This inhaled selective pulmonary vasodilator is generally supplied in a large tank
What is Nitric Oxide
Your patient is deemed a high risk/pediRES-Q patient. This should be filled out and displayed at the patients bedside.
What is Situational Awareness Sheet?
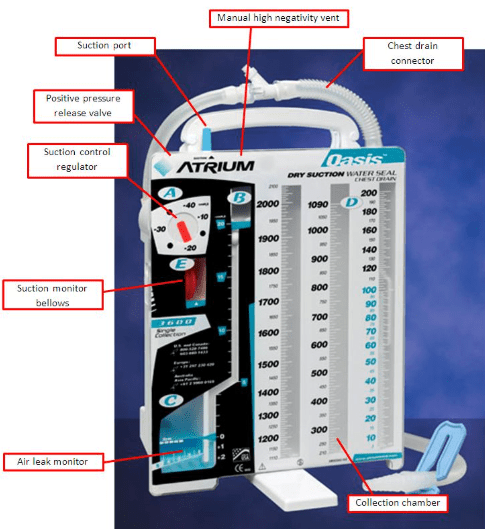
You have a chest tube that is set to -20 mmHg, what visual indicators on the front of the Atrium shows this suction parameter is correct and working appropriately.
What is the orange bellow and float ball located in the water-seal chamber?
This simple equation (HR x SV) speaks volumes for a patient.
What is Cardiac Output?
This is a way to assess oxygenation, ventilation and acid-base balance in critically ill patients.
What is an Arterial Blood Gas (ABG)?
This term describes how big each breath is when it is delivered.
What is Tidal Volume (ml/kg)?
What two measurements are monitored during a code event to ensure we a demonstrating effective chest compressions.
What are ETCO2 and diastolic blood pressure ( if arterial line present)
In septic shock, this is the standard initial fluid bolus volume given for resuscitation.
What is 20 mL/kg?
Name at least 2 indications for invasive arterial monitoring.
What are:
Continuous interpretation of waveform?
Continuous numeric data collection?
Titration of medicatons and fluid resuscitation?
Frequent lab draws?
Normal Range is 7.35 to 7.45
What is pH?
This "button" intervention can be useful to help prepare your patient for the act of suctioning.
What is suction support or disconnection/suction button?
These are 2 different types of strokes.
What are ischemic and hemorrhagic?
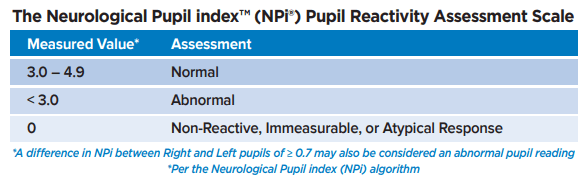
When performing pupillary assessment with a Pupillometer, a NPI > 3.0 is considered this.
What is normal or brisk?
This optimal location sits at the SVC and RA junction and comes with a normal reading of 2-8.
What is Central Venous Pressure (CVP)?
If your pH is out of balance because of a respiratory disorder, what system will attempt to correct it?
What is the Renal System?
Prior to hand ventilating an intubated patient on Nitric Oxide, the RN or RT must remember this "logistical" intervention.
What is turn the switch on the Nitric Oxide tank to bag?
Your patient is intubated and unresponsive. What is their GCS?
What is "3T"?
Name at least 3 safety checks you must perform at the start of your shift when caring for a patient with a tracheostomy.
Trachs:
Same size in bag, labeled, with ties and lubricant. Down-size in bag, labeled, with ties and lubricant in go-bag. Second same size in go-bag as well.
Ambu bag at bedside
Suction set-up
Appropriate size mask (BMV)
Trach Go-Bag with all necessary supplies.
LDA documentation/information sheet
The fraction of oxygen delivered in the blood that is utilized or consumed by a tissue, organ or entire body.
What is Oxygen Extraction?
Your intubated patient is receiving a stat CXR, what role is needed to help maintain ETT placement and security?
What is an Airway Guardian?
When hand ventilating a patient, aside from watching chest rise, it is important to monitor these values.
What are PEEP, PIP, ETCO2 and oxygen saturations
This is the 2nd most common risk factor for strokes in children.
What are cardiac disorders/cardiac patients.
Your patient begins to acutely decompensate and becomes hypotensive, what dose (mcg and mL) of Dwindle Epinephrine do you anticipate you will give your 7 kg patient.
What is 7 mcg in 0.7 mL's?
Normal is 10-15% less than an arterial saturation.
What is Somatic (Renal) NIRS Monitoring?
Describe proper positioning of your intubated patient when performing a CXR.
What is head midline, bed flat, lines and ETT safely out of the way.