TBI is the acronym for this:
"What is" Traumatic Brain injury
SRC is the acronym for this:
What is Sport related Concussion
SCAT in the acronym for this:
What is Sport Concussion Assessment Tool

MOI is the acronym for this:
What is Mechanism of Injury
RTP is the acronym for this:
Return to play
This is the injury that can occur when young athletes return to play before the first concussion resolves.
Second Impact Syndrome
The name of a nerve CELL
Neuron!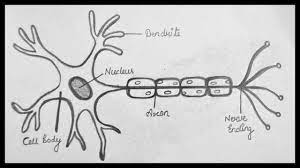
This is the number of minimal days before a competition once a concussion diagnosis occurs
What is: 7
This is the approximate time it takes for someone to fully recover from a sport concussion.
What is: 10-14 days
CTE is the acronym for:
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
T/F: SRC can often have delayed symptoms, especially in youth
TRUE
T/F SRC is a structural injury
False! (A sport Concussion is a functional injury, not structural- so you wouldn't see any structural damage in an MRI or microscope)
T/F Most sport concussions result in an LOC
False: only about 10% of SRC result in an LOC
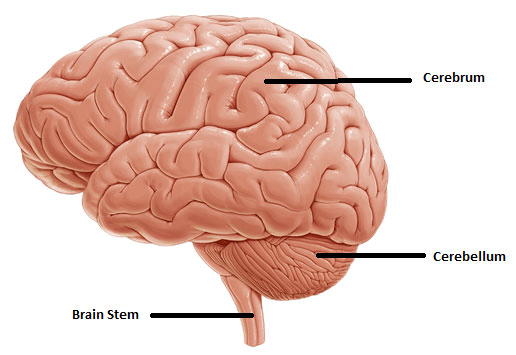
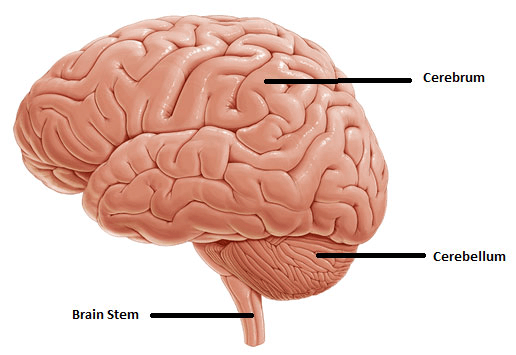
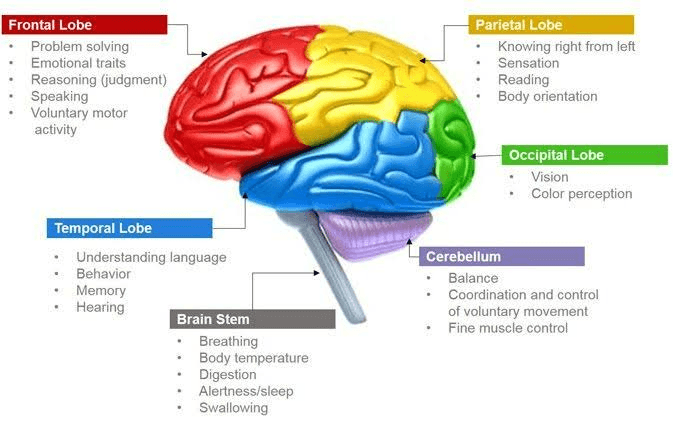
The largest Part of the Brain is called the:
Cerebrum
This is the definition of a SYMPTOM
What is: how the person feels (what they report to you)
This is the definition of a SIGN
What is: something you can see/observe/measure
LOC is an acronym for:
what is Loss of Consciousness
Sy/Sx of a Second Impact Syndrome
 These are the RED FLAGS we look for post head trauma: worsening headache, projectile vomiting, + PERL (pupil size), seizure, weakness in limbs, LOC, increased confusion....
These are the RED FLAGS we look for post head trauma: worsening headache, projectile vomiting, + PERL (pupil size), seizure, weakness in limbs, LOC, increased confusion....
RTL is the acronym for
Signs of a sport related concussion:
a. Balance problems
b. Memory Problems
c. Personality Changes
d. All of the above
d. All of the above are SIGNS (clues the coach, parent, AT can SEE, measure, observe)
The part of the brain most associated with Balance
a. Cerebrum
b. Cerebellum
c. Brain stem
b. Cerebellum
These are some "Dont's" of a sport concussion
Don't:
Drive/ride bikes
Take IBProfen before cleared by MD
go to school if you have severe symptoms
play video games
participate in physical activity if symptomatic
A (medical) term for "Bloody Tumor"
HEMATOMA!
Heme= blood
toma=tumor

Hemorrhage refers to:
Escape of Blood from a vessel
Heme= blood
Rhage= a break/burst
When a player shows any symptoms or signs of an SRC (Sports Related Concussion), the player should... (Give a brief description of two)
examples:
be removed from play
perform SCAT 5, VOMS
Be evaluated by a physician or other licensed healthcare provider.
NOT be left alone after the injury.
be monitored for signs of deterioration (red flags)
T/F Each stage of the RTP requires a minimum of 48 hour period in between them
False: the consensus statement requires a minimum of 24 hours in between each stage of RTP
This is the purpose of baseline testing (of SCAT or Neuropsych test)
A baseline gives a personal comparison of an athlete pre and post head injury.
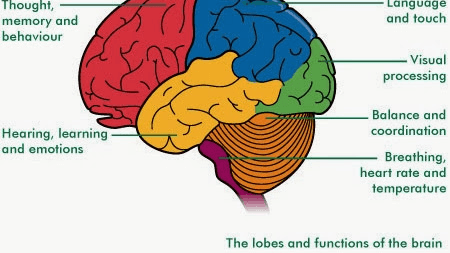
The part of the Brain associated with thoughts, memories, senses, emotions and critical thinking skills:
a. Cerebrum
b. Cerebellum
c. Brain stem
a. Cerebrum
Multiple choice: The time frame for RTP may vary with
a. player age
b. history (# of previous concussions)
c. level of sport
d. All of the above
D. All of the above can affect a person's RTP timeline
This is the strongest indicator of slow recovery in individuals after a sport related concussion
What are: The severity of a person's initial symptoms (of the first few days)
T/F: Subdural hematomas are generally associated with a skull fracture
False: subdural hematoma- blood clot under the dura is associated with closed head injury
This is the CA assembly Bill that specifically addresses SRC in youth sports.
What is CA AB 2007
These are the 4 steps to the Graduated Return to school strategy post SRC:
1. daily activities at home
2. school activities like HW, reading
3. Return to school part time
4. Return to school full time
These are the MOI of SRC
direct mechanical force to the head/body OR indirect blow, causing an impulsive force to the head
(ie: blow to the head or body)
Part of the Brain associated with vital signs- heart rate, breathing, temperature, etc:
a. Cerebrum
b. Cerebellum
c. Brain Stem
C. Brain stem!
These are the RED FLAGS of TBI: (be able to name 3)
what are: Headache that worsens; seizure; numbness in limbs; repeated vomiting; Changes in vision, LOC/ALOC, can't recognize people or places; drowsy/can't be awakened; unusual behavior/ increased confusion; slurred speech; drainage of blood/fluid from ear/nose; loss of bladder/bowel control
Name the 7 RTP steps post SRC
1. rest/ daily activities
2. light activity
3. moderate activity (sport specific)
4. Heavy Activity
5. non-contact practice
6. full- contact practice
7. contact game
True/False: Most SRC will have a NEGATIVE MRI
True. SRC are functional injuries (meaning they affect HOW the brain works) but you wouldn't see structural damage in radiologic imaging.
This is the most essential component in assessment of SCR
a. neuropsych testing
b. medical history
c. sideline evaluation
d. rest
c: sideline evaluation
Describe the similarities & differences between CTE and SIS
Similarities: head trauma, brain injury, both are structural injuries
Differences: SIS= acute, mostly young people
CTE= chronic, mostly in older
O&A x4 means...
oriented and alert to:
1. person
2. Place
3. Time
4. event
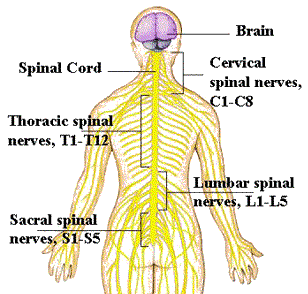
The Structure that connects the Brain to the rest of the body.
The SPINAL CORD
The Spinal Cord is the "highway" carrying nerve impulses (information) to and from the brain to the body!