Test
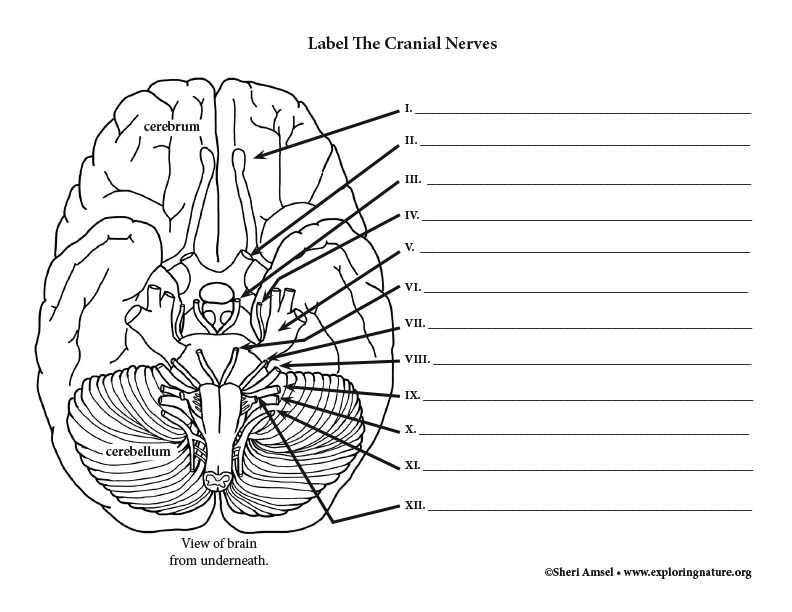
What is number one & it's function?
Number 1 is the olfactory nerve & it controls the sense of smell.

What is number 6 and its function?
Number 6 is the abducens nerve and it controls the lateral movement of the eye.
 What is number 11 and what does it control?
What is number 11 and what does it control?
Number 11 is the spinal accessory and it controls movement of the trapezius and sternomastoid muscles.
Test for nerve 5?
Motor Function: Assess the muscles of mastication by palpating the temporal and masseter muscles as the person clenches the teeth. Muscles should feel equally strong on both sides. Next try to separate the jaws by pushing down on the chin; normally you cannot.
Sensory Function: With the person’s eyes closed, test light touch sensation by touching a cotton wisp to these designated areas on person’s face: forehead, cheeks, and chin. Ask the person to say “Now” whenever the touch is felt. This tests all three divisions of the nerve: (1) ophthalmic, (2) maxillary, and (3) mandibular.
Test for nerve 12?
Inspect the tongue. No wasting or tremors should be present. Note the forward thrust in the midline as the person protrudes the tongue. Also ask the person to say “light, tight, dynamite” and note that lingual speech (sounds of letters l, t, d, n) is clear and distinct.

What is number 2 and it's function?
Number 2 is the optic nerve and it's function is vision.

What is number 7 and its function?
Number 7 is the facial nerve and it controls the muscles of facial expression, taste from anterior tongue, and lacrimal as well as the salivary glands.

What is number 12 and its function?
Number 12 is hypoglossal and it controls the movement of the tongue.
Test for nerve 7?
Motor Function: Note mobility and facial symmetry as the person responds to these requests: smile, frown, close eyes tightly (against your attempt to open them), lift eyebrows, show teeth, and puff cheeks. Press the person’s puffed cheeks in and note that the air should escape equally from both sides.

What is number 3 and it's function?
This is the oculomotor nerve and it controls opening of eyelids and pupil constriction.

What is number 8 and its function?
Number 8 is vestibulocochlear/acoustic, and it control hearing & sense of balance.
Test for nerve 1?
Do not test routinely. With the person’s eyes closed, occlude one nostril and present an aromatic substance. Use familiar, obtainable, and nonnoxious smells such as coffee, toothpaste, orange, vanilla, soap, or peppermint. Alcohol wipes smell familiar and are easy to find.
Normally a person can identify an odor on each side of the nose. Smell normally is decreased bilaterally with aging. Any asymmetry in the sense of smell is important.
Test for nerve 8?
Test hearing acuity by the ability to hear normal conversation and by the whispered voice test.

What is number 4 and its function?
This is the trochlear nerve and it controls inward and downward movement of the eyes.

What is number 9 and its function?
Number 9 is glossopharyngeal, and it controls phonation and swallowing, parotid gland and carotid reflex, and taste on the posterior one third of the tongue, and the gag reflex.
Test for nerve 2?
Test visual acuity and visual fields by confrontation.
Using the ophthalmoscope, examine the ocular fundus to determine the color, size, and shape of the optic disc.
Test for nerve 9 & 10?
Motor Function: Depress the tongue with a tongue blade and note pharyngeal movement as the person says “ahhh” or yawns; the uvula and soft palate should rise in the midline, and the tonsillar pillars should move medially.
Touch the posterior pharyngeal wall with a cotton applicator stick and note presence of pharyngeal sensation. Avoid the gag reflex. Also note that the voice sounds smooth and not strained.

What is number 5 and its function?
Number 5 is the trigeminal nerve and it controls the muscles of mastication.

What is number 10 and its function?
This is the vagus nerve and it controls talking and swallowing; general sensation from the carotid body, carotid sinus, pharynx, viscera; and carotid reflex.
The vagus nerve is responsible for the regulation of internal organ functions, such as digestion, heart rate, and respiratory rate, as well as vasomotor activity, and certain reflex actions, such as coughing, sneezing, swallowing, and vomiting
Test for nerve 3, 4, & 6?
Palpebral fissures are usually equal in width or nearly so. Check pupils for size, regularity, equality, direct and consensual light reaction, and accommodation. Assess extraocular movements by the cardinal positions of gaze.
Nystagmus is a back-and-forth oscillation of the eyes. End-point nystagmus, a few beats of horizontal nystagmus at extreme lateral gaze, occurs normally.
Assess any other nystagmus carefully, noting:
Pendular movement (oscillations move equally left to right) or jerk (a quick phase in one direction, then a slow phase in the other); classify the jerk nystagmus in the direction of the quick phase:
Amplitude (degree of movement is fine, medium, or coarse);
Frequency (constant or fade after a few beats);
Plane of movement (horizontal, vertical, rotary, or a combination).
Test for nerve 11?
Examine the sternomastoid and trapezius muscles for equal size. Check equal strength by asking the person to rotate the head forcibly against resistance applied to the side of the chin. Then ask the person to shrug the shoulders against resistance. These movements should feel equally strong on both sides.