Define: System
A set of interacting parts forming a complex whole.
What type of rock forms from heat and lots of pressure?
Metamorphic Rock
All of Earth’s energy comes from either…
The sun
Earth’s interior
Why does Wisconsin not have earthquakes or volcanoes?
Because Wisconsin falls in the middle of a plate not on a plate boundary.
Define: Sediment
Small, solid pieces of material that come from rocks or living things.
Fill in the blanks on the image below:
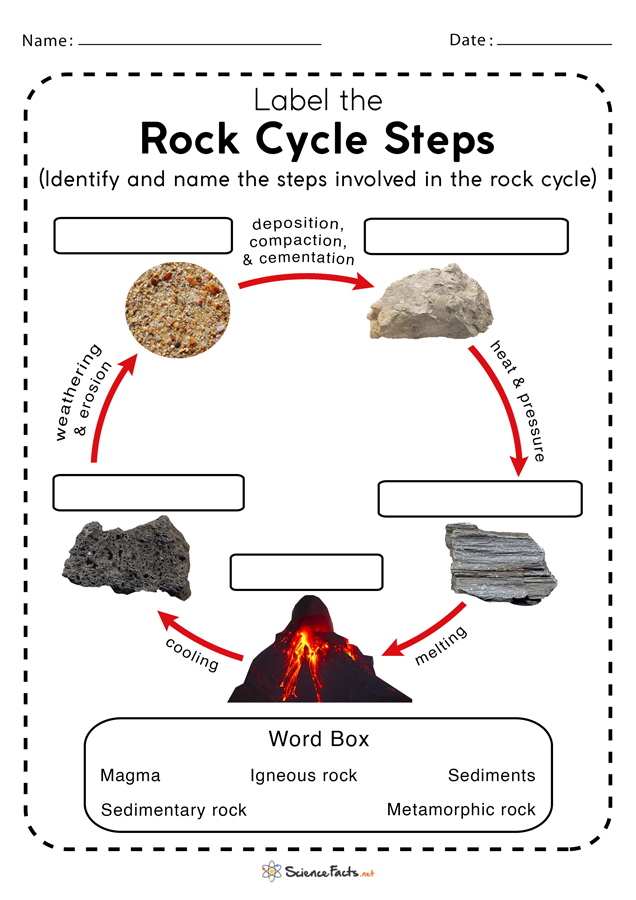
1: Sediment
2: Sedimentary Rock
3: Igneous Rock
4: Magma
5: Metamorphic Rock
What part of the Earth fits this description?
CONSTANTLY BEING BROKEN DOWN AND REFORMED. INCLUDES CONTINENTAL AND OCEANIC CRUSTS. SEPARATED INTO INDIVIDUAL PLATES
Crust
At a plate boundary, one is sinking below the other. What type of plate boundary must this be?
Convergent (continental-oceanic) boundary
Define: Crystallization
The process by which atoms form a crystal arrangement as they cool and lose kinetic energy.
What type of rock fits this description?
Found at divergent boundaries, like mid-ocean ridges, plates drift apart and form gaps that are filled by magma.
Igneous
What part of the Earth fits this description?
SOLID (BUT SOFT) ROCK. ALTHOUGH VERY HOT, PRESSURE KEEPS IT SOLID, SLOWLY FLOWS
Mantle
What plate is the oldest? Why?
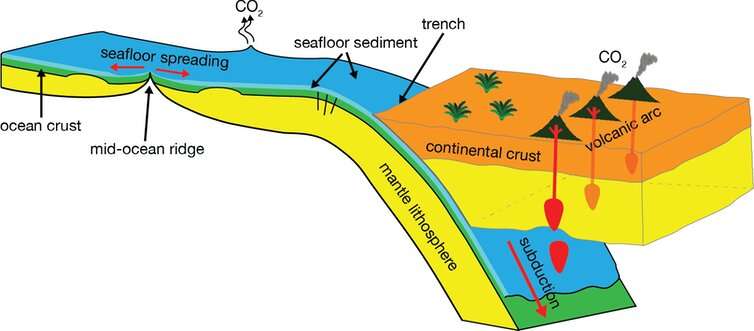
Plate B: It is more dense than plate A. Its more dense due to cooling.
Define: metamorphic rock
A type of rock that forms from an existing rock that is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions.
What type of rock is this?

Metamorphic
Earth's tectonic plates are moving and therefore have ______ energy, which can be traced back to energy from ______.
kinetic; Earth's interior
What is the movement of plates powered by?
Geothermal energy.
Define: Weathering
The breaking down of rocks and other materials on the Earth's surface.
What rock type is this?
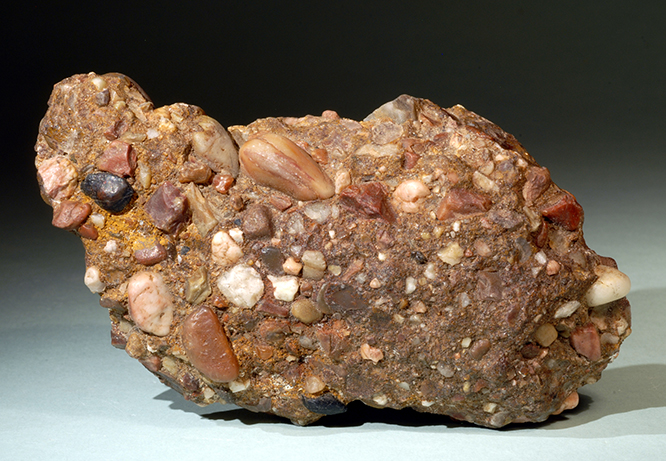

Sedimentary.
Describe how both the sun and the Earth's interior power the rock cycle.
Earth’s internal heat engine, which moves material around in the core and the mantle and leads to slow but significant changes within the crust and the movement of water, ice, and air at the surface, and is powered by the sun.
What is the Plate Tectonic Theory?
Plate Tectonic Theory – the Earth's solid outer crust is separated into plates that “float” around on the upper mantle