This warning sign—often described as a persistent, severe and unrelieved by medication—signals worsening hypertension in a client with preeclampsia.
What is a preeclampsia-related severe headache?
This is the normal percentage of weight loss a newborn may experience after birth without it being worrisome.
What is 10%?
This is the most common side effect of an epidural.
DD: This is the priority intervention for the side effect.
Daily triple: This is priority medication for the side effect.
What is hypotension?
DD: IV fluid bolus
DT: Ephedrine
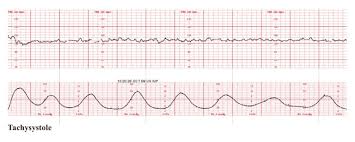
Pitocin is running as 12 ml/hr. This is your priority intervention.
What is d/c the pitocin.
During pregnancy, the fundal height measurement helps to assess this.
What is gestational age?
A client is 12 hours postpartum and has a history of severe pre-eclampsia with a BP of 185/112. What is the primary intervention for this patient?
What is initiate the Labetalol protocol?
This complication is more likely to occur in a newborn with a cephalohematoma due to the breakdown of accumulated red blood cells.
What is jaundice?
A G5P5 patient is 30 minutes post delivery. The patient's uterus is boggy. This is the primary intervention.
What is fundal massage?

When assessing the FHR, what is the priority intervention?
What is maternal position change (preferably left lateral).
After delivery, fundal height measurement helps to assess this.
What is involution?
A client is 12 hours postpartum and has a history of severe preeclampsia. The nurse notes the client is restless, and reports "seeing spots." The client also complains of shortness of breath and has crackles in her lung bases upon auscultation. What is the priority intervention?
What is place the client in a high-Fowler's position and apply oxygen?
A newborn has just been delivered. Which action is the most effective to prevent heat loss?
What is dry the infant?
A G1P0 patient has contractions every 4-5 min, mild in strength, resulting in slow cervical change and labor dystocia. This medication is the priority intervention.
What is oxytocin?
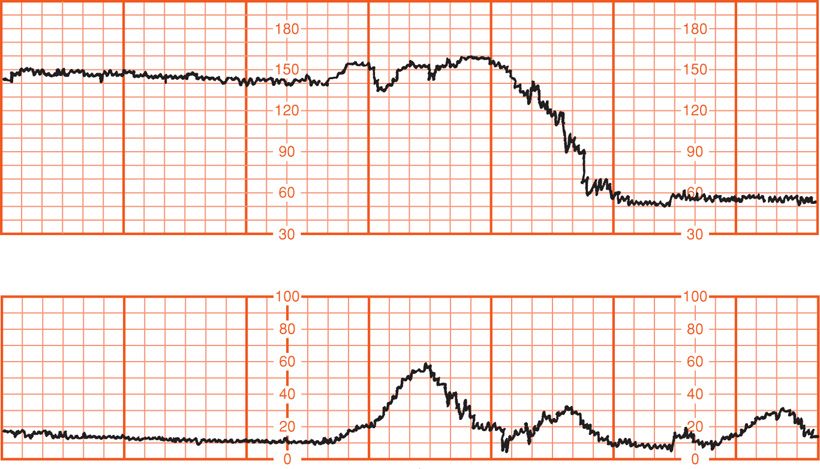
Your patient just ruptured. This is your priority intervention.
I will take either: position change or relieve pressure on the presenting part
When this maternal serum marker is elevated in the second trimester, it can indicate open neural tube defects such as spina bifida or anencephaly.
DD: what could a decrease level indicate?
What is AFP?
What is Down's Syndrome?
This is the priority intervention a nurse should take when a pre-eclamptic patient receiving magnesium sulfate develops signs of toxicity such as loss of deep tendon reflexes, respiratory depression, or decreased urine output.
What is discontinue the magnesium?
The nurse is preparing to administer erythromycin eye ointment to a newborn. This is the purpose of this medication.
Daily double: education for mom
What is gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum? (I will accept bacterial infection)
Daily double: What is don't wipe off the medication, let it absorb?
A postpartum patient with pre-eclampsia has been on a magnesium infusion for 18 hours and is showing s/s of toxicity. This is the priority medication to administer.
DD: 3 signs of mag toxicity
What is calcium gluconate?
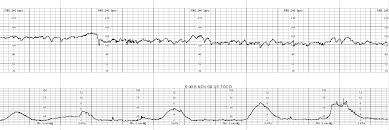
This is the priority intervention.
What is continue to monitor?
Smoking during pregnancy is linked to this complication, where the baby’s size and growth fall behind what is expected for their gestational age.
What is intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)?
This dangerous cardiovascular complication may occur in a postpartum client with a history of severe preeclampsia who suddenly develops shortness of breath, chest discomfort, and crackles in the lungs.
What is pulmonary edema?
A newborn is delivered by c-section to a mother who is HIV positive. The mother received antiretroviral (ART) therapy during pregnancy. This is the priority medication for the infant.
Daily double: This is the recommended timeframe to administer the medication.
What is zidovudine?
What is 6-12 hours post birth.
An infant is born and taken to the warmer due to apnea. This is the primary intervention.
What is ventilate and stimulate? (I will take either one.)
This is the priority intervention.
What is continue to monitor?
A deficiency of this essential nutrient before conception and in early pregnancy increases the risk of neural tube defects such as spina bifida.
What is folic acid?