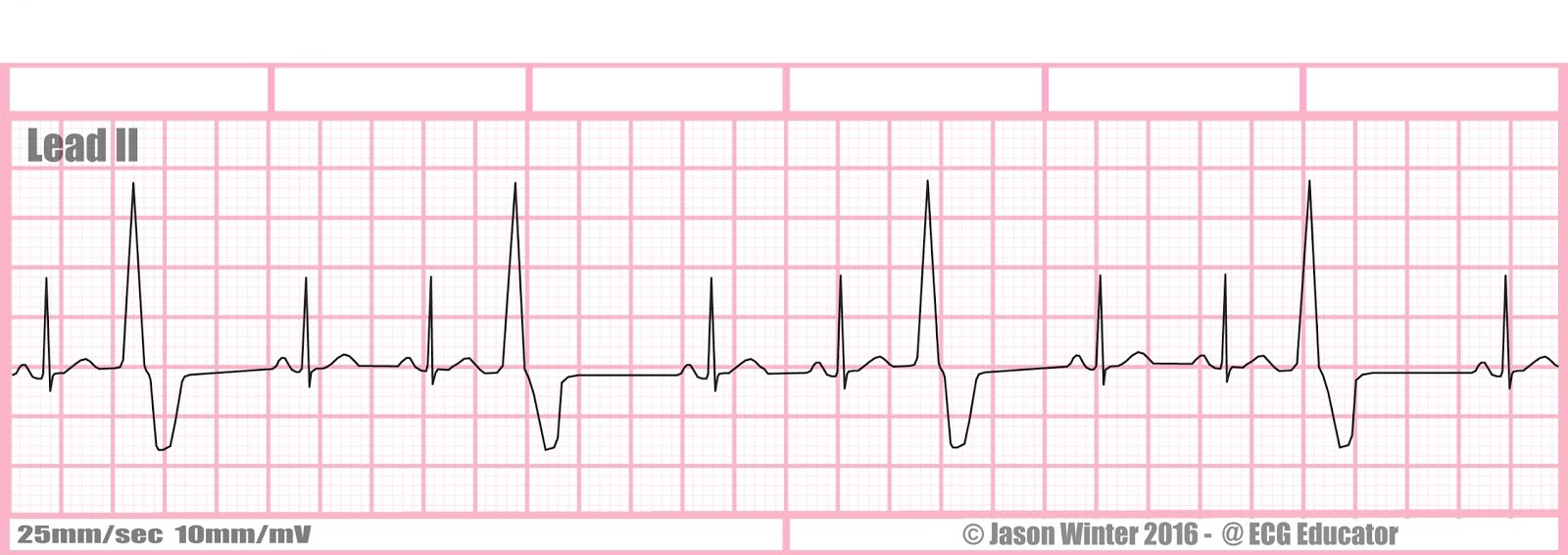
What is ventricular trigeminy?
Tx?
▪Premature ventricular complexes (PVCs) result from increased irritability of ventricular cells
▪Premature ventricular contractions are common, and their frequency increases with age
▪They may be insignificant or may occur with problems such as MI, chronic heart failure, chronic COPD, anemia, low potassium or magnesium
▪Drugs, stress, nicotine, caffeine, alcohol, infection, or surgery can also cause PVCs, especially older adults
▪Post-menopausal women often find that caffeine causes palpitations and PVCs
▪If there is no underlying disease, PVCs are usually not treated other than eliminating the cause
▪If the number of PVCs in a 24 hour period is excessive, the pt may be placed on a beta blocker
Describe the basic components of an ECG strip.
p wave- atrial depolarization
qrs complex- ventricular depolarization
t wave- ventricular repolarization
Leads I, aVL, V5, V6 correlate with part of the heart?
What is lateral?
What is the normal PR interval?
3-5 small squares
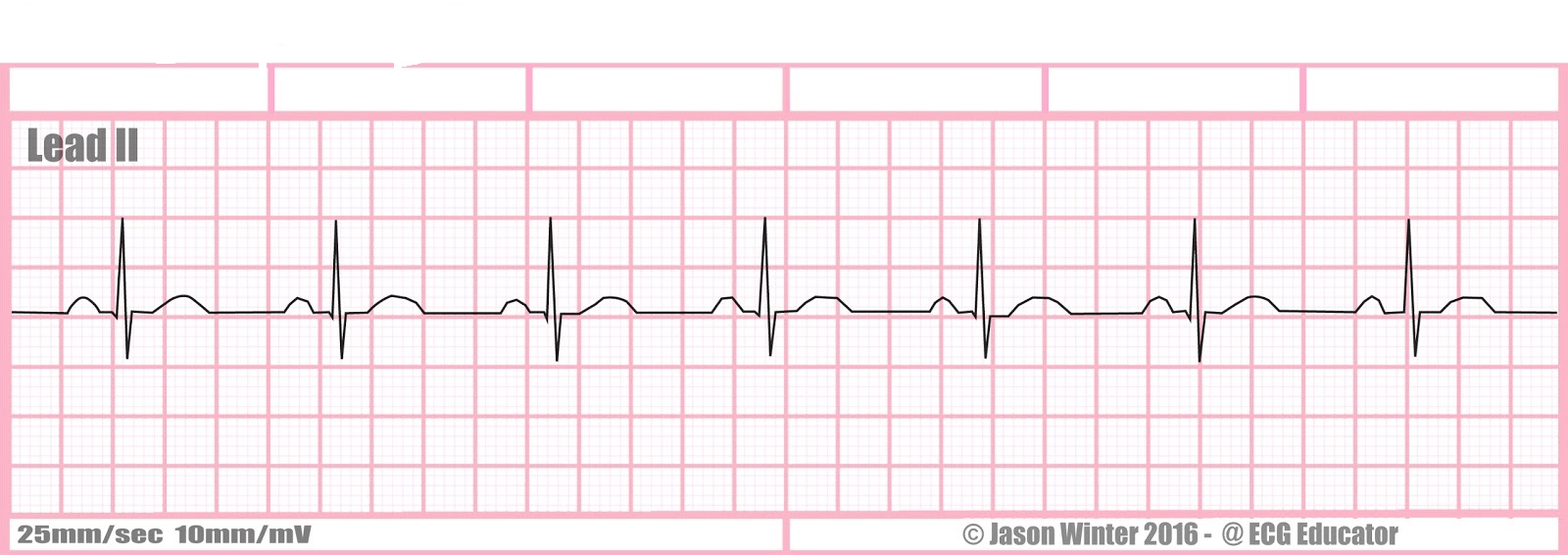
What is normal sinus rhythm?
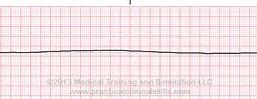
What is asystole?
High quality CPR, epinephrine 1mg q 3-5 minutes
Consider causes (H's and T's)
A-
C, C-
E-
automaticity
conductivity, contractility
excitability
What ECG findings can be seen with a myocardial infarction?
inverted T waves, pronounced Q wave, ST depression or elevation
What is the normal QRS complex duration?
0.06 to 0.10 seconds
wide complex- v tachs
narrow complex- svt
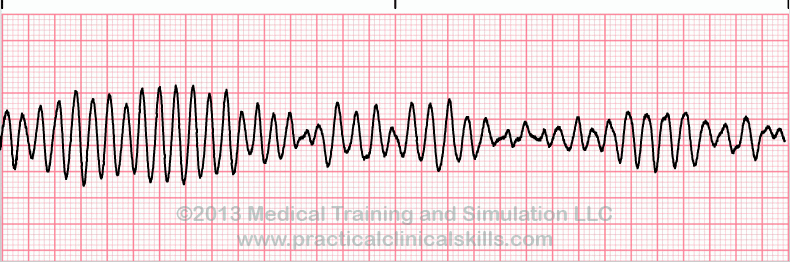
What is torsades?
What is the treatment for torsades?
Magnesium 1-2 grams iv in 30-60 seconds, can be repeated in 5-15 minutes
or continuous infusion 3-10 mg/min
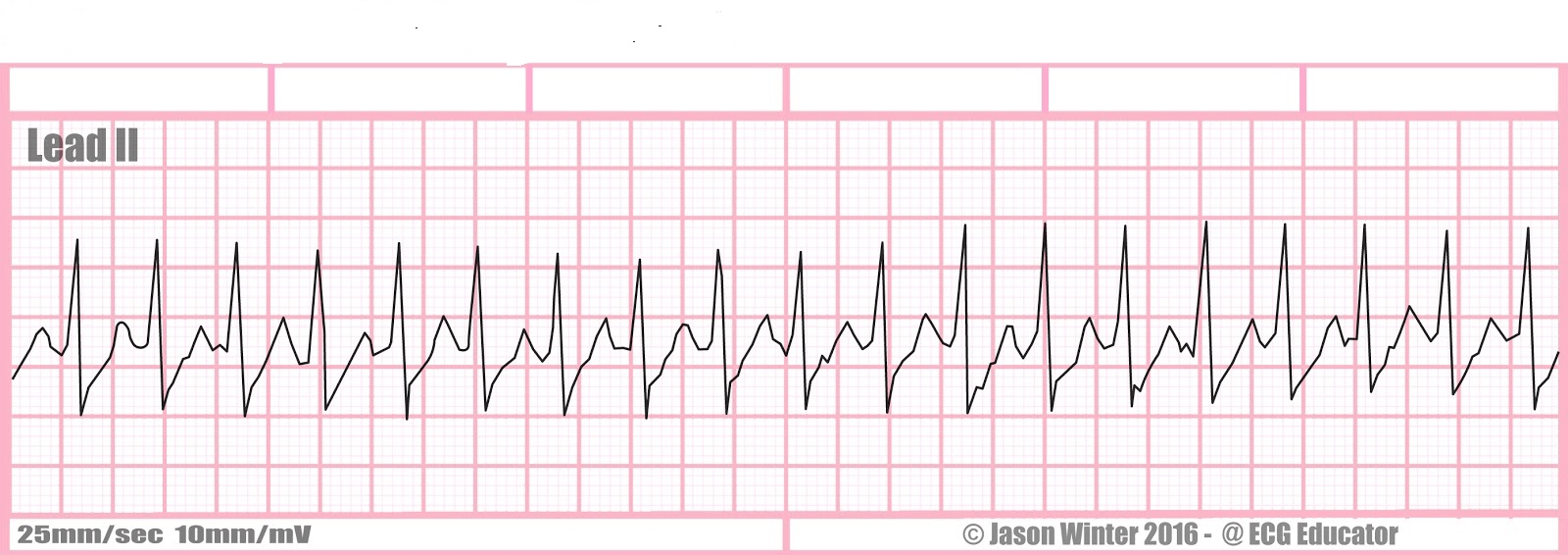
What is supraventricular tachycardia? (SVT)
nonsymptomatic: vagal maneuvers, adenosine 6mg rapid iv push elevated arm, followed by rapid ns flush, may repeat 12 mg IVP
symptomatic: synchronized cardioversion
What is inferior?
What parts of the heart has infarction occurred?
When is ST depression or elevation significant?

septal and anterior
▪ST elevation or depression is significant if displacement is 1mm (one small box) or more above or below the line and is seen in two or more leads
What could the presence of a U wave indicate?
What do depressed T waves usually indicate?
What do peaked T waves usually indicate?
hypokalemia
hypokalemia
hyperkalemia
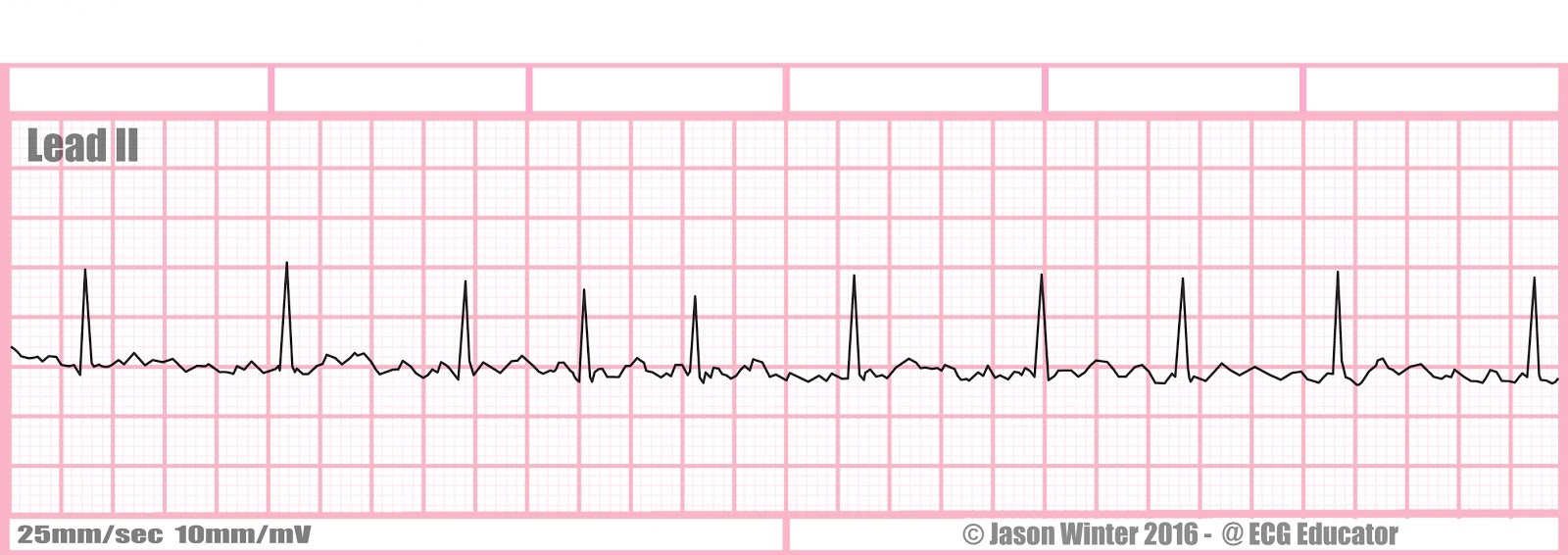
What is atrial fibrillation?
What are pts with atrial fibrillation at risk for?
heart failure and thrombotic events
tx: symptomatic: synchronized cardioversion
▪Treatment
▪Antidysrhythmic drugs: Calcium channel blockers (Cardizem)
▪Beta blockers (metoprolol)
▪Digoxin
▪Rhythm control medications
▪Anticoagulants: warfarin (Coumadin), NOAC (novel oral anticoagulants)
▪Dabigatran (Pradaxa), oxaban (Xarelto), apixaban (Eliquis)
▪Only drug with antidote is Pradaxa (Praxbind)
▪Electrical Cardioversion- may be performed to restore NSR in a hospitalized pt with new onset AF
▪Left Atrial Appendage Closure- for pts who are at high risk for stroke and are not candidates for anticoagulation
▪Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation- waves are delivered to abolish the bad pathway
▪Biventricular Pacing- increase ventricular function to help pts who have AF and heart failure
▪Maze Procedure- open procedure, surgeon places maze of sutures in strategic places to get rid of bad conduction pathway
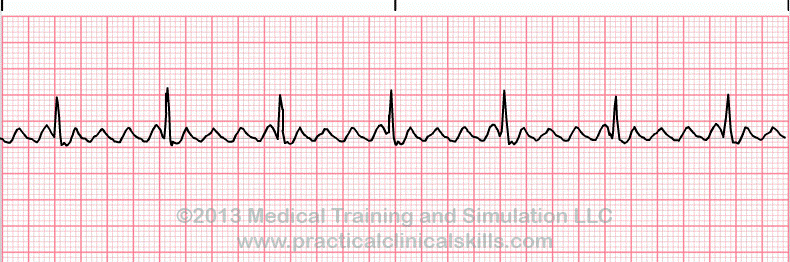
What is atrial flutter?
tx: same as atrial fibrillation!!!! :D
▪It results from changes in intrathoracic pressure during breathing
▪The heart rate increases slightly with inspiration and decreases slightly during expiration
▪This “irregular” rhythm is frequently observed in healthy adults
▪Has all the characteristics of NSR expect for a difference of no more than 3 small blocks in the PP or RR intervals
What is a sinus arrhythmia?
A large determinant for treatment of dysrhythmias is whether or not the patient is symptomatic. Name at least 5 symptoms indicating the patient is "symptomatic"
▪Chest discomfort, pressure, or pain, which may radiate to the jaw, back, or the arm
▪Restlessness, anxiety, nervousness, confusion
▪Dizziness, syncope
▪Palpitations (in tachydysrhythmias)
▪Change in the pulse strength, rate, and rhythm
▪Pulse deficit (difference in apical/peripheral pulses, assess both for a full minute)
▪Shortness of breath, dyspnea
▪Tachypnea
▪Pulmonary crackles
▪Orthopnea
▪S3 or S4 heart sounds
▪Jugular venous distention (JVD)
▪Weakness, fatigue
▪Pale, cool, skin; diaphoresis
▪Nausea, vomiting
▪Decreased urine output
▪Delayed capillary refill
▪Hypotension
Name the 8 steps to interpret an ECG strip
1. Determine the HR
2. Determine the rhythm (ventricular and atrial)
3. Analyze the P waves
4. Measure the PR interval
5. Measure the QRS duration
6. Examine the ST segment
7. Assess the T wave
8. Measure the QT interval
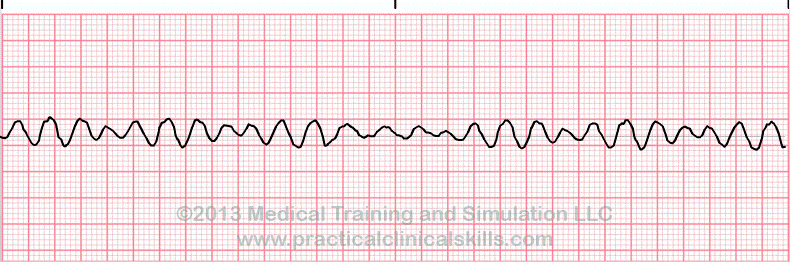
What is ventricular fibrillation?
tx; vfib dfib!
immediate defibrillation, high quality CPR until then
epinephrine 1mg q 3-5 minutes
after the third shock: amiodarone or lidocaine 2nd line therapy
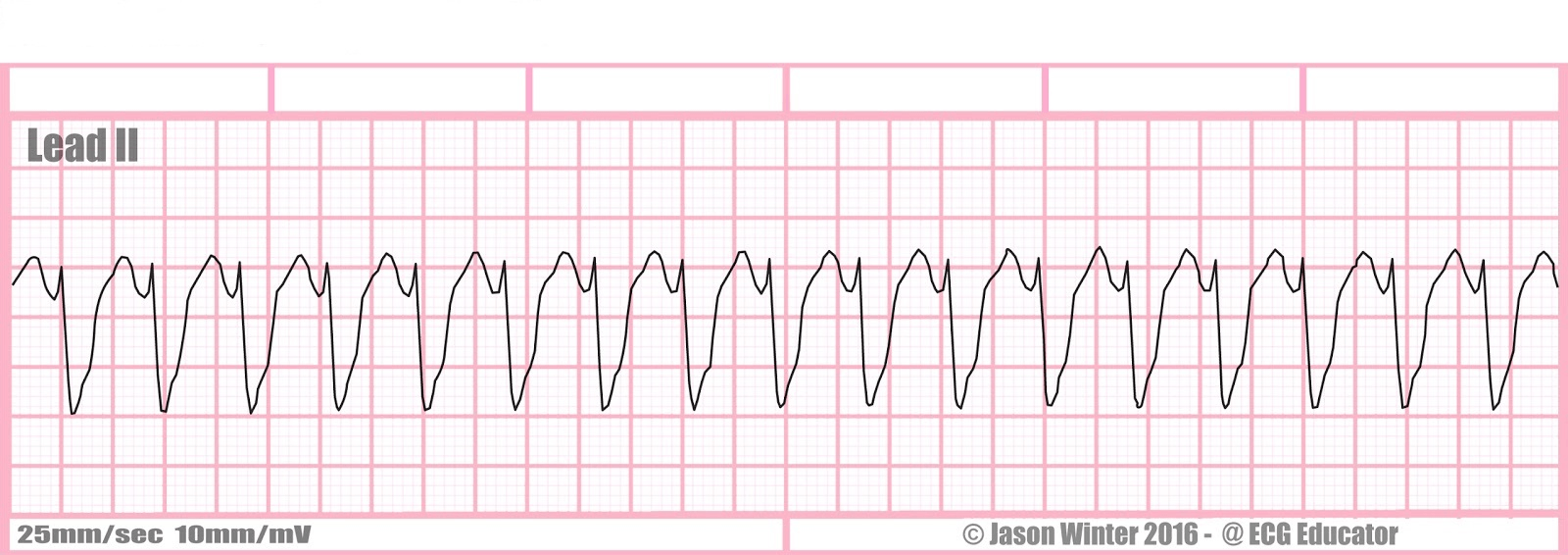
What is ventricular tachycardia?
tx: palpate for a pulse to ensure it is v tach with a pulse
synchronized cardioversion
hold digoxin 48 hours before cardioversion of any kind
medications: Procainamide 20-50 mg/min until dysrhythmia depressed, hypotension ensues, QRS increases > 50% or maximum dose of 17 mg/kg is given, maintenance infusion 1-4 mg/min
Amiodarone: First dose: 150mg over 10 minutes, repeat as needed if VT recurs. Follow by maintenance infusion of 1mg/min for first 6 hours
Sotalol: 100 mg over 5 minutes, avoid if prolonged QT interval