In reference to hormones, what are the three broad categories of contraceptives?
(1) Non-hormonal (condoms, copper IUD)
(2) Combined Hormonal Contraceptives
- Combined oral contraceptives
- Transdermal combined patch (“Xulane”)
- Intravaginal ring (“Nuvaring” – monthly; “Annovera” – yearly)
(3) Progestin-Only Contraceptives
- Progestin only pills (POPs)
- Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA)
- Progestin implants (“Nexplanon”) - LARC
- Progestin intrauterine devices (IUD) - LARC
In a patient starting on an oral contraceptive, it is recommended to prescribe what else?
An emergency contraceptive
Provide three known side effects of ethinyl estradiol:
Nausea, bloating, migraine or vascular headaches, cyclic weight gain, irritability, cystic breast changes, breast tenderness, melasma/hyperpigmentation, telangiectasia
What is the difference between “heavy menstrual bleeding” (HMB) and “abnormal uterine bleeding” (AUB)?
- HMB = patient’s subjective experience of increased blood loss
- AUB = Clinically concerning bleeding that occurs outside of normal cyclic menstruation (terms like “dysfunctional uterine bleeding” and “menorrhagia” are no longer encouraged)
In what way is menstrual physiology different between an adolescent and a mature individual?
In the first 1-2 years, the HPO axis feedback loops may not be mature:
(1) They may not achieve the coordinated negative- and positive- feedback to achieve ovulation (= oligoovulation or anovulation)
(2) In some cases, estrogen negative feedback loop does not work properly, causing continued ovarian estrogen production, endometrial proliferation, and asynchronous shedding
What monitoring should be done after starting a combined oral contraceptive?
Blood pressure check 1-2 months after starting
Name two IUD options for emergency contraception.
Bonus point: In what time frame must the IUD be placed?
(2) Mirena (52 mg total dose, elutes at 21 mcg/day)
Bonus: IUD must be placed within 120 hours (5 days)
True or false: Combined hormonal contraceptives are associated with increased weight gain
False. Studies have demonstrated no significant correlation between weight gain and combined hormonal contraceptive use.
HOWEVER: Use of Depot-Provera is known to increase risk for excessive weight gain (between 1-14 kg)
One in ___ adolescents with abnormal uterine bleeding has an underlying bleeding disorder
One in five
In a young female, the menstrual cycle is typically expected to have an interval of ____ to 45 days.
21
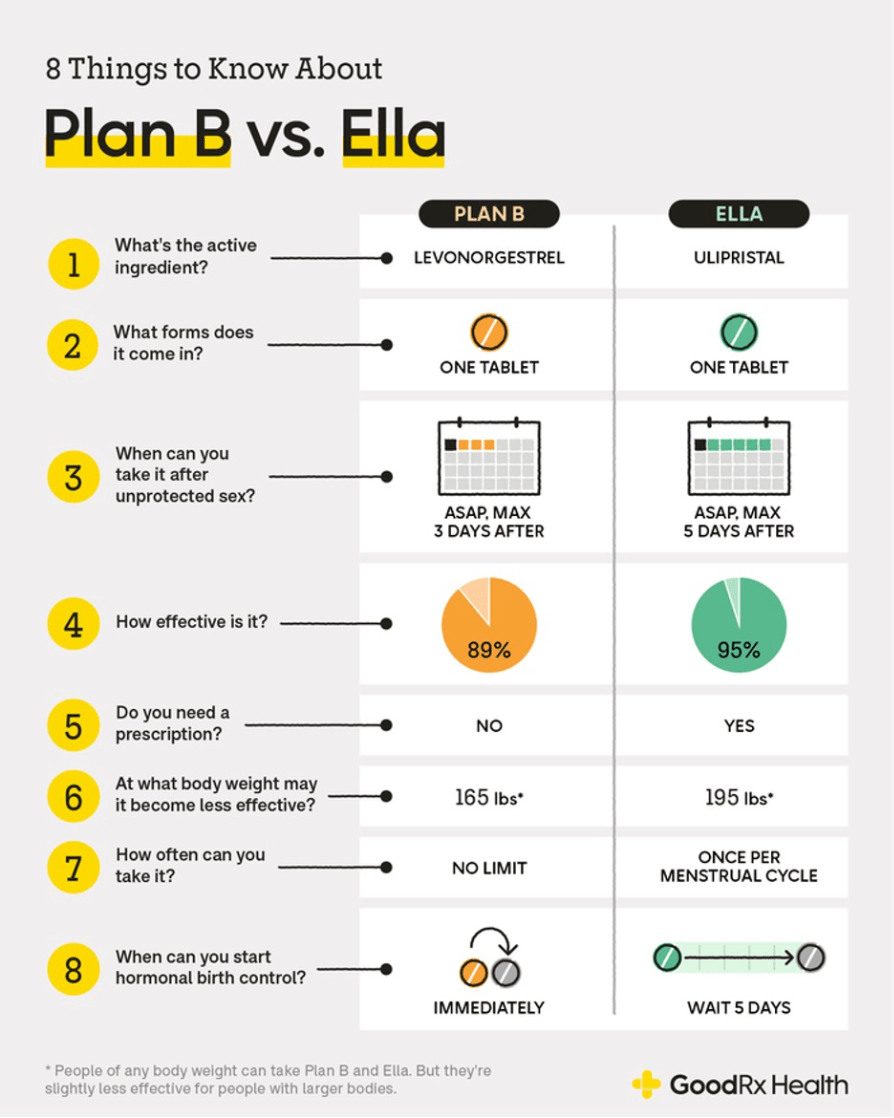
Name the two options for ORAL emergency contraception.
Bonus points: Describe the time frame in which each should be given
(1) Single dose levonorgestrel 1.5 mg (Plan B One-Step). Must be given within 72 hours.
(2) Single dose of ulipristal acetate 30 mg (Ella). Must be given within 120 hours.
**Both are FDA approved for nonprescription purchase. No medical evaluation is necessary prior to starting.
True or false: prolonged use of combined hormonal contraceptives decreases risk for ovarian and endometrial cancer
True
Unlike combined hormonal contraceptives, progestin-only contraceptives are associated with what undesirable side effect (which typically resolves within a few months)?
Irregular bleeding
What laboratory work up should be considered in the patient with abnormal uterine bleeding?
- Pregnancy test, CBC, thyroid studies, iron studies. In the patient with heavy bleeding, one should also pursue coagulopathy work up including PT, PTT, von Willebrand factor and consider additional clotting factor work up.
- Depending on the clinical scenario, one can also consider STI testing, prolactin, total and free testosterone, 17-hydroxyprogesterone, DHEAS, FSH, LH, and estradiol.
- Fun fact: When should von Willebrand assay be collected?
What should the menstrual history include?
- Age at time of menarche (including time of year)
- Shortest and longest duration between cycles
- Shortest and longest duration of bleeding
- Presence/absence and characterization of premenstrual symptoms
- If bleeding pattern has changed over time
- Relative volume of menstrual flow (and if there are blood clots)
- Do accidents occur? (bleeding through clothes or bedsheets)
When should a combined oral contraceptive be started to provide the most effective contraception?
Bonus points if you can describe the additional counseling to give if COCs are started at other times during the cycle
Ideal to start on the first day of menstruation. This confers immediate contraceptive efficacy
Bonus: Some patients prefer a “Sunday start” method (first Sunday after starting to menstruate) or “quick start” method (anytime during the cycle). In these cases, a backup contraceptive method should be used for one week.
What two methods of contraception are considered first line per the AAP for contraception in sexually active adolescents? (the answer does not include condoms)
Long Acting Reversible Contraceptives:
(1) Sub-dermal implants (Nexplanon)
(2) IUDs
True or false: IUDs increase risk for pelvic inflammatory disease
False, unless inserted during a period of active infection.
Other important misconceptions about IUDs:
- If exposure to gonorrhea or chlamydia occurs after insertion, treatment can occur without need for IUD removal
- IUDs do not increase risk of infertility
What are some things you are looking for on a pelvic ultrasound in a patient with abnormal uterine bleeding?
- Uterine lining thickness (is there hyperplasia?)
- Uterine abnormalities (fibroids, polyps, congenital abnormalities)
Name at least 3 conditions should you assess for in the patient with abnormal uterine bleeding:
- Evidence of anemia: Fatigue, lightheadedness, tachycardia, headaches, PICA, syncope
- PCOS (hirsutism, acne, weight gain, HS, acanthosis nigricans, fam hx of diabetes or infertility)
- Thyroid disease (weight changes, hair loss or changes, constipation, palpitations, cold or heat intolerance)
- Bleeding disorders (epistaxis, gingival bleeding, easy bruising, bleeding issues with surgery, family history of abnormal bleeding)
- Cervicitis (vaginal discharge or odor, pain with intercourse, postcoital bleeding, fever, pelvic pain)
- Hypothalamic amenorrhea (psychosocial stressors, disordered eating, wt loss, intensive athletics)
- Hyperprolactinemia (breast discharge, headache, peripheral vision loss)
How do combined hormonal contraceptives prevent pregnancy by what methods? (name 2)
- Inhibits the mid-cycle gonadotropin surge that triggers ovulation (this varies from progestin-only methods, where inhibition of ovulation is more variable)
- Alters the endometrium to impair implantation
- Alters tubal motility (progestin-mediated)
- Thickens the cervical mucous (progestin-mediated)
Fun fact: Progestin-only pills inhibit ovulation only about 50% of the time, and therefore must be taken daily within a strict 3-hr window
What is the approximate failure rate of combined oral contraceptive in adolescents? (as compared to perfect use and typical use)
25%
(as compared to 1% in perfect use, and 8% with typical use)
Synthetic progestins: Name two androgenic side effects and one progesterone-related side effect
(1) Androgenic S/E: Oily skin, acne, noncyclical weight gain, hirsutism
(2) Fatigue, bloating
Of the following characteristics, what is preferred for a combined oral contraceptive to control abnormal uterine bleeding?
- Mononophasic vs triphasic?
- What dose of ethinyl estradiol component?
- Weaker vs stronger progestin?
- Monophasic
- 30-35 mcg of ethinyl estradiol (higher end)
- Moderate to strong dose progestin
What are the most common causes of abnormal uterine bleeding in adolescents?
- Anovulatory cycles (immature HPO axis)
- Other hormonal imbalance (PCOS, thyroid disease)
- Bleeding disorders
- Localized pathology of the genital tract (ex: cervicitis with STIs, foreign bodies, polyps, hymenal tears)
Name at least three important components of the history to obtain before prescribing a contraceptive in an adolescent
- Goals of contraception
- Prior pregnancy, pregnancy goals
- Thrombotic risks: Migraines with aura, smoking, anticipated major surgery/prolonged immobilization, family history of DVT or clotting disorders
- HTN, hyperlipidemia, liver disease
- Heavy or unexplained menstrual bleeding
- Preferred method to promote adherence
- All current medications, vitamins, and herbal supplements (check to ensure no interactions)
Helpful guide in identifying contraindications: https://www.cdc.gov/contraception/media/pdfs/2024/07/us-mec-summary-chart-color-508.pdf
Name at least two of the available four doses of ethinyl estradiol in combined hormonal contraceptives
Bonus points if you can recommend the optimal dose in adolescents
20 mcg, 25 mcg, 30 mcg, and 35 mcg
Bonus: Optimal dose in teens is 30-35 mg due to ongoing bony development. Ultra low doses of estrogen can impede development of optimal bone mass
Depot Provera: When used for >1 year, risk for _______ significantly increases. To mitigate this risk, patients should be started on _______
Risk for decreased bone mineral density (black box warning, though this effect has not been associated with increased risk for osteoporotic fracture)
Patients should be started on Vitamin D and calcium supplementation and instructed to start weight-bearing exercises
Fun fact:Depot Provera DECREASES risk for sickle cell crises and seizure (raises the seizure threshold)
What prescriptions can the primary care provider initiate to address heavy menstrual bleeding? (name 2)
NSAIDS: work by altering the balance of vasodilatory/vasoconstrictive prostaglandins (preferred agent is naproxen)
Combined oral contraceptives: progestin is the star of the show
- In mild cases, a typical COC course can be initiated. Ideally pick a more androgenic progestin, as these are stronger.
- In moderate to more severe cases, COC taper is preferred (many protocols exist)
Progestins: Norethindrone 5-10 mg daily, Mirena IUD, Depot-Provera
Describe distinguishing characteristics between ovulatory abnormal uterine bleeding and anovulatory abnormal uterine bleeding
- Ovulatory: cyclic, predictable bleeding that occurs with premenstrual symptoms and is heavy and/or prolonged. This is most commonly associated with a bleeding disorder (common in adolescents) or uterine pathology (uncommon in adolescents)
- Anovulatory: Irregular, unpredictable, or frequent episodes of bleeding in the absence of premenstrual symptoms. Most common cause is HPO axis immaturity, but the differential is broad