The name of the cleft with intact skin and interrupted orbicularis oris muscle.
What is a microform cleft?
The law stating the skull bones grow perpendicular to open sutures and parallel to fused sutures.
What is Virchow's law?
The syndrome associated with: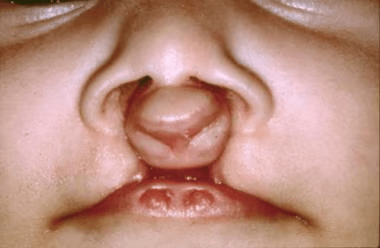
What is Van der Woude syndrome?
The type of malocclusion most likely to develop in this patient:
What is Class 3 malocclusion?
The most likely source of devastating bleed in this condition: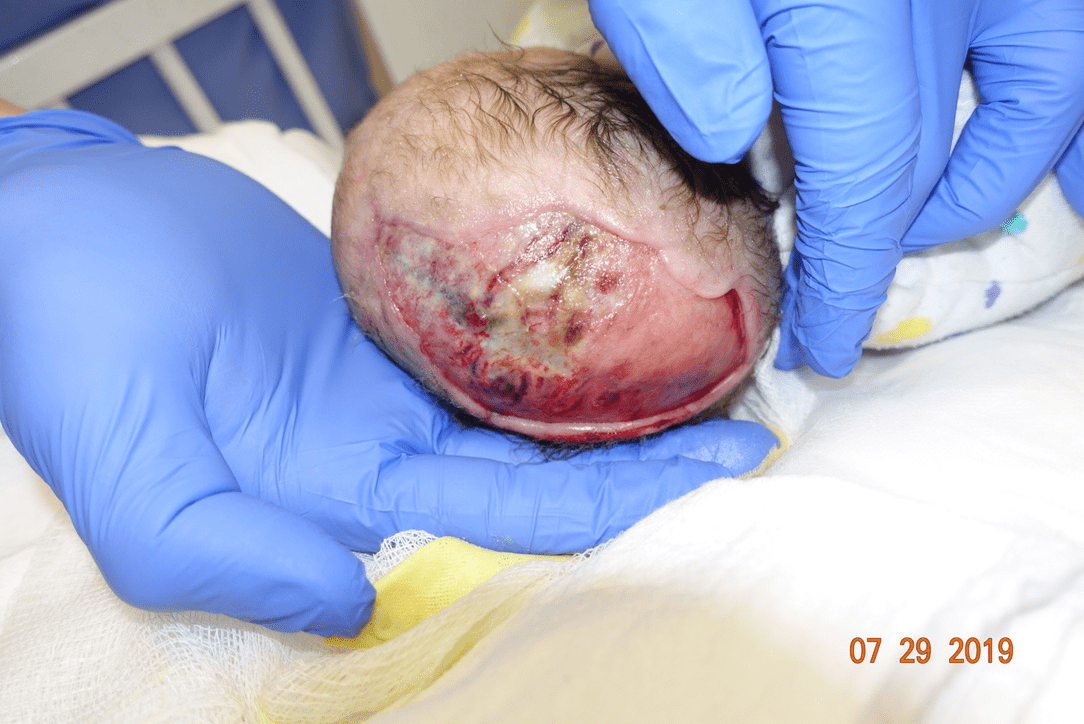
What is the sagittal sinus
The normal anatomic position of the levator veli palatini.
What originates from the medial aspect of the Eustachian tube and runs transversely through the central velum.
The age at which this affected suture is supposed to fuse: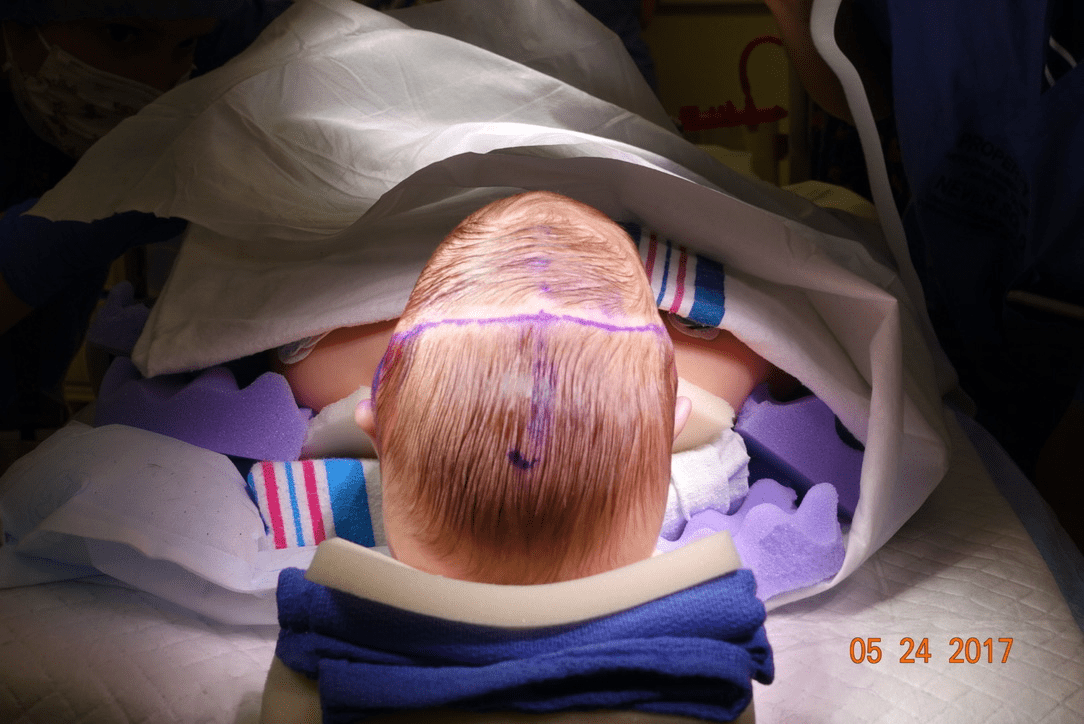
What is 22?
Syndromes associated with micrognathia and this finding:
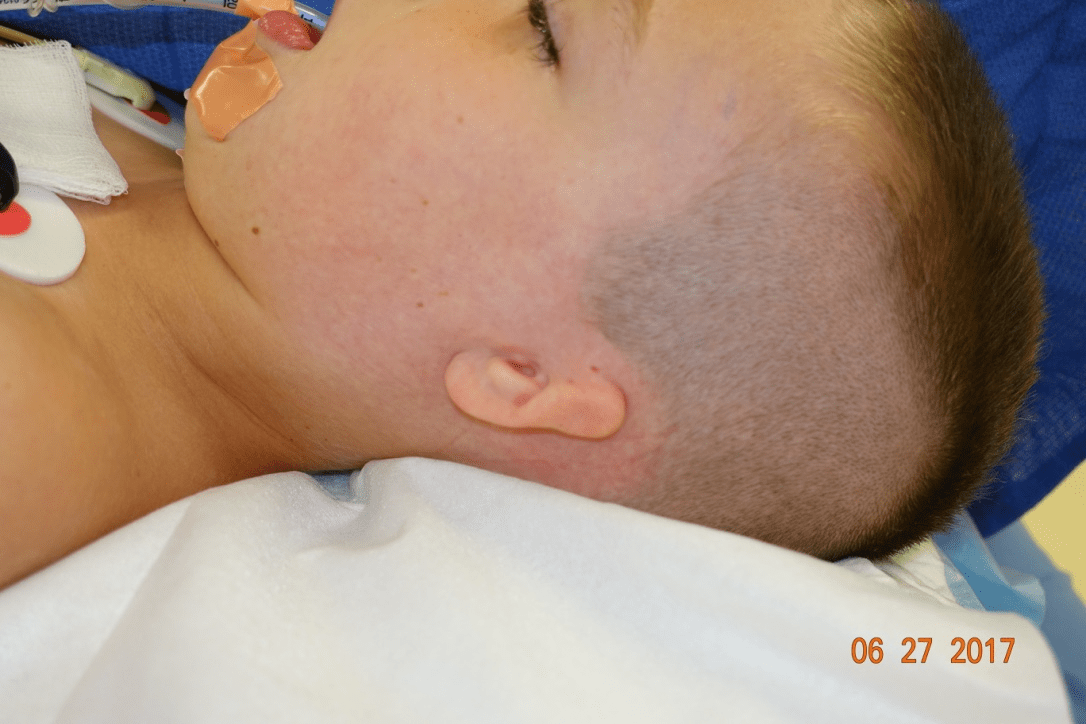
What are Treacher Collins, Goldenhar, hemifacial microsomia?
The two arteries most likely to be disrupted during LeFort I osteotomy with impaction.
What are the nasopalatine and descending palatine?
The best reconstructive option for: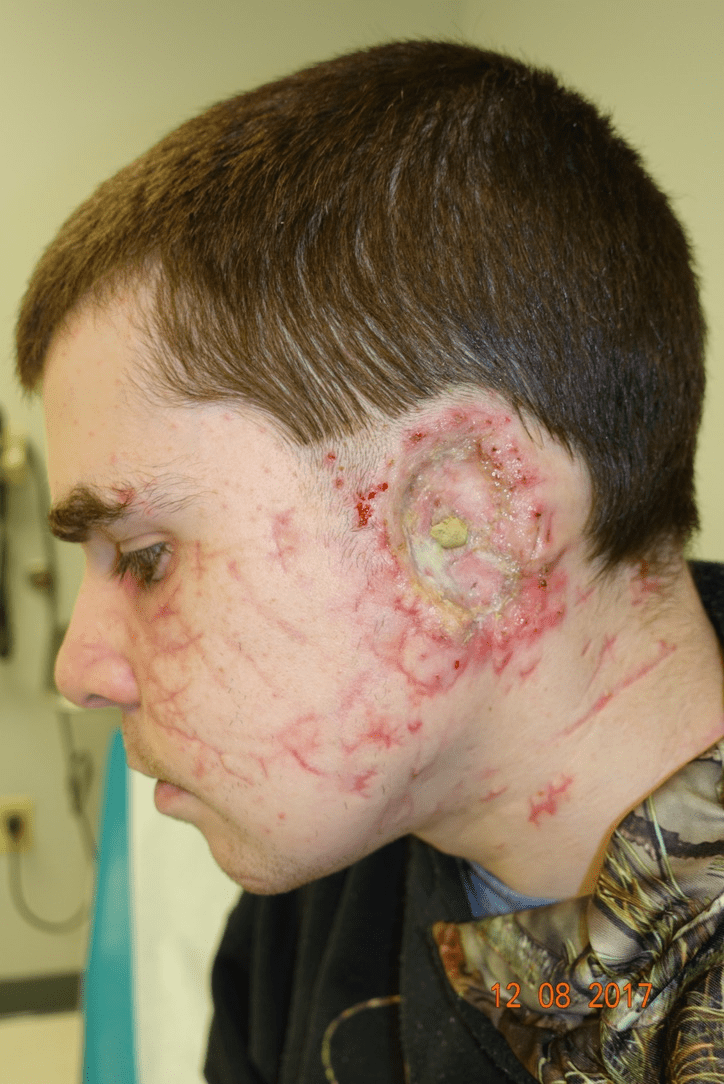
What is an osteointegrated prosthetic?
The repair type shown in this photo: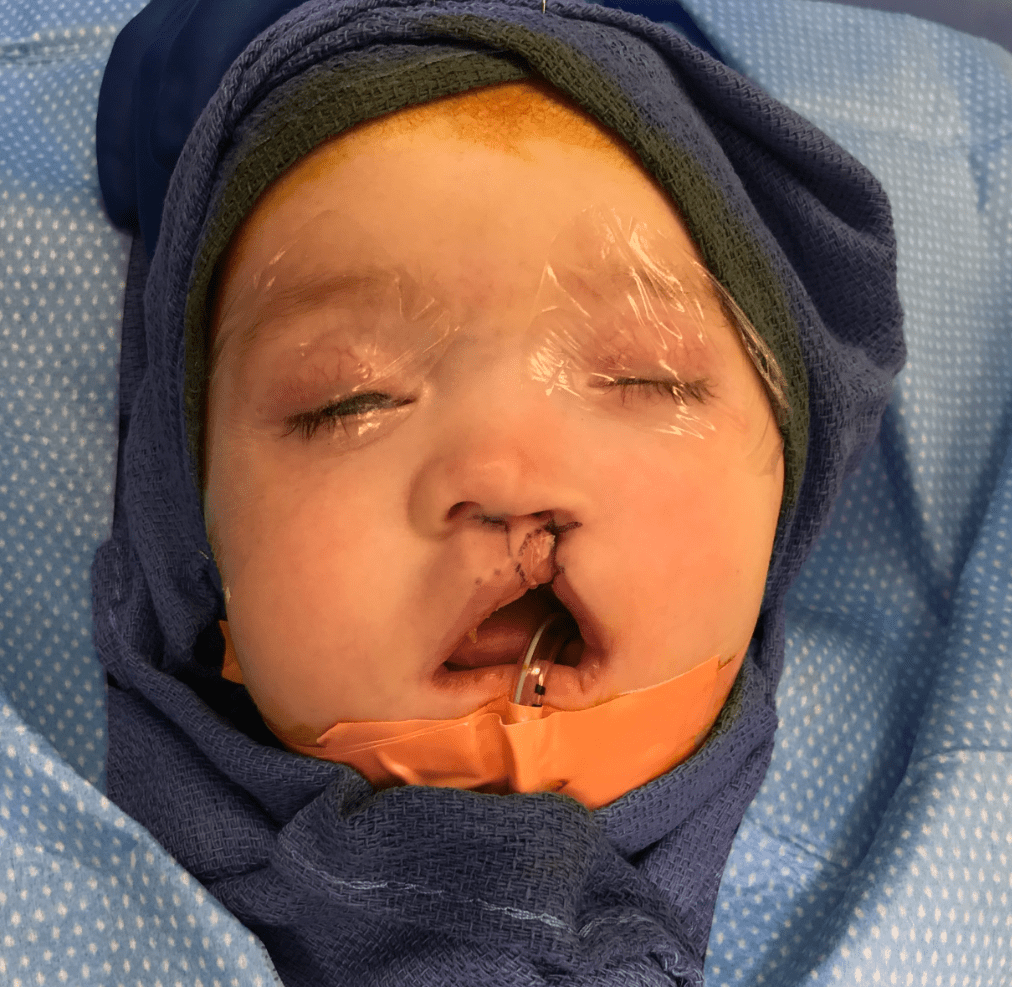
What is the Millard unilateral rotation/advancement flap?
The term to describe this head shape: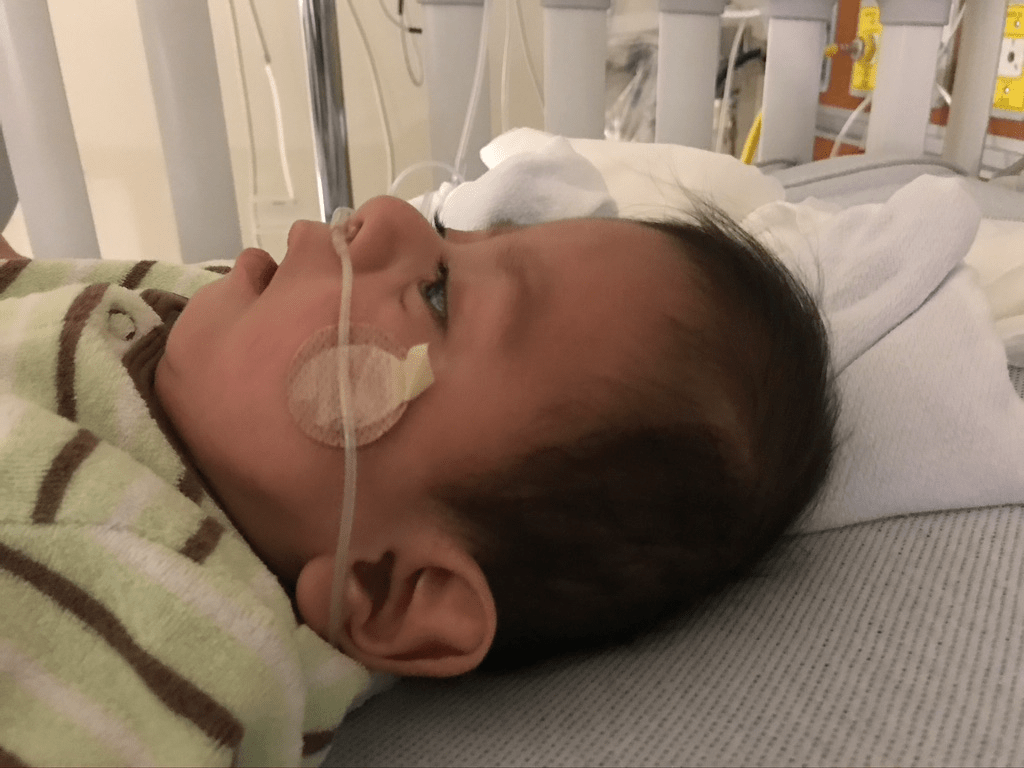
What is turribrachycephaly?
All the syndromic craniosynostoses associated with FGFR mutations. (At least 4)
What are Apert, Crouzon, Crouzon with acanthosis, Pfeiffer, Meunke, Beare-Stevenson, Jackson-Weiss?
The sequence that leads to this presentation
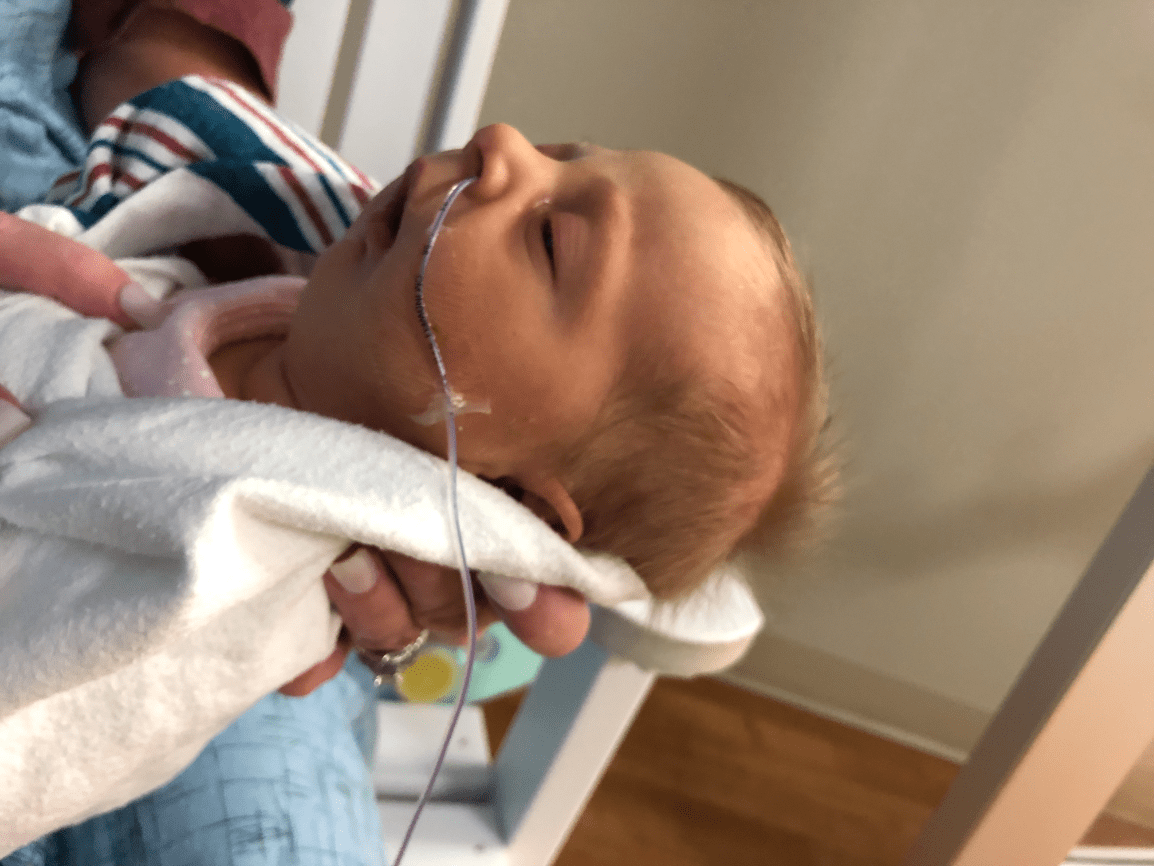
Hyperflexion of neck leads to hypoplasia of mandible, leads to superior displacement of the tongue with or without cleft palate, tongue overgrows the oral cavity leading to glossoptosis anteriorly and obstruction posteriorly.
Condition associated with MSX2 or ALX4 genes: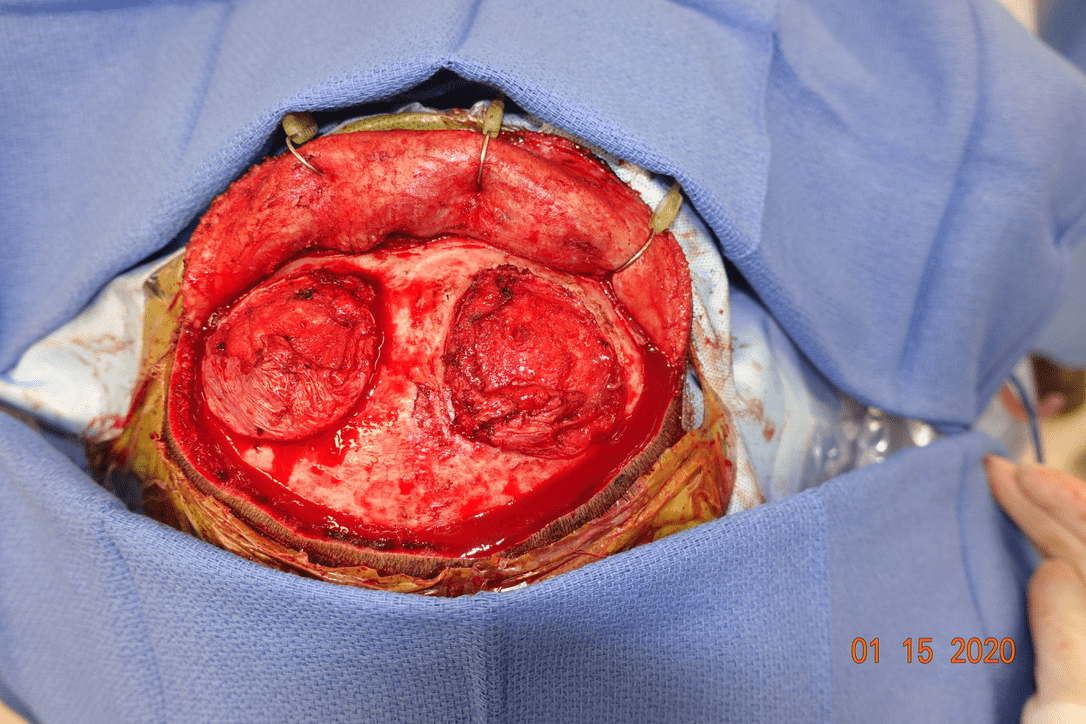
What is Foramina Parietalia Permagna?
The triad is associated with the condition for which this is the 1st-line treatment?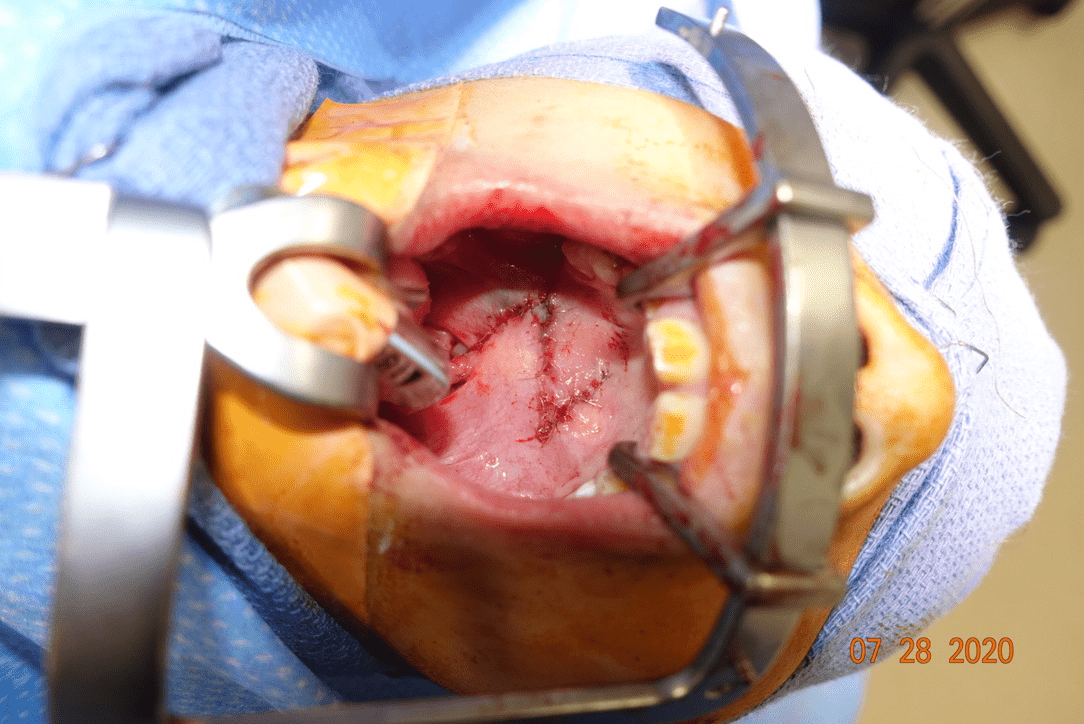
What are bifid uvula, zona pelucida, palpable notch?
The treatment for this head shape: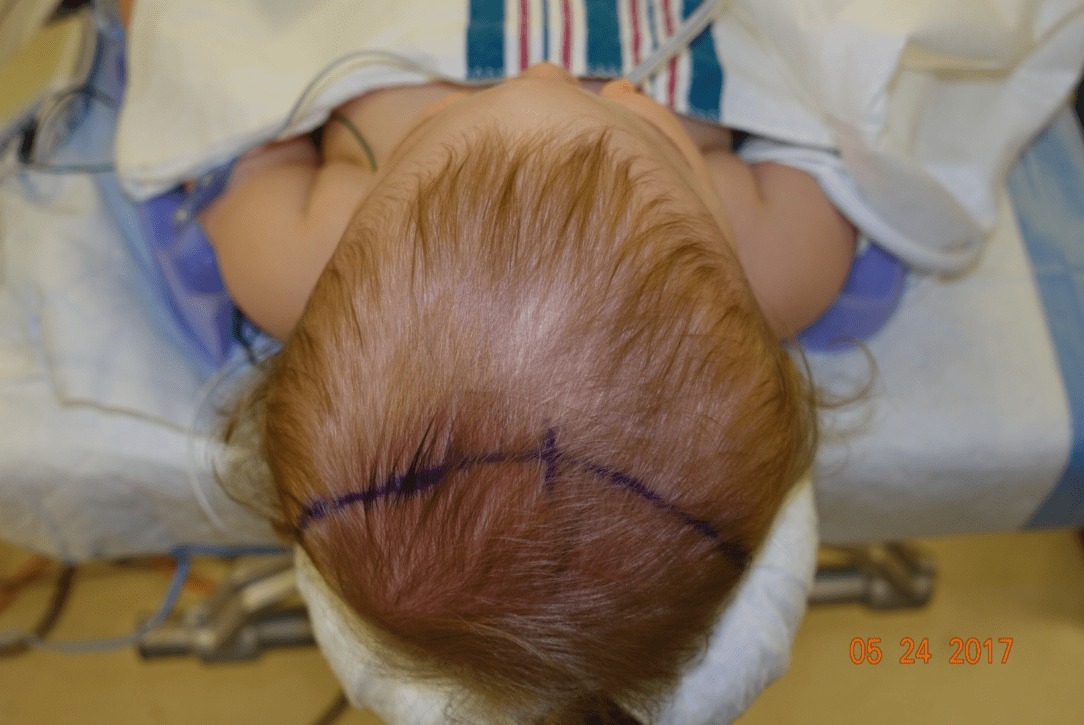
What is a fronto-orbital advancement?
The condition associated with this finding: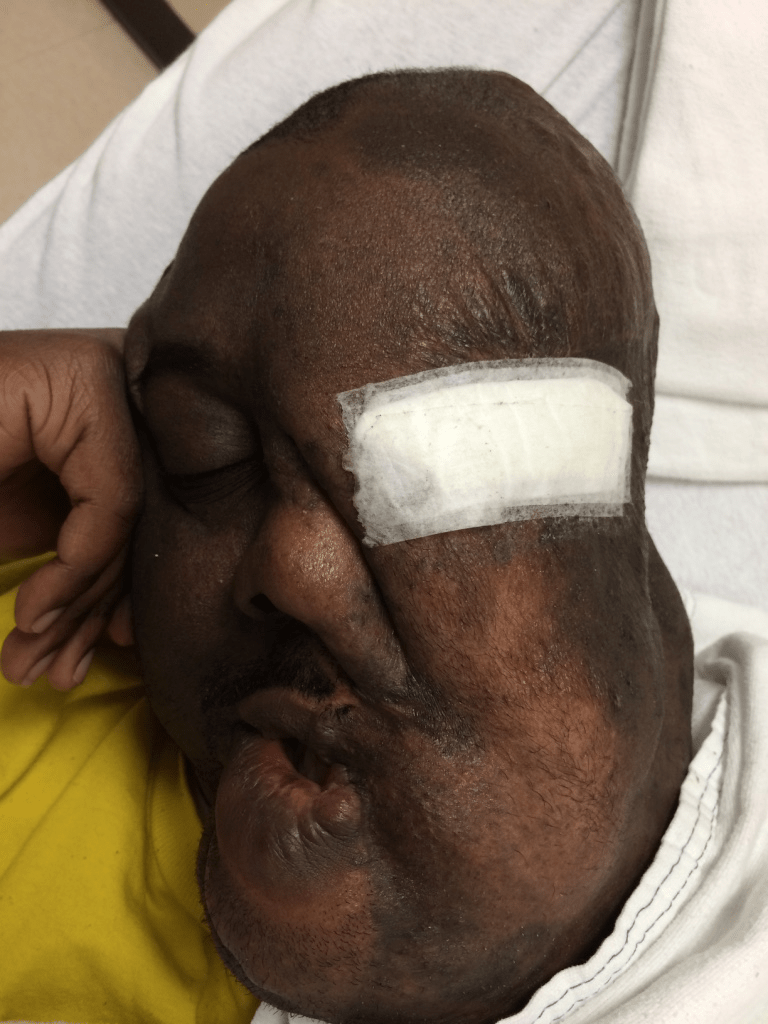
What is neurofibromatosis type 1 with plexiform neurofibroma?
The landmark used to determine the lingual mandibular osteotomy to protect the inferior alveolar nerve as it enters the mandibular foramen.
What is the lingula?
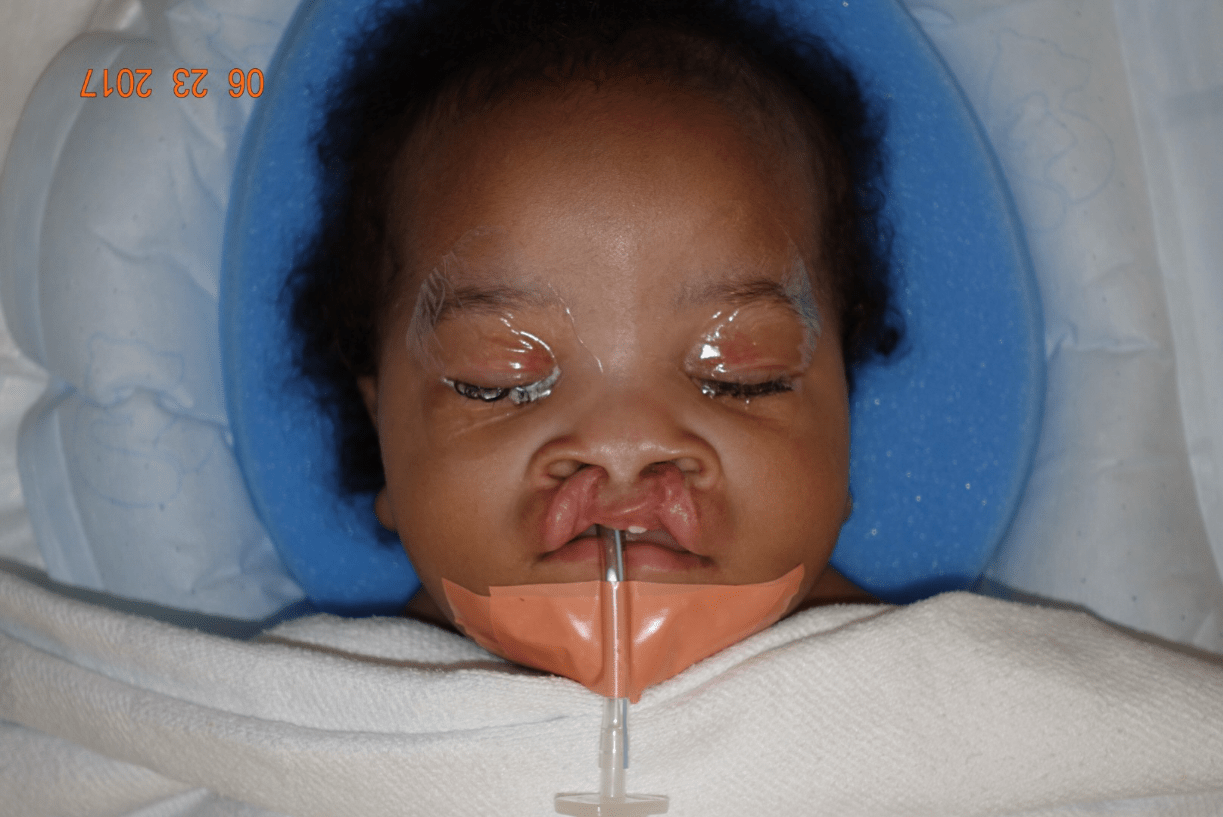
The cleft in this picture: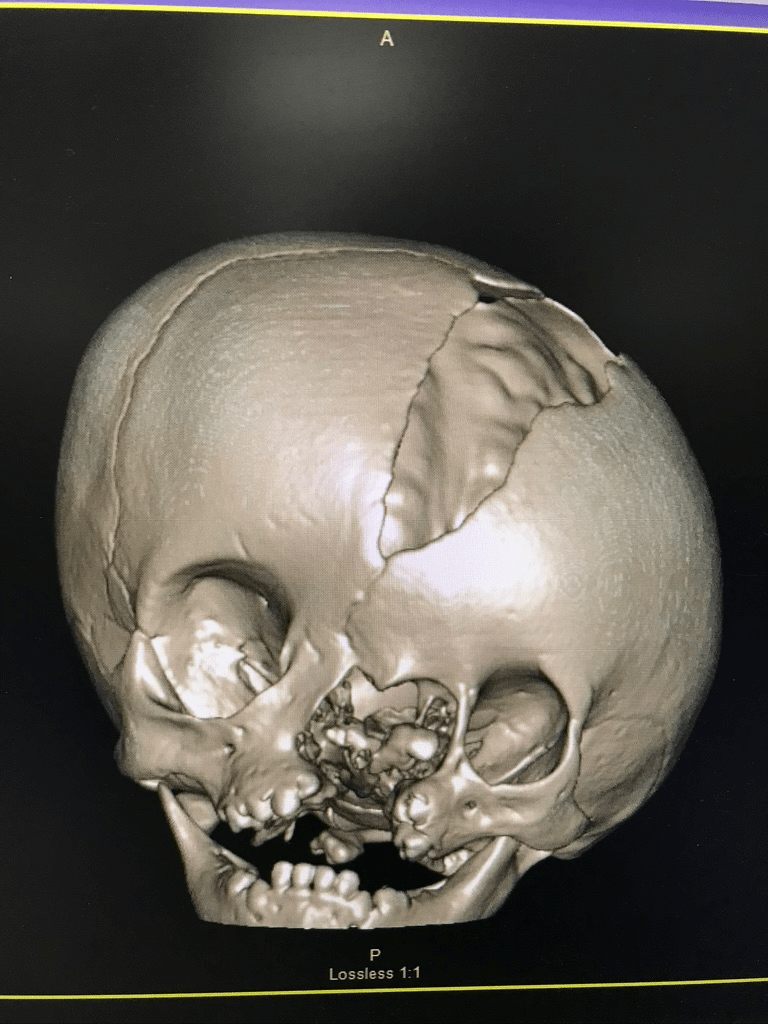
What is the 1 - 13 cleft
The options available to correct this deformity?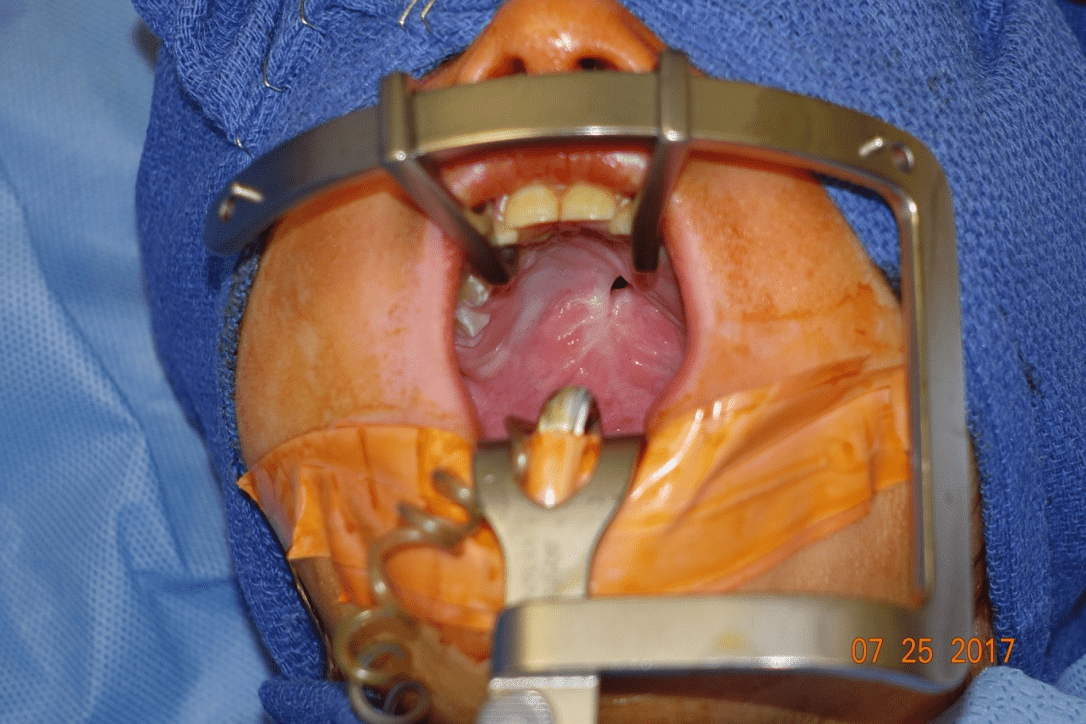
What are buccal flap, tongue flap, FAMM flap
The mechanism of increased ICP in craniosynostosis
What is the combination of cerebral venous hypertension, hydrocephalus with Chiari 1 malformation, air way obstruction, and craniocerebral disproportion.
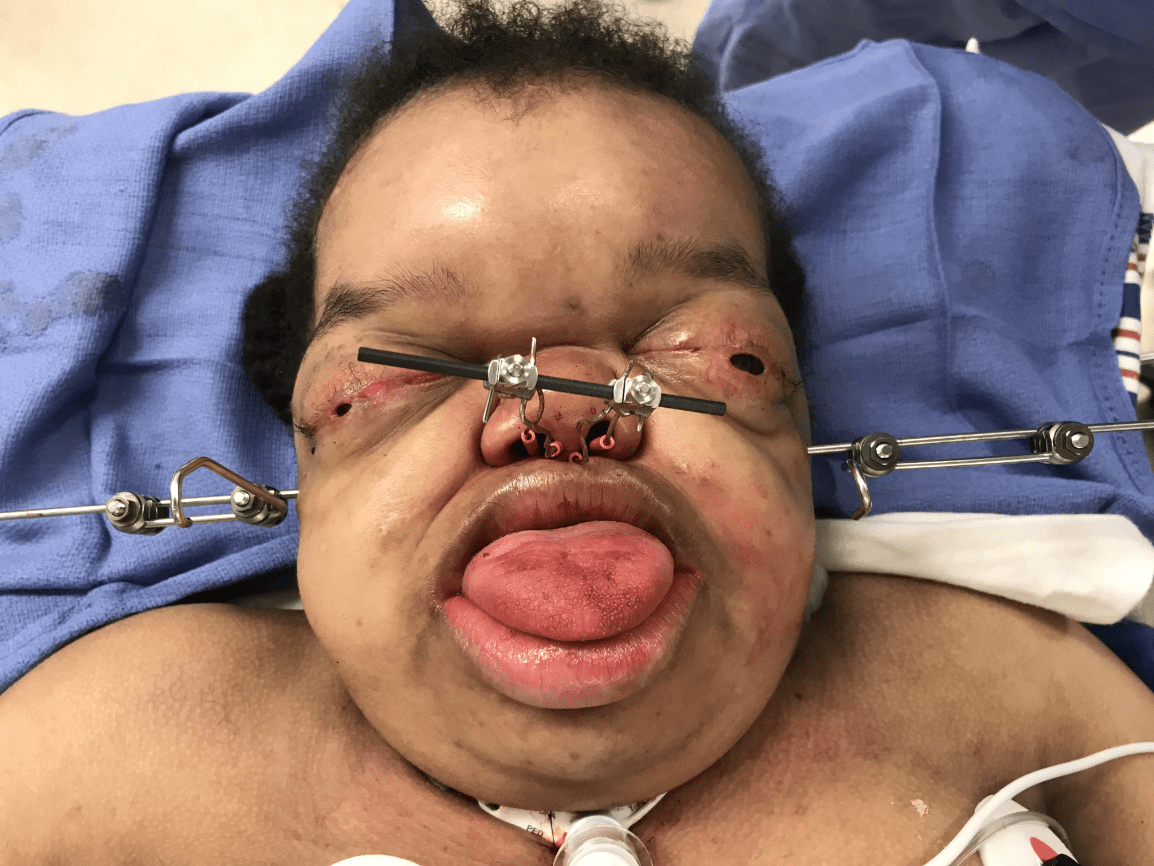 The syndrome associated with these facial features:
The syndrome associated with these facial features:
What is Pfeiffer syndrome type 3
The management of this complication:
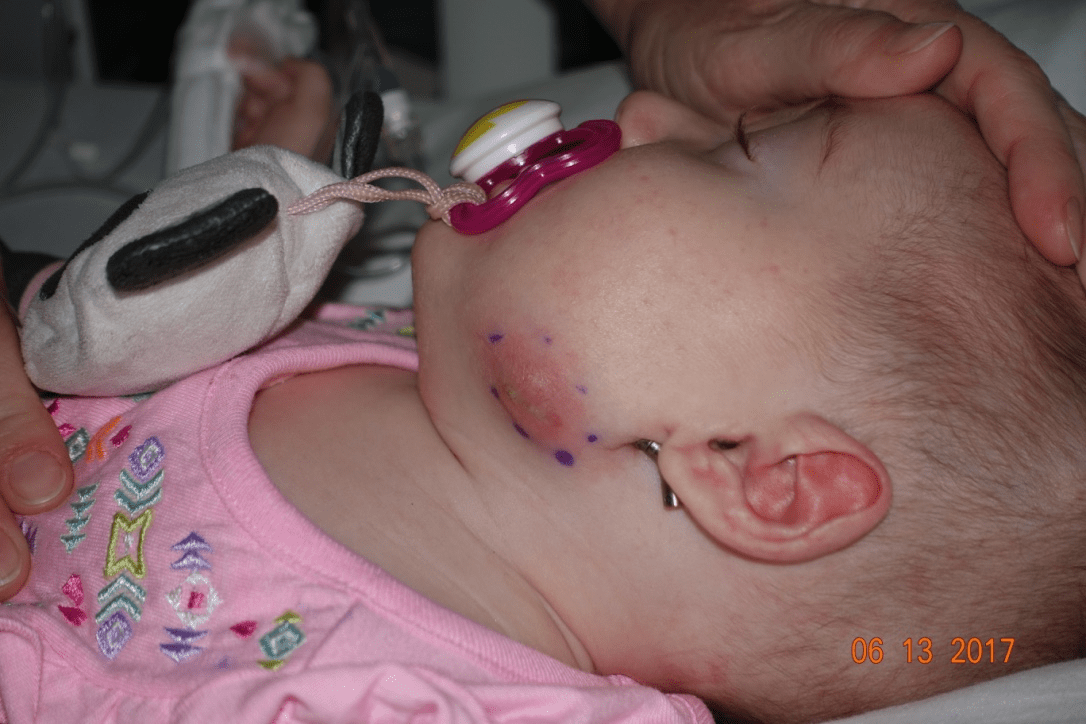
What is incision and drainage, suppressive antibiotics, exchange to external device, possible need for bone grafting
The proper medical name for this condition, also called incomplete twinning: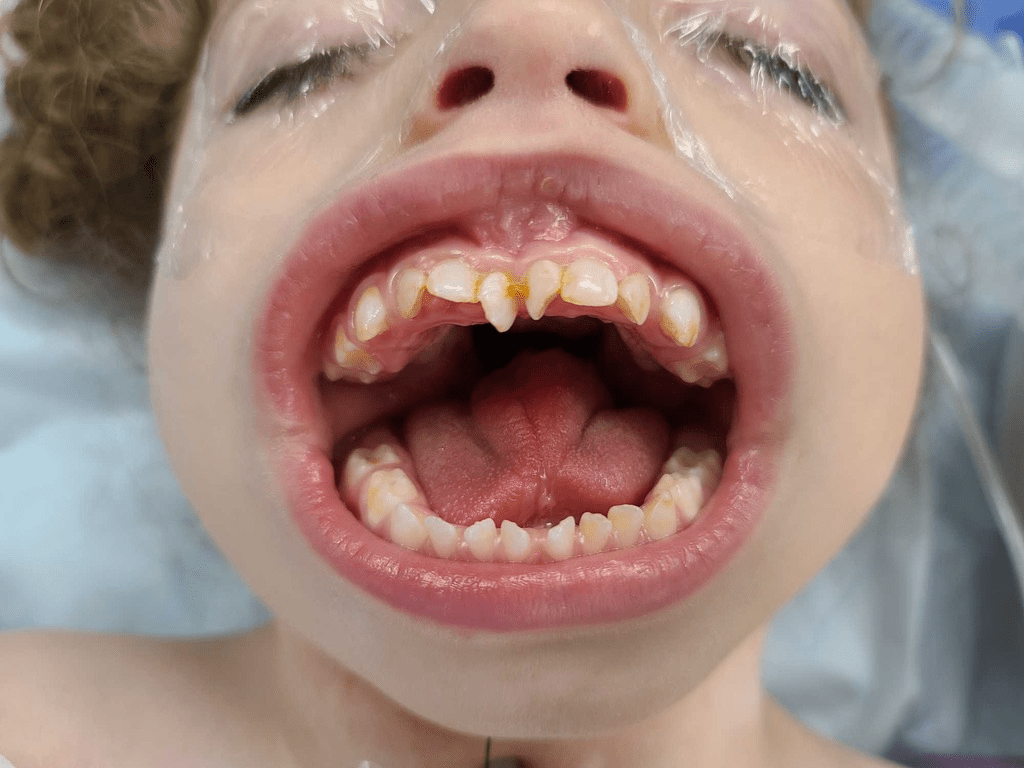
What is diprosopus